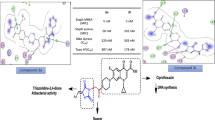
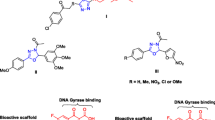
Abstract
New ciprofloxacin/ quaternary ammonium salts 3a–e were designed and synthesized as potential antimicrobial agents. Most of the prepared derivatives showed promising dual antibacterial/antifungal activities. Compound 3e was the most potent and afforded vast spectrum antibacterial activity against S. aureus and most of the tested Gram-negative bacterial strains with MIC values ranging from 1.53–9.54 µg/mL. Moreover, ciprofloxacin and compound 3e induced DNA cleavage in S. aureus DNA gyrase and S. aureus TOPO IV DNA by 1 and 10 µM, respectively. In addition, docking study results agreed with results of DNA cleavage assays where all the tested compounds showed no additional significant interactions over the parent ciprofloxacin. On the other side, compounds 3e and 3f exhibited outstanding antifungal activity better than the reference itraconazole with MICs of 1.87, 4.67, and 11.22 µg/mL, respectively, against Candida. albicans. These data suggest the prevalence of another mechanism in addition to DNA gyrase circumvention, like metal chelation, antibiofilm, and/or improvement of lipophilicity and subsequent penetration.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xue Y, Xiao H, Zhang Y. Antimicrobial polymeric materials with quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:3626–55.
Romani L. Immunity to fungal infections. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:11–24.
Cui S, Ren Y, Zhang S, Peng X, Damu G, Geng R et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a class of quinolone triazoles as potential antimicrobial agents and their interactions with calf thymus DNA. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013;23:3267–72.
Wang X, Wan K, Zhou C. Synthesis of novel sulfanilamide-derived 1,2,3-triazoles and their evaluation for antibacterial and antifungal activities. Eur J Med Chem. 2010;45:4631–9.
Walters J, Zhang F, Nakkula R. Mechanisms of fluoroquinolone transport by human neutrophils. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999;43:2710–5.
Correia S, Poeta P, Hébraud M, Capelo JL, Igrejas G. Mechanisms of quinolone action and resistance: where do we stand. J Med Microbiol. 2017;66:551–9.
Gao C, Fan Y, Zhao F, Ren Q, Wu X, Chang L et al. Quinolone derivatives and their activities against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Eur J Med Chem. 2018;157:1081–95.
Sasaki E, Maesaki S, Miyazaki Y, Yanagihara K, Tomono K, Tashiro T et al. Synergistic effect of ofloxacin and fluconazole against azole-resistant Candida albicans. J Infect Chemother. 2000;6:151–4.
Nakajima R, Kitamura A, Someya K, Tanaka M, Sato K. In vitro and in vivo antifungal activities of DU-6859a, a fluoroquinolone, in combination with amphotericin B and fluconazole against pathogenic fungi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995;39:1517–21.
Krug LM, Crawford J, Ettinger DS, Shapiro GI, Spigel D, Reiman T et al. Phase II multicenter trial of voreloxin as second-line therapy in chemotherapy-sensitive or refractory small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6:384–6.
Schaeffer A, Anderson R. Efficacy and tolerability of norfloxacin vs. ciprofloxacin in complicated urinary tract infection. Urology. 1992;40:446–9.
Aliprandis E, Ciralsky J, Lai H, Herling I, Katz H. Comparative efficacy of topical moxifloxacin versus ciprofloxacin and vancomycin in the treatment of P. aeruginosa and ciprofloxacin-resistant MRSA keratitis in rabbits. Cornea. 2005;24:201–5.
Zhang G, Zhang S, Pan B, Liu X, Feng L. 4-Quinolone derivatives and their activities against Gram positive pathogens. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;143:710–23.
Zhang X, Lionberger R, Davit B, Yu L. Utility of physiologically based absorption modeling in implementing quality by design in drug development. AAPS J. 2011;13:59–71.
Harder S, Fuhr U, Beermann D, Staib A. Ciprofloxacin absorption in different regions of the human gastrointestinal tract. Investigations with the hf-capsule. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;30:35–9.
Lehto P, Kivisto K, Neuvonen P. The effect of ferrous sulphate on the absorption of norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1994;37:82–5.
Dahan A, Miller J. The solubility–permeability interplay and its implications in formulation design and development for poorly soluble drugs. AAPS J. 2012;14:244–51.
Grigoras A. Natural and synthetic polymeric antimicrobials with quaternary ammonium moieties: a review. Environ Chem Lett. 2021;19:3009–22.
Wei L, Mi Y, Zhang J, Li Q, Dong F, Guo Z. Evaluation of quaternary ammonium chitosan derivatives differing in the length of alkyl side-chain: synthesis and antifungal activity. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;129:1127–32.
