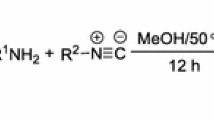Abstract
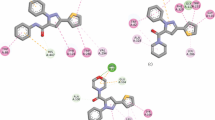
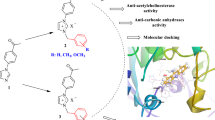
When N-arylisomaleimides were transformed under enzymatic reaction conditions, the transformation reaction proved to be influenced by electronic effects. This was demonstrated qualitatively by 1H NMR spectroscopy and quantitatively by monitoring the kinetic of isomerization of N-phenylisomaleimide to N-phenylmaleimide. Subsequently, the first pseudo-order and activation energy (E a) of the process were determined. The compounds showed in situ influence on AChE inhibition. The derivatives with electron-withdrawing groups exhibited a better effect than those having electron-donating groups. The in silico experiments show that the ligands evaluated established interactions with the CAS site. This suggests that these compounds could be useful for generating better reversible and competitive inhibitors of AChE.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apweiler R, Bairoch A, Wu C (2004) Protein sequence databases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 8:76–80
Barba V, Hernández C, Rojas-Lima S, Farfán N, Santillán R (1999) Preparation of N-aryl-substituted spiro-β-lactames via Staudinger cycloaddition. Can J Chem 77:2025–2032
Berman H, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne P (2000) The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28:235–242
Bonting SL, Featherstone RM (1956) Ultramicro assay of the cholinesterases. Arch Biochem Biophys 61:89–98
Bourne Y, Grassi J, Bougis P, Marchot P (1999) Conformational flexibility of the acetylcholinesterase tetramer suggested by X-ray crystallography. J Biol Chem 274:30370–30376
Breine U, Henderberg I, Liljedahl SO (1958) Treatment of paralytic ileus with cholinesterase inhibitors in intravenous drip. Acta Chir Scand 114:172–180
Constantinescu M, Ivanov D (2005) Computational study of maleamic acid cyclodehydration with acetic anhydride. Intern J Quantum Chem 106:1330–1337
Correa-Basurto J, Espinosa-Raya J, González-May M, Espinoza-Fonseca LM, Vázquez-Alcántara I, Trujillo-Ferrara J (2006) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by two arylderivatives: 3a-acetoxy-5H-pyrrolo(1,2-a) (3,1)benzoxazin-1,5-(3aH)-dione and cis-N-p-acetoxy-phenylisomaleimide. J Enzym Inhib Med Chem 21:133–138
Correa-Basurto J, Flores-Sandoval C, Marín-Cruz J, Rojo-Domínguez A, Espinoza-Fonseca M, Trujillo-Ferrara J (2007) Docking and quantum mechanic studies on cholinesterases and their inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 42:10–19
Cotter RJ, Sauers CK, Whelan JM (1961) The synthesis of N-substituted isomaleimides. J Org Chem 26(10):10–15
Cummings J, Lai TJ, Hemrungrojn S, Mohandas E, Yun Kim S, Mair G, Dash A (2016) Role of donepezil in the management of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease and demetia with Lewy bodies. CNS Neurosci Ther 22:159–166
Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA (2016) Discovery studio, v.16. Dassault Systèmes, San Diego
Davies P, Maloney AJ (1976) Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2:1403
Desmidt T, Hommet C, Camus V (2016) Pharmacological treatments of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia in Alzheimer’s disease: role of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and memantine. Geriatr Psychol Neuropsychiatr Vieil 14:300–306
Durai R (2009) Colonic pseudo-obstruction. Singapore Med J 50:237–244
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres Jr V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Fersht A (1999) Structure and mechanism in protein science: a guide to enzyme catalysis and protein folding. WH Freeman and Company, New York
Fortier LP, McKeen D, Turner K, de Médicis É, Warriner B, Jones PM, Chaput A, Pouliot JF, Galarneau A (2015) The RECITE study: a Canadian prospective, multicenter study of the incidence and severity of residual neuromuscular blockade. Anesth Analg 121:366–372
Frisch M, Trucks G, Schlegel H, Scuseria G, Robb M, Cheeseman J, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson G, Nakatsuji H, Caricato M, Li X, Hratchian H, Izmaylov A, Bloino J, Zheng G, Sonnenberg J et al. (2009) Gaussian 09W, 9.5 Version. Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT
Fruk L, Graham D (2003) The electronic effects on the formation of N-aryl-maleimides and isomaleimides. Heterocycles 60(10):2305–2313
Graipaspong N, Thaipisuttikul P, Vallipakorn SA (2016) Cholinesterase inhibitors and behavioral & psychological symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. J Med Assoc Thai 99:433–440
Guevara-Salazar JA, Espinoza-Fonseca M, Beltrán HI, Correa-Basurto J, Quintana-Zavala D, Trujillo-Ferrara J (2007) The electronic influence on the active site-directed inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by N-aryl-substituted-succinimides. J Mex Chem Soc 51:222–227
Guevara-Salazar JA, Quintana-Zavala D, Jiménez-Vázquez HA, Trujillo-Ferrara J (2011) Synthesis of Diels-Alder adducts of N-arylmaleimides by a multicomponent reaction between maleic anhydride, dienes, and anilines. Monatsh Chem 142:827–836
Gupta S, Mohan CG (2014) Dual binding site and selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitors derived from integrated pharmacophore models and sequential virtual screening. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/291214.
