Abstract
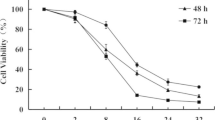
Twenty-eight compounds, including 24 new (4–22, 25–26, and 28–30) and four known (2, 23, 24, and 27) have been synthesized starting from asiatic acid (1), which was isolated from Centella asiatica. The preparation procedure included the acetylation, hydrolyzation on the 2-, 3-, 23-, and the side chain hydroxyl, amino groups, as well as the amidation of the 28-carboxylic group. All the synthesized derivatives were structurally confirmed by 1H, 13C NMR, and MS spectra. Besides, they were evaluated for their cytotoxicity against three cancer cell lines: KB (human carcinoma in the mouth), HepG2 (human hepatocellular carcinoma), and SK-LU-1 (human lung carcinoma). Eleven of the tested compounds, including nine newly synthesized and two known ones showed very strong activity against three tested cell lines with the IC50 values ranging from 0.67 to 37.39 µM. Three compounds showed good activity against KB and HepG2 cell lines with the IC50 values ranging from 1.95 to 32.12 µM. The activity against the KB and HepG2 cell lines was in general higher than that against the SK-LU-1 cell line. The acetylation of the hydroxyl groups in the A-ring and the OH or NH groups in the amide side chains strongly enhanced the activity of the compounds. In addition, five potent compounds (9, 12, and 15–17) were also evaluated for apoptosis-inducing activities. The ratio of apoptosis and necrotic cells increased when lung cancer cells were treated with these compounds. On the other hand, compound 9 increased caspase 3 activities (P < 0.05). Thus, these compounds induced lung cancer cell death by apoptosis and necrosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinkhaus B, Lindner M, Schuppan D, Hahn EG (2000) Chemical, pharmacological and clinical profile of the East Asian medical plant Centella asiatica. Phytomedicine 7:427–448
Cos P, Vlietinck AJ, Vanden BD, Maes L (2006) Anti-infective potential of nature products: how to develop a stronger in vitro ‘proof-of-concept’. J Ethnopharmacol 106:290–302
Do HB, Dang QC, Bui XC, Nguyen TD, Do TD, Phan VH, Vu NL, Pham DM, Phan KM, Doan TN, Nguyen T, Tran T (2003) Cây thuốc và động vật làm thuốc ở Việt Nam (Vietnamese medicinal plants and animals). Publishing House for Science and Technology, Hanoi, Part II, pp 582–586
Dong MS, Jung SH, Kim HJ, Kim JR, Zhao LX, Lee ES, Lee EJ, Yi JB, Lee N, Cho YB, Kwuk WJ, Park YI (2004) Structure-related cytotoxicity and anti-hepatofibric effect of asiatic acid derivatives in rat hepatic stellate cell-line, HSC-T6. Arch Pharm Res 27:512–517
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516
Fink SL, Cookson BT (2005) Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necrosis: mechanistic description of dead and dying eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun 73:1907–1916
Goncalves BMF, Salvador JAR, Marin S, Cascante M (2016) Synthesis and anticancer activity of novel fluorinated asiatic acid derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 114:101–117
Hashim P, Sidek H, Helan MHM, Sabery A, Palanisamy UD, Ilham M (2011) Triterpene composition and bioactivities of Centella asiatica. Molecules 16:1310–1322
James JT, Dubery IA (2009) Pentacyclic triterpenoids from the medicinal herb, Centella asiatica (L.) urban. Molecules 14:3922–3941
Jeong BS, Kim Y, Lee ES (2007a) Modification of C2,3,23,28 functional groups on asiatic acid and evaluation of hepatoprotective effects. Bull Korean Chem Soc 28:977–982
Jeong BS, Lee MK, Kim YC, Lee ES (2007b) Modification of C2 functional group on asiatic acid and the evaluation of hepatoprotective effects. Arch Pharm Res 30:282–289
Jeong BS (2006) Structure-activity relationship study of asiatic acid derivatives for new wound healing agent. Arch Pharm Res 29:556–562
Jew SS, Kim HD, Jung JH, Park JH, Seo SK, Nam TG, Hahn DK, Park JH, Sim PJ, Lim MJ, Lin KH (1998a) Asiatic acid derivatives, its manufacturing method and dermatological agent containing it. US5834437 A, Filled 1 Dec 1995, issued 10 Nov 1998
Jew SS, Park HG, Kim HD, Joung HJ, Kim JC, Kim HP, Lee MK, Choi HS, Lee ES, Yoo CH, Lim DY, Kim JH, Seo SK, Nam TG, Han D, Shim PJ, Jung JE, Beom HJ (1998b) Asiatic acid dervatives having modified A-ring. WO1998023575 A1, Filled 27 Nov 1997, issued 4 Jun 1998
Jing Y, Wang G, Ge Y, Xu M, Gong Z (2015) Synthesis, anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic activity evaluations of asiatic acid amino acid derivatives. Molecules 20:3709–3724