Zhang J, Tan W, Luan F, Yin X, Dong F, Li Q et al. Synthesis of quaternary ammonium salts of chitosan bearing halogenated acetate for antifungal and antibacterial activities. Polymers. 2018;530:10.
Gilbert P, Al-taae A. Antimicrobial activity of some alkyltrimethylammonium bromides. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1985;6:101–4.
Zhao T, Sun G. Hydrophobicity and antimicrobial activities of quaternary pyridinium salts. J Appl Microbiol. 2008;104:824–30.
Garipov MR, Sabirova AE, Pavelyev RS, Shtyrlin NV, Lisovskaya SA, Bondar OV et al. Targeting pathogenic fungi, bacteria and fungal-bacterial biofilms by newly synthesized quaternary ammonium derivative of pyridoxine and terbinafine with dual action profile. Bioorg Chem. 2020;104:104306.
Fedorowicz J, Saczewski J, Konopacka A, Waleron K, Lejnowski D, Ciura K et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of hybrid quinolone-based quaternary ammonium antibacterial agents. EJMC. 2019;179:576–90.
Insuasty D, Vidal O, Bernal A, Marquez E, Guzman J, Insuasty B et al. Antimicrobial activity of quinoline-based hydroxyimidazolium hybrids. Antibiotics. 2019;8:239.
Tischer M, Pradel G, Ohlsen K, Holzgrabe U. Quaternary ammonium salts and their antimicrobial potential: targets or nonspecific interactions. Chem Med Chem. 2012;7:22–31.
Diz M, Manresa A, Pinazo A, Erra P, Infante MaR. Synthesis, surface active properties and antimicrobial activity of new bis quaternary ammonium compounds. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans.1994;2:1871–6.
Perinelli D, Petrelli D, Vitali L, Vllasaliu D, Cespi M, Giorgioni G et al. Quaternary ammonium surfactants derived from leucine and methionine: novel challenging surface active molecules with antimicrobial activity. J Mol Liq. 2019;283:249–56.
Xu Z, Zhao S, Deng J, Wang Q, Lv Z. Ciprofloxacin-isatin hybrids and their antimycobacterial activities. J Heterocycl Chem. 2019;56:319–24.
Alptüzün V, Parlar S, Taşlı H, Erciyas E. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some pyridinium salts. Molecules. 2009;14:5203–5215.
Wolfson J, Hooper D. Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agents. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989;2:378–424.
Okazaki K. Synthesis and antimicrobial characteristics of N,N’-hexamethylenebis (4-carbamoy1-1-decylpyridinium bromide). Biocontrol Sci. 2000;5:65–71.
Alptüzün V, Parlar S, Taşlı H, Erciyas E. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some pyridinium salts. Molecules. 2009;14:5203–15.
Spanu P, Mannu A, Ulgheri F. An unexpected reaction of pyridine with acetyl chloride to give dihydropyridine and piperidine derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014;55:1939–42.
Abdel-Aziz M, Park S-E, Abuo-Rahma GE-DAA, Sayed.M A, Kwon Y. Novel N-4-piperazinyl-ciprofloxacin-chalcone hybrids: Synthesis, physicochemical properties, anticancer and topoisomerase I and II inhibitory activity. Eur J Med Chem. 2013;69:427–38.
Raj H, Patel Y. Synthesis, characterization and antifungal activity of metal complexes of 8-hydroxyquinoline based azo dye. Adv Appl Sci Res. 2015;6:119–23.
You Z, Ran X, Dai Y, Ran Y. Clioquinol, an alternative antimicrobial agent against common pathogenic microbe. J Mycol Med. 2018;28:492–501.
Szczepaniak J, Cieślik W, Romanowicz A, Musioł R, Krasowska A. Blocking and dislocation of Candida albicans Cdr1p transporter by styrylquinolines. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2017;50:171–6.
Bush NG, Diez-Santos I, Abbott LR, Maxwe AL. Quinolones: mechanism, lethality and their contributions to antibiotic resistance. Molecules. 2020;25:5662.
Dighe SN, Collet TA. Recent advances in DNA gyrase-targeted antimicrobial agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;199:112326.
Silhavy TJ, Kahne D, Walker S. The bacterial cell envelope. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2:a000414.
Mugumbate G, Overington JP. The relationship between target-class and the physicochemical properties of antibacterial drugs. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015;23:5218–24.
Tao R, Uratsu SL, Dandekar AM. Sorbitol synthesis in transgenic tobacco with apple cDNA encoding NADP-dependent sorbitol-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Plant Cell Physiol. 1995;36:525–32.
Gerwien F, Skrahina V, Kasper L, Hube B, Brunke S. Metals in fungal virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018;42:1–21.
Pfaller MA, Gerarden T, Yu M, Wenzel RP. Influence of in vitro susceptibilitytesting conditions on the anti-candidal activity of LY121019. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988;11:1–9.
