Abstract
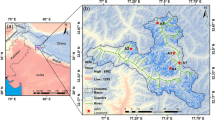
Trend analysis benefits collecting and analyzing reliable data in climate change studies. In this context, long-term temperature and precipitation data analysis, two variables sensitive to climate change, is essential. This study aims to holistically and partially determine the annual trends of precipitation and temperature time series for 1970–2019 at nine selected stations in the Susurluk Basin, Turkey. The innovative trend significance test (ITST), innovative crossing trend analysis (ICTA) method, and Mann-Kendall (MK) test were used to determine holistic trends. Also, partial trends were determined using successive average methodology (SAM). For the precipitation variable, while an increasing trend was determined for the ITST, there was mostly no trend for the other methods. While a strong increasing trend was detected for the temperature according to the ITST and MK methods, no trend was observed in any station according to the ICTA method. According to the SAM results, the maximum trend durations for the peak and trough change points were 4.9 (10.3) and 5.3 (8.4) years, respectively, for precipitation (temperature). The strong temperature trends in the basin will likely continue, requiring precautions against extreme events such as drought.













Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Some or all data that support this study's findings are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code Availability
The models or codes used to develop this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Acar, E., Kankal, M., Akçay, F., & Şan, M. (2022). Innovative polygon trend analyses with star graph for rainfall and temperature data in agricultural regions of Turkey. Environmental Earth Sciences, 81(23), 530.
Ahmadi, F., Nazeri Tahroudi, M., Mirabbasi, R., Khalili, K., & Jhajharia, D. (2018). Spatiotemporal trend and abrupt change analysis of temperature in Iran. Meteorological Applications, 25(2), 314–321.
Akçay, F., Kankal, M., & Şan, M. (2022). Innovative approaches to the trend assessment of streamflows in the Eastern Black Sea basin, Turkey. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 67(2), 222–247.
Albayrak, S., Caglar, S., Mulayim, A., Kurt-Sahin, G., Balkis, H., Cinar, N. F., & Bahceci, H. (2019). A case study: ecological quality status of Susurluk river basin (Marmara Sea). Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 28(2), 769–776.
Alifujiang, Y., Abuduwaili, J., & Ge, Y. (2021). Trend analysis of annual and seasonal river runoff by using innovative trend analysis with significant test. Water, 13(1), 95.
Allen M, Babiker M, Chen Y, et al (2018) Summary for Policymakers Global Warming of 1.5 C. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): Geneva, Switzerland
Arias, P., Bellouin, N., Coppola, E., Jones, R., Krinner, G., Marotzke, J., Zickfeld, K. (2021). Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Technical Summary.
Ay, M. (2020). Trend and homogeneity analysis in temperature and rainfall series in western Black Sea region, Turkey. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 139(3–4), 837–848.
Ay, M., & Kisi, O. (2015). Investigation of trend analysis of monthly total precipitation by an innovative method. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 120, 617–629.
Bayazit, M., & Önöz, B. J. H. S. J. (2007). To prewhiten or not to prewhiten in trend analysis? Hydrological Sciences Journal, 52(4), 611–624.
Bickici Arikan, B., & Kahya, E. (2019). Homogeneity revisited: analysis of updated precipitation series in Turkey. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 135(1–2), 211–220.
BISO (2020). Bursa Investment Support Office. https://bursainvest.gov.tr/ (Accessed 21 Dec 2020).
Buyukyildiz, M. (2023). Evaluation of annual total precipitation in the transboundary Euphrates-Tigris River Basin of Türkiye using innovative graphical and statistical trend approaches. Applied Water Science, 13(2), 38.
Caloiero, T. (2020). Evaluation of rainfall trends in the South Island of New Zealand through the innovative trend analysis (ITA). Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 139(1–2), 493–504.
Caloiero, T., Coscarelli, R., & Ferrari, E. (2018). Application of the innovative trend analysis method for the trend analysis of rainfall anomalies in southern Italy. Water Resources Management, 32, 4971–4983.
Ceribasi, G., & Aytulun, U. (2020). Investigation of the effect of climate change on precipitation and temperature data of Susurluk basin and Van Lake Closed Basin. International Journal of Global Warming, 22(1), 54–71.
Ceribasi, G., & Ceyhunlu, A. I. (2021). Analysis of total monthly precipitation of Susurluk Basin in Turkey using innovative polygon trend analysis method. Journal of Water and Climate Change, 12(5), 1532–1543.
