Abstract
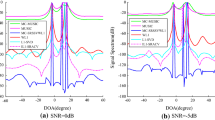
Recent research on sparse signal reconstruction (SSR) shows that the sparse Bayesian learning (SBL) method is one of the most popular methods for direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation. However, the high computational complexity and the time-consuming iterations in the Bayesian learning make the SBL-based methods difficult in practical applications. To address this problem, the iterative process in the SBL method is improved in this paper. Inspired by the spatial sparsity of the signal variance, an \(l_0\) norm constraint Bayesian strategy for DOA estimation is proposed. An additional \(l_0\) norm penalty is integrated into the objective function of the signal variance vector to achieve zero attraction. With a few user-adjusted parameters, the proposed strategy achieves a faster implementation while inheriting the superior performance of the SBL method for DOA estimation. Numerical simulations demonstrate that the proposed strategy can significantly improve the convergence rate and accelerate the iterative process. The innovative work increases the possibility of real-time implementation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
H. Bai, M.F. Duarte, R. Janaswamy, Direction of arrival estimation for complex sources through L1 norm sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26(5), 765–769 (2019)
M. Chen, X. Mao, C. Zhao, Direct localization of emitters based on sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 68(6), 5769–5781 (2019)
P. Chen, Z. Cao, Z. Chen et al., Off-grid DOA estimation using sparse Bayesian learning in MIMO radar with unknown mutual coupling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 67(1), 208–220 (2019)
J. Dai, X. Bao, W. Xu et al., Root sparse Bayesian learning for off-grid DOA estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 24(1), 46–50 (2017)
A. Das, Real-valued sparse Bayesian learning for off-grid direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation in ocean acoustics. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 46(1), 172–182 (2021)
H. Ge, L. Wang, J. Wen et al., An RIP condition for exact support recovery with covariance-assisted matching pursuit. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26(3), 520–524 (2019)
Y. Gu, J. Jin, S. Mei, \(l_0\) Norm constraint LMS algorithm for sparse system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 16(9), 774–777 (2009)
D.A. Harville, Maximum likelihood approaches to variance component estimation and to related problems. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 72(358), 320–338 (1977)
Z. He, X. Yuan, L. Chen, Super-resolution channel estimation for massive MIMO via clustered sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 68(6), 6156–6160 (2019)
K. Huang, Z. Yang, Robust sparse Bayesian learning for sparse signal recovery under unknown noise distributions. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 40, 1365–1382 (2021)
Y. Huang, Z. Zheng, Difference coarray-based direction finding via covariance fitting. IEEE Commun. Lett. 25(8), 2569–2573 (2021)
J. Kim, J. Wang, B. Shim, Nearly optimal restricted isometry condition for rank aware order recursive matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 67(17), 4449–4463 (2019)
P. Li, J. Li, Q. Zhang et al., A DOA estimation method for UCA based on orthogonal subspace compensation. IEEE Commun. Lett. 14(8), 3267–3271 (2021)
T. Long, J. Chen, G. Huang et al., Acoustic source localization based on geometric projection in reverberant and noisy environments. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 13(1), 143–155 (2019)
D. Malioutov, M. Cetin, A.S. Willsky, A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(8), 3010–3022 (2005)
E. Michael, Tipping, sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 1(3), 211–244 (2001)
D.P. Wipf, B.D. Rao, An empirical Bayesian strategy for solving the simultaneous sparse approximation problem. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 55(7), 3704–3716 (2007)
D.P. Wipf, B.D. Rao, Sparse Bayesian learning for basis selection. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 52(8), 2153–2164 (2004)
H. Yang, P. Wang, Z. Ye, Robust adaptive beamforming via covariance matrix reconstruction under colored noise. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 28, 1759–1763 (2021)
J. Yang, Y. Yang, Sparse bayesian DOA estimation using hierarchical synthesis lasso priors for off-grid signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 68, 872–884 (2020)
J. Yang, Y. Yang, J. Lu, A variational Bayesian strategy for solving the DOA estimation problem in sparse array. Digit. Signal Prog. 90, 28–35 (2019)
Z. Yang, L. Xie, C. Zhang, Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(1), 38–43 (2013)
R. Zdunek, A. Cichocki, Improved M-FOCUSS algorithm with overlapping blocks for locally smooth sparse signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(10), 4752–4761 (2008)
Z. Zhang, B.D. Rao, Sparse signal recovery with temporally correlated source vectors using sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 5(5), 912–926 (2011)
J. Zhao, R. Gui, X. Dong, PHD filtering for multi-source DOA tracking with extended co-prime array: an improved MUSIC pseudo-likelihood. IEEE Commun. Lett. 25(10), 3267–3271 (2021)
Z. Zheng, Y. Huang, W.-Q. Wang et al., Augmented covariance matrix reconstruction for DOA estimation using difference coarray. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 69, 5345–5358 (2021)
Z. Zheng, Y. Huang, W.-Q. Wang et al., Direction-of-arrival estimation of coherent signals via coprime array interpolation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 27(1), 585–589 (2020)
T. Zhou, J. Huang, W. Du et al., 2-D Deconvolved conventional beamforming for a planar array. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 40, 5572–5593 (2021)
H. Zhu, G. Leus, G.B. Giannakis, Sparsity-cognizant total least-squares for perturbed compressive sampling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(5), 2002–2016 (2011)
Funding
The research of this project was supported by the National Key R & D Program of China (2016YFC1400101) and National Defense Basic Scientific Research Project (JCKY2019604B001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The research of this project was supported by the National Key R & D Program of China (2016YFC1400101) and National Defense Basic Scientific Research Project (JCKY2019604B001).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, G., Li, C., Qiu, L. et al. \(l_0\) Norm Constraint Bayesian Strategy for Direction-of-Arrival Estimation. Circuits Syst Signal Process 41, 4028–4040 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-01972-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-01972-1