Górka-Nieć W, Perlińska-Lenart U, Zembek P, Palamarczyk G, Kruszewska JS. Influence of sorbitol on protein production and glycosylation and cell wall formation in Trichoderma reesei. Fung. Bio. 2010;114:855–62.
Leite MCA, De B Bezerra AP, De Sousa JP, Guerra FQS, Lima E, de O. Evaluation of antifungal activity and mechanism of action of citral against Candida albicans. Evid Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2014;2014:Article ID 378280.
Odds FC. Synergy, antagonism, and what the chequerboard puts between them. J Antimicrob Chemother 2003;52:1–1.
Zuo R, Garrison AT, Basak A, Zhang P, Huigens RW, Ding Y. In vitro antifungal and antibiofilm activities of halogenated quinolone analogues against Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016;48:208–211.
Delattin N, Bardiot D, Marchand A, Chaltin P, De Brucker K, Cammue BPA et al. Identification of fungicidal 2,6-disubstituted quinolines with activity against Candida biofilms. Molecules. 2012;17:12243–51.
Breda SA, Jimenez-Kairuz AF, Manzo RH, Olivera ME. Solubility behavior and biopharmaceutical classification of novel high-solubility ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin pharmaceutical derivatives. Int J Pharm. 2009;371:106–113.
Ross D, Riley C. Aqueous solubilities of some variously substituted quinolone antimicrobials. Int J Pharm. 1990;63:237–250.
Abuo-Rahma GE-DAA, Sarhan.H A, Gad GFM. Design, synthesis, antibacterial activity and physicochemical parameters of novel N-4-piperazinyl derivatives of norfloxacin. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009;17:3879–86.
Salem MA, Ragab A, El-Khalafawy A, Makhlouf AH, AskarAhmed A, Ammar YA. Design, synthesis, in vitro antimicrobial evaluation and molecular docking studies of indol-2-one tagged with morpholinosulfonyl moiety as DNA gyrase inhibitors. Bioorg Chem. 2020;96:103619.
Bax BD, Chan PF, Eggleston DS, Fosberry A, Gentry DR, Gorrec F et al. Type IIA topoisomerase inhibition by a new class of antibacterial agents. Nature. 2010;466:935–40.
Ghannam IAY, Abd El-Meguid EA, Ali IH, Sheir DH, El Kerdawy AM. Novel 2-arylbenzothiazole DNA gyrase inhibitors: Synthesis, antimicrobial evaluation, QSAR and molecular docking studies. Bioorg Chem. 2019;93:103373.
Ushiyama F, Amada H, Takeuchi T, Tanaka-Yamamoto N, Kanazawa H, Nakano K et al. Lead identification of 8-(Methylamino)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline derivatives as DNA gyrase inhibitors: hit-to-lead generation involving thermodynamic evaluation. ACS Omega. 2020;5:10145–10159.
Monk BC, Keniya MV. Roles for structural biology in the discovery of drugs and agrochemicals targeting sterol 14α-demethylases. JoF. 2021;7:67.
Sagatova AA, Keniya MV, Wilson RK, Monk BC, Tyndall JDA. Structural insights into binding of the antifungal drug fluconazole to saccharomyces cerevisiae lanosterol 14α-demethylase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:4982–4989.
Aziz HA, Moustafa GAI, Abbas SH, Derayea SM, Abuo-Rahma GE-DAA. New norfloxacin/nitric oxide donor hybrids: Synthesis and nitric oxide release measurement using a modified Griess colorimetric method. Eur J Chem. 2017;8:119–124.
Bonev B, Hooper J, Parisot J. Principles of assessing bacterial susceptibility to antibiotics using the agar diffusion method. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008;61:1295–1301.
Nitiss JL, Soans E, Rogojina A, Seth A, Mishina M. Topoisomerase assays. Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 2012;57:1–7.
Abate G, Aseffa A, Selassie A, Goshu S, Fekade B, WoldeMeskal D et al. Direct colorimetric assay for rapid detection of rifampin-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clinic Microbiol. 2004;42:871–3.
Vazquez JL, Merino S, Domenech O, Berlanga M, Vinas M, Montero MT et al. Determination of the partition coefficients of a homologous series of ciprofloxacin: influence of the N-4 piperazinyl alkylation on the antimicrobial activity. Int J Pharm. 2001;220:53–62.
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Dr. Rehab Mahmoud Abdel-Baky, professor of Microbiology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Minia University, for her great help in performing antibacterial and antifungal screening studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ezelarab, H.A.A., Abbas, S.H., Abourehab, M.A.S. et al. Novel antimicrobial ciprofloxacin-pyridinium quaternary ammonium salts with improved physicochemical properties and DNA gyrase inhibitory activity. Med Chem Res 30, 2168–2183 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-021-02798-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-021-02798-3