Abstract
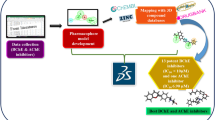
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder arising due to genetic and non-genetic causes. One of the major therapies adapted for symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease is by targeting acetylcholinesterase enzyme based on the cholinergic hypothesis. Acetylcholinesterase is a substrate-specific enzyme that degrades the neuro-transmitter acetylcholine. An optimum level of acetylcholine should be maintained in the brain for its proper function. In order to identify potent and selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitors we adopted an integrated in silico and bioassay methodologies. In silico approach involves creating chemical features based 3D-pharmacophore models using AChE specific inhibitors. This model was then used for sequential virtual screening from the small molecule databases. Finally, five molecules were selected on the basis of the best docking scores and pharmacokinetics properties. These molecules were subjected to docking analysis with the recently solved crystal structure of human acetylcholinesterase enzyme, in order to reveal its binding mode and interactions at the dual binding sites of the enzyme. The acetylcholinesterase enzyme inhibitory activity of these five lead molecules was further assessed by in-vitro analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accelrys Discovery Studio 2.5 (2009) Accelrys, San Diego, CA
Amat-Ur-Rasool H, Ahmed M (2015) Designing Second generation anti-alzheimer compounds as inhibitors of human acetylcholinesterase: computational screening of synthetic molecules and dietary phytochemicals. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0136509
Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K, Arrighi HM (2007) Forcasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Alz Dement 3:186–191
Bolognesi ML, Minarini A, Rosini M, Tumiatti V, Melchiorre C (2008) From dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors to multi-target-directed ligands (MTDLs): a step forward in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Mini Rev Med Chem 8:960–967
Clark DE (2003) In silico prediction of blood–brain barrier permeation. Drug Discov Today 8:927–933
Cheung J, Rudolph MJ, Burshteyn F, Cassidy MS, Gary EN, Love J, Franklin MC, Height JJ (2012) Structure of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligand. J Med Chem 55:10282–10286
De Ferrari GV, Canales MA, Shin I, Weiner LM, Silman I, Inestrosa NC (2001) A structural motif of acetylcholinesterase that promotes amyloid beta-peptide fibril formation. Biochemistry 40:10447–10457
DEREK 10.0 (2010) LHASA Limited, Leeds, UK
Eldridge MD, Murray CW, Auton TR, Paolini GV, Mee RP (1997) Empirical scoring functions: I. The development of a fast empirical scoring function to estimate the binding affinity of ligands in receptor complexes. J Comput Aid Mol Des 11:425–445
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres Jr V, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–89
Fallarero A, Oinonen P, Gupta S, Blom P, Galkin A, Mohan CG, Vuorela PM (2008) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by coumarins: the case of coumarin 106. Pharmacol Res 58:215–221
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, Mainz DT, Repasky MP, Knoll EH, Shaw DE, Shelley M, Perry JK, Francis P, Shenkin PS (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem 47:1739–1749
Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Halgren TA, Sanschagrin PC, Mainz DT (2006) Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J Med Chem 49:6177–6196
GLIDE, version 5.7 (2011) Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY.
Gupta S, Fallarero A, Järvinen P, Karlsson D, Johnson MS, Vuorela PS, Mohan CG (2011) Discovery of dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors identified by pharmacophore modeling and sequential virtual screening techniques. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:1105–1112
Huang L, Lin J, Xiang S, Zhao K, Yu J, Zheng J, Xu D, Nirasha S, Wang C, Chen X, Zhang J, Xu S, Wei X, Zhang Z, Zhou D, Han Y, Zhou W, Cui W, Hu Z, Wang Q (2016) Sunitinib, a clinically used anticancer drug, is a potent ache inhibitor and attenuates cognitive impairments in mice. ACS Chem Neurosci. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00329
Irwin JJ, Sterling T, Mysinger MM, Bolstad ES, Coleman RG (2012) ZINC: a free tool to discover chemistry for biology. J Chem Inf Model 52:1757–1768
Jain V, Saravanan P, Arvind A, Mohan CG (2011) First pharmacophore model of CCR3 receptor antagonists and its homology model assisted, stepwise virtual screening. Chem Biol and Drug Design 77:373–387
Jarvinen P, Fallarero A, Gupta S, Mohan CG, Hatakka A, Vuorela P (2010) Miniaturization and validation of the Ellmans reaction based acetylcholinesterase inhibitory assay into 384-well plate format and screening of a chemical library. Comb Chem and High Throughput Screen 13:278–284
Kryger G, Silman I, Sussman JL (1999) Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with E2020 (Aricept®): implications for the design of new anti-Alzheimer drugs. Structure 7:297–330
Kumar J, Meena P, Singh A, Jameel E, Maqbool M, Mobashir M, Shandilya A, Tiwari M, Hoda N, Jayaram B (2016) Synthesis and screening of triazolopyrimidine scaffold as multi-functional agents for Alzheimer’sdisease therapies. Eur J Med Chem 119:260–277
Lahiri DK, Farlow MR, Sambamurti K, Greig NH, Giacobini E, Schneider LS (2003) A critical analysis of new molecular targets and strategies for drug developments in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Drug Targets 4:97–112
Leonetti F, Catto M, Nicolotti O, Pisani L, Cappa A, Stefanachi A, Carotti A (2008) Homo- and hetero-bivalent edrophonium-like ammonium salts as highly potent, dual binding site AChE inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 16:7450–7456
