Abstract
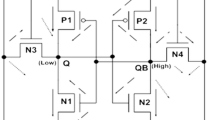
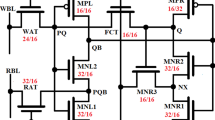
This paper presents a new nine-transistor (9T) SRAM cell operating in the subthreshold region. In the proposed 9T SRAM cell, a suitable read operation is provided by suppressing the drain-induced barrier lowering effect and controlling the body–source voltage dynamically. Proper usage of low-threshold voltage (L-\(V_{\mathrm{t}}\)) transistors in the proposed design helps to reduce the read access time and enhance the reliability in the subthreshold region. In the proposed cell, a common bit-line is used in the read and write operations. This design leads to a larger write margin without using extra circuits. The simulation results at 90 nm CMOS technology demonstrate a qualified performance of the proposed SRAM cell in terms of power dissipation, power–delay product, write margin, read access time and sensitivity to process, voltage and temperature variations as compared to the other most efficient low-voltage SRAM cells previously presented in the literature.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.R. Ahmadimehr, B. Ebrahimi, A. Afzali-Kusha, A high speed subthreshold SRAM cell design. In Proceedings of Asia Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (2009), pp. 8–13
M. Alioto, Understanding DC behavior of sub-threshold CMOS logic through closed-form analysis. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 57(7), 1597–1607 (2010)
B.H. Calhoun, A.P. Chandrakasan, A 256-kb 65-nm sub-threshold SRAM design for ultra-low-voltage operation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 42(3), 680–688 (2007)
I.J. Chang, J.J. Kim, S.P. Park, K. Roy, A 32 kb 10T sub-threshold SRAM array with bit-interleaving and differential read scheme in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 44(2), 650–658 (2009)
B. Ebrahimi, M. Rostami, A. Afzali-Kusha, M. Pedram, Statistical design optimization of FinFET SRAM using back-gate voltage. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 19(10), 1911–1916 (2011)
B. Ebrahimi, A. Afzali-Kusha, H. Mahmoodi, Robust FinFET SRAM design based on dynamic back-gate voltage adjustment. Els. J. Microelectron. Reliab. 54(11), 2604–2612 (2014)
D. Hodges, H. Jackson, R. Saleh, Analysis and Design of Digital Integrated Circuits, 3rd edn. (McGraw Hill, London, 2006)
Z. Liu, V. Kursun, Characterization of a novel nine-transistor SRAM cell. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 16(4), 488–492 (2008)
E. Macii, Ultra Low-Power Electronics and Design (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, 2004)
M.H. Moaiyeri, R. Faghih Mirzaee, K. Navi, T. Nikoubin, O. Kavehei, Novel direct designs for 3-input XOR function for low power and high-speed applications. Int. J. Electron. 97(6), 647–662 (2010)
M. Moghaddam, M. Eshghi, M.H. Moaiyeri, A low-voltage single-supply level converter for sub-\(V_{\rm TH}\) operation: 0.3 V to 1.2 V. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 69(2), 14–18 (2013)
S. Mukhopadhyay, H. Mahmoodi, K. Roy, Modeling of failure probability and statistical design of SRAM array for yield enhancement in nanoscaled CMOS. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 24(12), 1859–1880 (2005)
S. Narendra, V. De, S. Borkar, D. Antoniadis, A.P. Chandrakasan, Full-chip sub-threshold leakage power prediction and reduction techniques for sub-0.18-um CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 39(3), 501–510 (2004)
S. Timarchi, K. Navi, Arithmetic circuits of redundant SUT-RNS. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 58(9), 2959–2968 (2009)
A. Teman, L. Pergament, O. Cohen, A. Fish, A 250 mV 8 kb 40 nm ultra-low power 9T supply feedback SRAM (SF-SRAM). IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 46(11), 2713–2726 (2011)
K. Takeda, H. Ikeda, Y. Hagihara, M. Nomura, H. Kobatake, Redefinition of write margin for next-generation SRAM and write-margin monitoring circuit. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Solid–State Circuits (2006), pp. 2602–2611
N. Verma, A.P. Chandrakasan, A 256 kb 65 nm 8T subthreshold SRAM employing sense-amplifier redundancy. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 43(1), 141–149 (2008)
A. Wang, B. Calhoun, A.P. Chandrakasan, Sub-Threshold Design for Ultra Low-Power Systems (Springer, New York, 2006)
M. Yamaoka, et al., Low-power embedded SRAM modules with expanded margins for writing. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Solid–State Circuits (2005), pp. 480–611
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moghaddam, M., Timarchi, S., Moaiyeri, M.H. et al. An Ultra-Low-Power 9T SRAM Cell Based on Threshold Voltage Techniques. Circuits Syst Signal Process 35, 1437–1455 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-015-0119-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-015-0119-0