Abstract
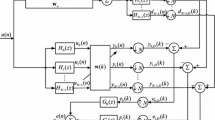
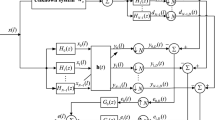
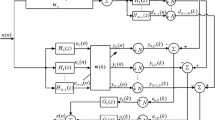
In this paper, two arctangent-based normalized subband adaptive filter (Arc-NSAF) algorithms are proposed, which are derived from two different forms of arctangent cost function and their difference is the order of the arctangent computation and the summation operation of the normalized subband error signal. Benefiting from the excellent property of the arctangent function for suppressing impulsive interferences, the proposed Arc-NSAF algorithms not only possess good robustness against impulsive interferences, but also obtain faster convergence rate for the colored input signals. To further improve the convergence performance of the Arc-NSAFs when identifying sparse system, the proportionate versions of the Arc-NSAF algorithms are also proposed. Simulation results have demonstrated the superiority of the proposed algorithms in impulsive interferences environments as compared to their respective competitors.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S.E. Abadi, S. Kadkhodazadeh, A family of proportionate normalized subband adaptive filter algorithms. J. Frankl. Inst. 348(2), 212–238 (2011)
J. Benesty, S.L. Gay, An improved PNLMS algorithm, in Proceedings of the ICASSP-02, (USA 2002), pp. 1881–1884
S. Haykin, Adaptive Filter Theory, 4th edn. (Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, 2002)
J.J. Jeong, K. Koo, G. Koo, S.W. Kim, Steady-state mean-square deviation analysis of improved normalized subband adaptive filter. Signal Process. 106, 49–54 (2015)
J.H. Kim, J.H. Chang, S.W. Nam, Sign subband adaptive filter with L\(_{1}\)-norm minimisation-based variable step-size. Electron. Lett. 49(21), 1325–1326 (2013)
K.A. Lee, W.S. Gan, Improving convergence of the NLMS algorithm using constrained subband updates. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11(9), 736–739 (2004)
K.A. Lee, W.S. Gan, Inherent decorrelating and least perturbation properties of the normalised subband adaptive filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(11), 4475–4480 (2006)
K.A. Lee, W.S. Gan, S.M. Kuo, Subband Adaptive Filter: Theory and Implementation (Wiley, Chichester, 2009)
L. Lu, H. Zhao, Diffusion leaky LMS algorithm: Analysis and implementation. Signal Process. 140, 77–86 (2017)
L. Lu, H. Zhao, C. Chen, A new normalized subband adaptive filter under minimum error entropy criterion. Signal Image Video Process. 10(6), 1097–1103 (2016)
V.J. Mathews, S.H. Cho, Improved convergence analysis of stochastic gradient adaptive filters using the sign algorithm. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 35(4), 450–454 (1987)
J. Ni, F. Li, Variable regularisation parameter sign subband adaptive filter. Electron. Lett. 46(24), 1605–1607 (2010)
J. Ni, X. Chen, J. Yang, Two variants of the sign subband adaptive filter with improved convergence rate. Signal Process. 96, 325–331 (2014)
K. Ozeki, T. Umeda, An adaptive filtering algorithm using an orthogonal projection to an affine subspace and its properties. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 67–A(5), 19–27 (1984)
R. Price, A useful theorem for nonlinear devices having Gaussian inputs. IRE Trans. Inf. Theory IT–4, 69–72 (1958)
A.H. Sayed, Adaptive Filters (Wiley, New York, 2008)
T. Shao, Y.R. Zheng, J. Benesty, An affine projection sign algorithm robust against impulsive interferences. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(4), 327–330 (2010)
Z. Shen, Y. Yu, T. Huang, Normalized subband adaptive filter algorithm with combined step size for acoustic echo cancellation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(7), 2991–3003 (2017)
J.W. Shin, J.W. Yoo, P.G. Park, Variable step-size sign subband adaptive filter. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 20(2), 173–176 (2013)
M.M. Sondhi, The history of echo cancellation. IEEE Signal Process. 23(5), 95–98 (2006)
P. Wen, S. Zhang, J. Zhang, A novel subband adaptive filter algorithm against impulsive noise and it’s performance analysis. Signal Process. 127, 282–287 (2016)
Z. Yang, Y.R. Zheng, S.L. Grant, Proportionate affine projection sign algorithms for network echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 19(8), 2273–2284 (2011)
W. Yin, A.S. Mehr, Stochastic analysis of the normalized subband adaptive filter algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 58(5), 1020–1033 (2011)
Y. Yu, H. Zhao, Memory proportionate APSA with individual activation factors for highly sparse system identification in impulsive noise environment, in IEEE International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), (China 2014), pp. 1–6
Y. Yu, H. Zhao, Novel sign subband adaptive filter algorithms with individual weighting factors. Signal Process. 122, 14–23 (2016)
Y. Yu, H. Zhao, Z. He, B. Chen, A robust band-dependent variable step size NSAF algorithm against impulsive noises. Signal Process. 119, 203–208 (2016)
Y. Yu, H. Zhao, Novel combination schemes of individual weighting factors sign subband adaptive filter algorithm. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. (2017). doi:10.1002/acs.2755
J. Zeng, Y. Lin, L. Shi, A normalized least mean square algorithm based on the arctangent cost function robust against impulsive interference. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(8), 3040–3047 (2016)
H. Zhao, Y. Yu, S. Gao, X. Zeng, Z. He, Memory proportionate APA with individual activation factors for acoustic echo cancellation. IEEE/ACM IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 22(6), 1047–1055 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant: 61473239) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Grant No. 2682014ZT28).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
In this Section, the detailed derivation of (14) is presented. Using Price’s theorem in [15] and the assumption (1), we have
with
where \(\eta _i (k)\) and \(v_i (k)\) are zero-mean Gaussian sequences with variances \(\sigma _{\eta _i }^2 =\frac{1}{N}(\kappa +1)\sigma _v^2 \) and \(\sigma _{v_i }^2 =\frac{1}{N}\sigma _v^2 \).
According to the assumption (3), we have
Then, we get
Based on the definitions of the c(k) and \(e_{a,i} (k)\), we have the following equation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Z., Yu, Y. & Huang, T. Two Novel Arctangent Normalized Subband Adaptive Filter Algorithms Against Impulsive Interferences. Circuits Syst Signal Process 37, 883–900 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0583-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0583-9