Lemes LF, de Andrade Ramos G, de Oliveira AS, da Silva FM, de Castro Couto G, da Silva Boni M, Guimarães MJ, Souza IN, Bartolini M, Andrisano V, do Nascimento Nogueira PC, Silveira ER, Brand GD, Soukup O, Korábečný J, Romeiro NC, Castro NG, Bolognesi ML, Romeiro LA (2016) Cardanol-derived AChE inhibitors: towards the development of dual binding derivatives for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Med Chem. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.12.024
Lipinski CA (2004) Lead and drug-like compounds: the rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discov Today Technol 1:337–341
Matamoros AJ, Baas PW (2016) Microtubules in health and degenerative disease of the nervous system. Brain Res Bull Jun 27. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.06.016
Mishra CB, Manral A, Kumari S, Saini V, Tiwari M (2016) Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel indandione derivatives as multifunctional agents with cholinesterase inhibition, anti-β-amyloid aggregation, antioxidant and neuroprotection properties against Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg Med Chem. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2016.06.027
Mohan CG, Gandhi T, Garg D, Shinde R (2007) Computer-assisted methods in chemical toxicity prediction. Mini Rev Med Chem 7:499–507
Mullan M, Crawford F, Axelman K, Houlden H, Lilius L, Winblad B, Lannfelt L (1992) A pathogenic mutation for probable Alzheimer’s disease in the APP gene at the N-terminus of beta- amyloid. Nat Genet 1:345–347
Naslund J, Haroutunian V, Mohs R, Davis KL, Davies P, Greengard P, Buxbaum JD (2000) Correlation between elevated levels of amyloid beta-peptide in the brain and cognitive decline. J Amer Med Assoc 283:1571–1577
Nalivaeva NN, Turner AJ (2016) AChE and the amyloid precursor protein (APP) - Cross-talk in Alzheimer’s disease. Chem Biol Interact. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2016.04.009
Nikolic K, Mavridis L, Djikic T, Vucicevic J, Agbaba D, Yelekci K, Mitchell JB. (2016) Drug design for CNS diseases: polypharmacological profiling of compounds using cheminformatic, 3D-QSAR and virtual screening methodologies. Front Neurosci doi:10.3389/fnins.2016.00265
Pang YP, Quiram P, Jelacic T, Hong F, Brimijoin S (1996) Highly potent, selective, and low cost bis-tetrahydroaminacrine inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem 271:23646–23649
Piazzi L, Rampa A, Bisi A, Gobbi S, Belluti F, Cavalli A, Bartolini M, Andrisano V, Valenti P, Recanatini M (2003) 3-(4-{[Benzyl (methyl) amino] methyl} phenyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-2H-2-chromenone (AP2238) Inhibits both acetylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase-induced beta-amyloid aggregation: a dual function lead for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. J Med Chem 46:2279–2282
Piazzi L, Cavalli A, Belluti F, Bisi A, Gobbi S, Rizzo S, Bartolini M, Andrisano V, Recanatini M, Rampa A (2007) Extensive SAR and computational studies of 3-{4-[(Benzylmethylamino) methyl] phenyl}-6, 7-dimethoxy-2 H-2-chromenone (AP2238) derivatives. J Med Chem 50:4250–4254
Raina P, Santaguida P, Ismaila A, Patterson C, Cowan D, Levine M, Booker L, Oremus M (2008) Effectiveness of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for treating dementia: evidence review for a clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med 148:379–397
Richard AM (1998) Commercial toxicology prediction systems: a regulatory perspective. Toxicol Lett 102:611–616
Rodríguez YA, Gutiérrez M, Ramírez D, Alzate-Morales J, Bernal CC, Güiza FM, Romero Bohórquez AR (2016) Novel N-allyl/propargyl tetrahydroquinolines: synthesis via three-component cationic imino Diels-Alder reaction, binding prediction and evaluation as cholinesterase inhibitors. Chem Biol Drug Des. doi:10.1111/cbdd.12773
Tanzi RE, Kovacs DM, Kim TW, Moir RD, Guenette SY, Wasco W (1996) The gene defects responsible for familial Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Disease 3:159–168
Walsh DM, Selkoe DJ (2004) Deciphering the molecular basis of memory failure in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 44:181–193
Wang QM, Jiang HL, Chen KX, Ji RY, Ye YJ (1999) Theoretical studies on the possible reaction pathway for the deacylation of the AChE catalyzed reaction. Int J Quantum Chem 74:315–325
Ye CY, Lei Y, Tang XC, Zhang HY (2015) Donepezil attenuates Aβ-associated mitochondrial dysfunction and reduces mitochondrial Aβ accumulation in vivo and in vitro. Neuropharmacology. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.02.020
Zhu Y, Xiao K, Ma L, Xiong B, Fu Y, Yu H, Wang W, Wang X, Hu D, Peng H (2009) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel dual inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and β-secretase. Bioorg Med Chem 17:1600–1613
Zhu K, Borrelli KW, Greenwood JR, Day T, Abel R, Farid RS, Harder EJ (2014) Docking covalent inhibitors: a parameter free approach to pose prediction and scoring. J Chem Inf Model 54:1932–1940
Acknowledgments
CGM is grateful to Amrita Centre for Nanosciences and Molecular Medicine, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham (Amrita University) for computational infrastructure support. JJ is supported by a senior research fellowship (Order No:45/16/2011/IMM-BMS) from a council of scientific and industrial research (CSIR), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Sneha Patil and Ankit Tyagi contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, S., Tyagi, A., Jose. , J. et al. Integration of common feature pharmacophore modeling and in vitro study to identify potent AChE inhibitors. Med Chem Res 25, 2965–2975 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-016-1716-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-016-1716-6