Inestrosa NC, Sagal JP, Colombres M (2005) Acetylcholinesterase interaction with Alzheimer amyloid beta. Subcell Biochem 38:299–317
Ivanov D, Constantinescu M (2005) Computational study of maleamic acid cyclodehydration. J Phys Org Chem 16:348–354
Joseph-Nathan P, Mendoza V, García E (1974) Aziridine induced isomerization of isomaleimides to maleimides. Can J Chem 52:129–131
Kelly JS (1999) Alzheimer's disease the tacrine legacy. TiPS 20:127–129
Kiametis A, Monica-Silva A, Luiz-Romeiro A, Martins J, Gargano R (2017) Potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: molecular docking, molecular dynamics, and in silico prediction. J Mol Model 23:67
Kirino O, Baruch R, Casida JE (1985) N-phenyl-maleimides, -isomaleimides and –maleamic acids as selective herbicide antidotes. Agric Biol Chem 49:267–268
Kolko M (2015) Present and new treatment strategies in the management of glaucoma. Open Ophthalmol J 15:89–100
Mehndiratta MM, Pandey S, Kuntzer T (2014) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor treatment for myasthenia gravis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006986.pub3
Morris G, Goodsell D, Halliday R, Huey R, Hart W, Belew R, Olson A (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comp Chem 19:1639–1662
Morris G, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) Autodock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexiblity. J Comput Chem 16:2785–2791
Oishi T, Fujimoto M, Yoshimoto N, Kimura T (1989) Anionic polymerization of N-substituted isomaleimide. Polym J 21(8):655–659
Pakaski M, Kasa P (2003) Role of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in the metabolism of amyloid precursor protein. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 2:163–171
Perry EK (1986) The cholinergic hypothesis—ten years on. Br Med Bull 42:63–69
Sadigh-Eteghad S, Sabermrouf B, Majdi A, Talebi M, Farhoudi M, Mahmoudi J (2015) Amyloid-beta: a crucial factor in Alzheimer’s disease. Med Princ Pract 24:1–10
Sauers CK (1969) The dehydration of N-arylmaleamic acids with acetic anhydride. J Org Chem 34:2275–2279
Schreiber JU (2014) Management of neuromulscular blocakade in ambulatory patients. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 27:583–588
Shakil S, Kamal M, Tabrez S, Abuzenadah A (2012) Molecular interaction of the antineoplastic drug methotrexate with human brain acetylcholinesterase: a docking study. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 11:142–147
Standaert DG, Roberson ED (2011) Tratamiento de enfermedades degenerativas del sistema nervioso central. In: Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollmann BC (eds) Goodman & Gilman: Las bases farmacológicas de la terapéutica. McGraw-Hill, China, pp 619–622
Taylor P (1991) The cholinesterases. J Biol Chem 266:4025–4028
Trujillo-Ferrara J, Montoya L, Espinoza-Fonseca M (2003a) Synthesis, anticholinesterase activity and structure-activity relationships m-aminobenzoic acid derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:1825–1827
Trujillo-Ferrara J, Vázquez I, Espinosa J, Santillán R, Farfán N, Höpfl H (2003b) Reversible and irreversible activity of succinic and maleic acid derivatives on acetylcholinesterase. Eur J Pharm Sci 18:313–322
Zeinali F, Stulberg JJ, Delaney CP (2009) Pharmacological management of postoperative ileus. Can J Surg 52:153–157
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Comisión de Operación y Fomento de Actividades Académicas (COFAA) of the Secretaría de Investigación y Posgrado of the IPN (SIP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guevara, J.A., Trujillo, J.G., Quintana, D. et al. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition by products generated in situ from the transformation of N-arylisomaleimides. Med Chem Res 27, 989–1003 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-2122-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-2122-4