Abstract
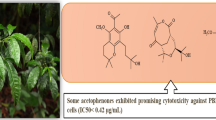
Three new 4-phenylcoumarins, mesuaferlinns A–C (1–3), together with ten other known 4-phenylcoumarins, 4–13, were isolated from the branches and leaves of Mesua ferrea Linn. (Clusiaceae). The structure of compounds 1–3 were determined on the basis of spectroscopic methods including extensive analysis of NMR and mass spectroscopic data. Ten 4-phenylcoumarins were tested for their cytochrome P450 family 1 enzymes (CYP1A1, CYP1A2, and CYP1B1) inhibitory effects. Compounds 5 and 10 were found to be the most potent two CYP1B1 inhibitors with inhibitory viabilities values of 56.64% and 47.46%, respectively.

Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The date that supports the findings of this study are available in the supplementary information of this article.
References
Pottenger LH, Christou M, Jefcoate CR. Purification and immunological characterization of a novel cytochrome P450 from C3H/10T1/2 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991;286:488–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(91)90070-Y.
Savas U, Bhattacharyya KK, Christou M, Alexander DL, Jefcoate CR. Mouse cytochrome P-450EF, representative of a new 1B subfamily of cytochrome P-450s. Cloning, sequence determination, and tissue expression. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:14905–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(17)36551-1.
Kleiner HE, Vulimiri SV, Reed MJ, Uberecken A, DiGiovanni J. Role of cytochrome P450 1a1 and 1b1 in the metabolic activation of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene and the effects of naturally occurring furanocoumarins on skin tumor initiation. Chem Res Toxicol. 2002;15:226–35. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx010151v.
Murray IA, Patterson AD, Perdew GH. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands in cancer: friend and foe. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14:801–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3846.
Leclerc D, Staats Pires AC, Guillemin GJ, Gilot D. Detrimental activation of AhR pathway in cancer: an overview of therapeutic strategies. Curr Opin Immunol. 2021;70:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2020.12.003.
Li F, Zhu W, Gonzalez FJ. Potential role of CYP1B1 in the development and treatment of metabolic diseases. Pharm Therapeut. 2017;178:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.03.007.
Liu JW, Pham PT, Skripnikova EV, Zheng SL, Lovings LJ, Wang YJ. et al. A Ligand-Based Drug Design. Discovery of 4-trifluoromethyl-7,8-pyranocoumarin as a selective inhibitor of human cytochrome P4501A2. J Med Chem. 2015;58:6481–93. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00494.
Anandakumar A, Balasubramanian M, Muralidharan R. Nagakesara-a comparative pharmacognosy. Anc Sci Life. 1986;4:263–8. https://www.ancientscienceoflife.org/text.asp?1986/5/4/263/88759.
Chanda S, Rakholiya K, Parekh J. Indian medicinal herb: antimicrobial efficacy of Mesua ferrea L. seed extracted in different solvents against infection causing pathogenic strains. J Acute Dis. 2013;2:277–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-6189(13)60143-2.
Verotta L, Lovaglio E, Vidari G, Finzi PV, Neri MG, Raimondi A. et al. 4-Alkyl- and 4-phenylcoumarins from Mesua ferrea as promising multidrug resistant antibacterials. Phytochemistry. 2004;65:2867–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.07.001.
Chukaew A, Saithong S, Chusri S, Limsuwan S, Watanapokasin R, Voravuthikunchai SP. et al. Cytotoxic xanthones from the roots of Mesua ferrea L. Phytochemistry. 2019;157:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.10.008.
Zar Wynn Myint K, Kido T, Kusakari K, Prasad Devkota H, Kawahara T, Watanabe T. Rhusflavanone and mesuaferrone B: tyrosinase and elastase inhibitory biflavonoids extracted from the stamens of Mesua ferrea L. Nat Prod Res. 2021;35:1024–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1613395.
Chakraborty DP, Chatterji D. Structure of mesuagin. A new 4-phenylcoumarin. J Org Chem. 1969;34:3784–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo01264a009.
Chakraborty DP, Das BC. The structure of mesuol. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966;7:5727–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(01)84186-1.
Govindachari TR, Pai BR, Subramaniam PS, Ramdas Rao U, Muthukumaraswamy N. Constituents of Mesua ferrea L.—II:: Ferruol A, a new 4-alkylcoumarin. Tetrahedron. 1967;23:4161–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)97929-3.
Guilet D, Helesbeux JJ, Seraphin D, Sevenet T, Richomme P, Bruneton J. Novel Cytotoxic 4-Phenylfuranocoumarins from Calophyllum dispar. J Nat Prod. 2001;64:563–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/np000517o.
Scio E, Ribeiro A, Alves TMA, Romanha AJ, Shin YG, Cordell GA. et al. New Bioactive Coumarins from Kielmeyera albopunctata. J Nat Prod. 2003;66:634–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/np020597r.
Reutrakul V, Leewanich P, Tuchinda P, Pohmakotr M, Jaipetch T, Sophasan S. et al. Cytotoxic coumarins from Mammea harmandii. Planta med. 2003;69:1048–51. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2003-45154.
Reyes CR, Estrada ME, Ramirez AT, Amekraz B, Aumelas A, Jankowski CK. et al. Cytotoxic effects of mammea type coumarins from Calophyllum brasiliense. Life Sci. 2004;75:1635–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2004.03.017.
Guilet D, Seraphin D, Rondeau D, Richomme P, Bruneton J. Cytotoxic coumarins from Calophyllum dispar. Phytochemistry. 2001;58:571–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(01)00285-0.
Go R, Hwang K, Choi K. Cytochrome P450 1 family and cancers. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015;147:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.11.003.
Yan J, Tung H, Li S, Niu Y, Garbacz WG, Lu P. et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling prevents activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrogenesis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:793–806. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.05.066.
Wang Y, Yang X, Zhu X, Xiao X, Yang X, Qin H. et al. Role of Metabolic Activation in Elemicin-Induced Cellular Toxicity[J]. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67:8243–52. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02137.
Berridge MV, Herst PM, Tan AS. Tetrazolium dyes as tools in cell biology: new insights into their cellular reduction. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2005;11:127–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-2656(05)11004-7.
Jabir NR, Rehman MT, Alsolami K, Shakil S, Zughaibi TA, Alserihi RF. et al. Concatenation of molecular docking and molecular simulation of BACE-1, γ-secretase targeted ligands: in pursuit of Alzheimer’s treatment. Ann Med. 2021;53:2332–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2021.2009124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fengxu Zhou performed the experiments, including isolation, structure identification, and prepared the manuscript. Ruoyue Huang has contributed to the study of active compounds, molecular docking and the writing of active parts. Tingting Cao and Jia Liu performed the auxiliary experiments. Weimin Yang guided the experiments. Fei Li and Xian Li were the supervisor of the present work, checked the structure determination of the isolated compounds and the biological study, and completed the redaction of the article.
Funding
This study was funded by the Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department (NoS. 2019HB025, 202005AE160004, 202005AF150043, 202201AY070001-004) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31860087).
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Informed consent
All authors revised and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, F., Huang, R., Cao, T. et al. 4-Phenylcoumarins from Mesua ferrea with selective CYP1B1 inhibitory activity. Med Chem Res 31, 2172–2181 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-022-02962-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-022-02962-3