Ceribasi, G., Ceyhunlu, A. I., & Ahmed, N. (2021a). Analysis of temperature data by using innovative polygon trend analysis and trend polygon star concept methods: A case study for Susurluk Basin, Turkey. Acta Geophysica, 69, 1949–1961.
Ceribasi, G., Ceyhunlu, A. I., & Ahmed, N. (2021b). Innovative trend pivot analysis method (ITPAM): A case study for precipitation data of Susurluk Basin in Turkey. Acta Geophysica, 69(4), 1465–1480.
Cui, L., Wang, L., Lai, Z., Tian, Q., Liu, W., & Li, J. (2017). Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal air temperature and rainfall in the Yangtze River Basin, China during 1960–2015. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 164, 48–59.
Dammo, M. N., Yadima, S. G., & Sangodoyin, A. Y. (2016). Observed trend of changes in relative humidity across North-East Nigeria (1981–2010). Civil and Environmental Research, 8, 73–76.
Danandeh Mehr, A., Hrnjica, B., Bonacci, O., & Torabi Haghighi, A. (2021). Innovative and successive average trend analysis of temperature and precipitation in Osijek Croatia. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 145(3–4), 875–890.
Dorum, A., Yarar, A., Sevimli, M. F., & Onüçyildiz, M. (2010). Modelling the rainfall–runoff data of susurluk basin. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(9), 6587–6593.
Esit, M. (2023). Investigation of innovative trend approaches (ITA with significance test and IPTA) comparing to the classical trend method of monthly and annual hydro-meteorological variables: A case study of Ankara region, Turkey. Journal of Water and Climate Change, 14(1), 305–329.
GDNCNP (2020). General Directorate of Nature Conservation and National Parks. http://kuscenneti.tabiat.gov.tr/ (Accessed 12 Dec 2020)
Gumus, V., Avsaroglu, Y., & Simsek, O. (2022). Streamflow trends in the Tigris river basin using Mann−Kendall and innovative trend analysis methods. Journal of Earth System Science, 131(1), 34.
Gumus, V., Simsek, O., & Avsaroglu, Y. (2023). Evaluation of long-term monthly mean streamflow trend in the Mediterranean basins using different methods. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 151(3–4), 1369–1382.
Haltas, I., Yildirim, E., Oztas, F., & Demir, I. (2021). A comprehensive flood event specification and inventory: 1930–2020 Turkey case study. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 56, 102086.
Hussain, M., & Mahmud, I. (2019). pyMannKendall: A python package for non parametric Mann Kendall family of trend tests. Journal of Open Source Software, 4(39), 1556.
Kendall, M. G. (1975). Rank correlation methods.Griffin, London.
Kron, W., Eichner, J., & Kundzewicz, Z. W. (2019). Reduction of flood risk in Europe-reflections from a reinsurance perspective. Journal of Hydrology, 576, 197–209.
Kumar, S., Merwade, V., Kam, J., & Thurner, K. (2009). Streamflow trends in Indiana: Effects of long term persistence, precipitation and subsurface drains. Journal of Hydrology, 374(1–2), 171–183.
Mallick, J., Talukdar, S., Alsubih, M., Salam, R., Ahmed, M., Kahla, N. B., & Shamimuzzaman, M. (2021). Analysing the trend of rainfall in Asir region of Saudi Arabia using the family of Mann-Kendall tests, innovative trend analysis, and detrended fluctuation analysis. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 143, 823–841.
Mann, H. B. (1945). Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica Journal of the Econometric Society, 13, 245–259.
Martinez-Austria, P. F., Bandala, E. R., & Patiño-Gómez, C. (2016). Temperature and heat wave trends in northwest Mexico. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts a/b/c, 91, 20–26.
Nourani, V., Danandeh Mehr, A., & Azad, N. (2018). Trend analysis of hydroclimatological variables in Urmia lake basin using hybrid wavelet Mann-Kendall and Şen tests. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77, 1–18.
Nyikadzino, B., Chitakira, M., & Muchuru, S. (2020). Rainfall and runoff trend analysis in the Limpopo river basin using the Mann Kendall statistic. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts a/b/c, 117, 102870.
Odemis, B., & Evrendilek, F. (2007). Monitoring water quality and quantity of national watersheds in Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 133, 215–229.
