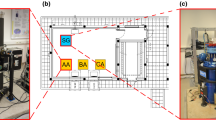
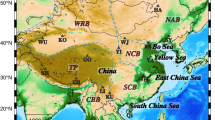
Abstract
The superconducting gravimeter (SG) can provide excellent data to infer Earth’s surface time-varying gravity signals. In this study, we analyze the measurements and experiments of the newly established iGrav-007 SG during 2013–2019. The SG calibration factors with relative precisions of 0.0923% and 0.0782% are determined from two parallel registrations with FG5 absolute gravimeters, and the SG sensitivity calibration to the 0.1 μGal level is presented from a moving external-mass experiment. The local synthesized tides are then calculated with ET34-ANA-V73 software, and nine different ocean tide models for the eight diurnal/semi-diurnal constituents are tested for corrections of the ocean tide gravity effects. After preprocessing the raw SG data, we compare the gravity residuals with colocated precipitation, groundwater level, and GPS height observations from June 2017 to December 2018. Meanwhile, the local precipitation gravity effects are modeled by considering the recharge and discharge time, and the groundwater variation influences are described using a regression model with an admittance coefficient of 0.65 μGal/m. We are able to show good correlations between the gravity residuals and height changes as well as the estimated local and global water storage loading effects in the annual and seasonal (about 140 days) terms.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Gelil, M., Pagiatakis, S., & El-Rabbany, A. (2008). Frequency-dependent atmospheric pressure admittance of superconducting gravimeter records using least squares response method. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 170(1–2), 24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2008.06.031
Achilli, V., Baldi, P., Casula, G., Errani, M., Focardi, S., Guerzoni, M., Palmonari, F., & Raguní, G. (1995). A calibration system for superconducting gravimeters. Bulletin Géodésique, 69(2), 73–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00819553
Amalvict, M., Hinderer, J., Mäkinen, J., Rosat, S., & Rogister, Y. (2004). Long-term and seasonal gravity changes at the Strasbourg station and their relation to crustal deformation and hydrology. Journal of Geodynamics, 38(3/5), 343–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2004.07.010
Baker, T. F., & Bos, M. S. (2003). Validating Earth and ocean tide models using tidal gravity measurements. Geophysical Journal International, 152(2), 468–485. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246X.2003.01863.x
Banka, D., & Crossley, D. (1999). Noise levels of superconducting gravimeters at seismic frequencies. Geophysical Journal International, 139(1), 87–97. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246X.1999.00913.x
Bonatz, M. (1967). Der gravitationseinub der bodenfeuchtigkeit. Zfv, 92, 135–139.
Boy, J. P., Gegout, P., & Hinderer, J. (2002). Reduction of surface gravity data from global atmospheric pressure loading. Geophysical Journal International, 149(2), 534–545. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01667.x
Boy, J. P., & Hinderer, J. (2006). Study of the seasonal gravity signal in superconducting gravimeter data. Journal of Geodynamics, 41(1/3), 227–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2005.08.035
Boy, J. P., Hinderer, J., & Gegout, P. (1998). Global atmospheric loading and gravity. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 109(3–4), 161–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9201(98)00122-8
Boy, J. P., Llubes, M., Hinderer, J., & Florsch, N. (2003). A comparison of tidal ocean loading models using superconducting gravimeter data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(B4), 2193. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JB002050
Boy, J. P., Llubes, M., Ray, R., Hinderer, J., Florsch, N., Rosat, S., Lyard, F., & Letellier, T. (2004). Non-linear oceanic tides observed by superconducting gravimeters in Europe. Journal of Geodynamics, 38(3), 391–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2004.07.017
Carrère, L., Lyard, F., Cancet, M., & Guillot, A. (2015). FES2014, a new tidal model on the global ocean with enhanced accuracy in shallow seas and in the Arctic region. In: EGU General Assembly 2015 (Vol. 17), Vienna, Austria.
Cheng, Y., & Andersen, O. B. (2010). Improvement in global ocean tide model in shallow water regions. In: Proceedings of the OSTST Meeting (2010), October, Lisbon, pp. 18–22.
Crossley, D., Xu, S., & van Dam, T. (1998). Comprehensive analysis of 2 years of SG data from Table Mountain, Colorado. In: Proceedings 13th International Symposium on Earth Tides, July 22–25, Brussels, pp. 659–668.