Jing Y, Wuang G, Ge Y, Xu M, Tang S, Gong Z (2016) AA-PMe, a novel asiatic acid derivative, induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther 17:1605–1621
Krysko DV, Berghe TV, D’Herde K, Vandenabeele P (2008) Apoptosis and necrosis: detection, discrimination and phagocytosis. Methods 44:205–221
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Porter GA, Booth CJ, Mehal WZ, Inayat I, Flavell RA (2006) Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science 311:847–851
Lavrik IN, Krammer PH (2009) Life and death decisions in the CD95 system: main proand anti-apoptotic modulators. Acta Nat 1:80–83
Li J, Yuan M, Jiang L, Yuan L, Zhang X, Zhang X, Li Y, Dong L, Bao X, Yin S (2015) Synthesis and evaluation of asiatic acid derivatives as anti-fibrotic agents: structure activity studies. Steroids 96:44–49
Li JF, Huang RZ, Yao GY, Ye MY, Wang HS, Pan YM, Xiao JT (2014) Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel aniline-derived asiatic acid derivatives as potential anticancer agents. Eur J Med Chem 86:175–188
Lizarbe MA, Barrasa JI, Olmo N, Gavilanes F, Turnay J (2013) Annexin-phospholipid interactions. Functional implications. Int J Mol Sci 14:2652–2683
Lv J, Sharma A, Zhang T, Wu Y, Ding X (2018) Pharmacological review on asiatic acid and its derivatives: a potential compound. SLAS Technol: 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1177/2472630317751840
Meng YQ, Cui HB, Li L, Zhang WC, Pan HS, Yu TT, Li W (2018) Synthesis and antitumor activity evaluation of asiatic acid derivatives as survivin inhibitor. J Asian Nat Prod Res 5:1–12
Orhan IE (2012) Centella asiatica (L.) urban: from traditional medicine to modern medicine with neuroprotective potential. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2012:8pp, Article ID 946259. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/946259
Porter AG, Jänicke RU (1998) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6:99–104
Qian Y, Xin Z, Lv Y, Wang Z, Zuo L, Huang X, Li Y, Xin HB (2018) Asiatic acid suppresses neuroinflammation in BV2 microglia via modulation of the Sirt1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Food Funct 9:1048–1057
Rasul A, Yu B, Khan M, Zhang K, Iqbal F, Ma T, Yang H (2012) Magnolol, a natural compound, induces apoptosis of SGC-7901 human gastric adenocarcinoma cells via the mitochondrial and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Oncol 40:1153–1161
Scudiero DA, Shoemaker RH, Kenneth DP, Monks A, Tierney S, Nofziger TH, Currens MJ, Seniff D, Boyd MR (1988) Evaluation of a soluable tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth and drug sensitivity in culture using human and other tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 48:4827–4833
Siddique AI, Mani V, Renganathan S, Ayyanar R, Nagappan A, Namasivayam N (2017) Asiatic acid abridges pre-neoplastic lesions, inflammation, cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in a rat model of colon carcinogenesis. Chem Biol Interact 278:197–211
Tabassum R, Vaibhav K, Shrivastava P, Khan A, Amed ME, Javed H, Islam F, Amad S, Siddiqui MS, Salhi MM, Islam F (2013) Centella asiatica attenuates the neuro behavioral, neuro chemical and histological changes in transient focal middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. Neuro Sci 34:925–933
Tim M (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assay. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Zhang L, Chen J, GongY, Liu J, Zhang L, Hua W, Sun H (2009) Synthesis and biological evaluation of asiatic acid derivatives as inhibitors of glycogen phosphorylases. Chem Biodivers 6:864–874
Zhao LX, Park HJ, Jew SS, Lee MK, Kim YC, Thapa P, Karki R, Jahng Y, Jeong BS, Lee ES (2007) Modification of C11, C28, C2,3,23 or C2,23,23 functional group on asiatic acid and evaluation of hepatoprotective effects. Bull Korean Chem 28:970–976
Zheng CJ, Qin LP (2007) Chemical components of Centella asiatica and their bioactivities. Chin J Integr Med 5:348–351
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 104.01-2012.33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tran Van, L., Vo Thi, Q.N., Tran Van, C. et al. Synthesis of asiatic acid derivatives and their cytotoxic activity. Med Chem Res 27, 1609–1623 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-018-2176-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-018-2176-y