Radziejewski, M. (2010). About trend detection in river floods. In extremis: disruptive events and trends in climate and hydrology, 144–165.
Salami, A. W., Ikpee, O. D., Ibitoye, A. B., & Oritola, S. F. (2016). Trend analysis of hydro-meteorological variables in the coastal area of Lagos using Mann-Kendall trend and Standard Anomaly Index methods. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 20(3), 797–808.
Şan, M., Akçay, F., Linh, N. T. T., Kankal, M., & Pham, Q. B. (2021). Innovative and polygonal trend analyses applications for rainfall data in Vietnam. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 144, 809–822.
Sang, Y. F., Wang, Z., & Liu, C. (2014). Comparison of the MK test and EMD method for trend identification in hydrological time series. Journal of Hydrology, 510, 293–298.
Sanikhani, H., Kisi, O., Mirabbasi, R., & Meshram, S. G. (2018). Trend analysis of rainfall pattern over the Central India during 1901–2010. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 1–14.
Şen, Z. (1991). Probabilistic modelling of crossing in small samples and application of runs to hydrology. Journal of Hydrology, 124(3–4), 345–362.
Şen, Z. (2012). Innovative trend analysis methodology. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 17(9), 1042–1046.
Şen, Z. (2017). Innovative trend significance test and applications. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 127, 939–947.
Şen, Z. (2018). Crossing trend analysis methodology and application for Turkish rainfall records. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 131, 285–293.
Şen, Z. (2019). Partial trend identification by change-point successive average methodology (SAM). Journal of Hydrology, 571, 288–299.
SMDA (2020). South Marmara Development Agency. https://www.gmka.gov.tr/ (Accessed 21 Dec 2020)
Tabari, H. (2020). Climate change impact on flood and extreme precipitation increases with water availability. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–10.
Tosunoglu, F., Can, I., & Kahya, E. (2018). Evaluation of spatial and temporal relationships between large-scale atmospheric oscillations and meteorological drought indexes in Turkey. International Journal of Climatology, 38(12), 4579–4596.
Von Storch, H. (1999). Misuses of statistical analysis in climate research. Analysis of Climate Variability Applications of Statistical Techniques Proceedings of an Autumn School Organized by the Commission of the European Community on Elba from October 30 to November 6, 1993 (pp. 11–26). Berlin Heidelberg, Springer: Springer.
Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Tabari, H., Wang, J., Wang, Q., Song, S., & Hu, Z. (2020). Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall in the Yangtze River Delta, eastern China. Atmospheric Research, 231, 104673.
Wang, Z., Xie, P., Lai, C., Chen, X., Wu, X., Zeng, Z., & Li, J. (2017). Spatiotemporal variability of reference evapotranspiration and contributing climatic factors in China during 1961–2013. Journal of Hydrology, 544, 97–108.
Wu, H., Adler, R. F., Hong, Y., Tian, Y., & Policelli, F. (2012). Evaluation of global flood detection using satellite-based rainfall and a hydrologic model. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 13(4), 1268–1284.
Wu, H., & Qian, H. (2017). Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall and extreme values in Shaanxi, China, since the 1950s. International Journal of Climatology, 37(5), 2582–2592.
Yarar, A. (2010). Modeling of precipitation-stream flow data of susurluk basın (Doctoral dissertation, PhD Thesis. Institute of Natural and Applied Sciences, Selcuk University).
Yilmaz, B. (2019). Analysis of hydrological drought trends in the gap region (southeastern Turkey) by Mann-Kendall test and innovative sen method. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 17(2), 3325–3342.
Acknowledgements
We thank The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) for the 2211-A Domestic Doctoral Scholarship Program and the Council of Higher Education for the 100/2000 Doctoral Scholarship Project for the scholarship they provided to the first author.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, FA, MŞ and MK. Investigation, FA and MŞ, Methodology, FA and MŞ. Supervision, MK and SN. Visualization, FA, MŞ, and SN. Writing original draft preparation, FA, MŞ, and SN. Writing review and editing, MK and SN.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akçay, F., Şan, M., Nacar, S. et al. Annual Trends of Precipitation and Temperature in the Northwestern Part of Turkey Using Innovative Approaches: A Holistic and Partial Study. Pure Appl. Geophys. 180, 3131–3156 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-023-03319-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-023-03319-6