Crossley, D., Hinderer, J., & Riccardi, U. (2013). The measurement of surface gravity. Reports on Progress in Physics, 76(4), 046101. https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/76/4/046101
de Linage, C., Hinderer, J., & Rogister, Y. (2007). A search for the ratio between gravity variation and vertical displacement due to a surface load. Geophysical Journal International, 171(3), 986–994. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03613.x
Dill, R., & Dobslaw, H. (2013). Numerical simulations of global-scale high-resolution hydrological crustal deformations. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 118(9), 5008–5017. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrb.50353
Ding, H., & Shen, W. B. (2013). Search for the Slichter modes based on a new method: Optimal sequence estimation. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 118(9), 5018–5029. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrb.50344
Ducarme, B. (2009). Limitations of high precision tidal prediction. Bulletin D’informations Des Marées Terrestres, 145, 11663–11677.
Egbert, G. D., & Erofeeva, S. Y. (2002). Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 19(2), 183–204. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0426(2002)019h0183:EIMOBOi2.0.CO;2
Fok, H. S. (2012). Ocean tides modeling using satellite altimetry. Technical report, Division of Geodetic Science, Ohio State University.
Francis, O., Niebauer, T. M., Sasagawa, G., Klopping, F., & Gschwind, J. (1998). Calibration of a superconducting gravimeter by comparison with an absolute gravimeter FG5 in Boulder. Geophysical Research Letters, 25(7), 1075–1078. https://doi.org/10.1029/98gl00712
Francis, O., Van Camp, M., van Dam, T., Warnant, R., & Hendrickx, M. (2004). Indication of the uplift of the Ardenne in long-term gravity variations in Membach (Belgium). Geophysical Journal International, 158(1), 346–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02310.x
Francis, O., & van Dam, T. (2002). Evaluation of the precision of using absolute gravimeters to calibrate superconducting gravimeters. Metrologia, 39(5), 485–488. https://doi.org/10.1088/0026-1394/39/5/9
Gillot, P., Cheng, B., Karcher, R., Imanaliev, A., Timmen, L., Merlet, S., & Santos, F. P. D. (2020). Calibration of a superconducting gravimeter with an absolute atom gravimeter. Journal of Geodesy, 95, 62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-021-01516-6
Goodkind, J. M., Czipott, P. V., Mills, A. P., Murakami, M., Platzman, P. M., Young, C. W., & Zuckerman, D. M. (1993). Test of the gravitational square law at 0.4 to 1.4 m mass separation. Physical Review D, 47(4), 1290–1297. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.47.1290
Harnisch, G., & Harnisch, M. (2006). Hydrological influences in long gravimetric data series. Journal of Geodynamics, 41(1–3), 276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2005.08.018
Harnisch, M., & Harnisch, G. (2002). Seasonal variations of hydrological influences on gravity measurements at Wettzell. Bulletin D’informations Des Marées Terrestres, 137, 10849–10861.
Hartmann, T., & Wenzel, H. (1995). The HW95 tidal potential catalogue. Geophysical Research Letters, 22(24), 3553–3556. https://doi.org/10.1029/95GL03324
Hasan, S., Troch, P. A., Boll, J., & Kroner, C. (2006). Modeling the hydrological effect on local gravity at Moxa, Germany. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 7(3), 346–354. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM488.1
Hinderer, J., Crossley, D., & Warburton, R. J. (2015). Superconducting gravimetry. Treatise on Geophysics (second Edition), 3, 59–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53802-4.00062-2
Hinderer, J., Florsch, N., Mäkinen, J., Legros, H., & Faller, J. E. (1991). On the calibration of a superconducting gravimeter using absolute gravity measurements. Geophysical Journal International, 106(2), 491–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1991.tb03907.x
Hinderer, J., Hector, B., Boy, J. P., Riccardi, U., Rosat, S., Calvo, M., & Littel, F. (2014). A search for atmospheric effects on gravity at different time and space scales. Journal of Geodynamics, 80, 50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2014.02.001
Hinderer, J., Riccardi, U., Rosat, S., Boy, J. P., Hector, B., Calvo, M., Little, F., & Bernard, J. D. (2020). A study of the solid Earth tides, ocean and atmospheric loadings using an 8-year record (2010–2018) from superconducting gravimeter OSG-060 at Djougou (Benin, West Africa). Journal of Geodynamics, 134, 101692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2019.101692
Hu, X. G., Liu, L. T., Hinderer, J., & Sun, H. P. (2005). Wavelet filter analysis of local atmospheric pressure effects on gravity variations. Journal of Geodesy, 79(8), 447–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-005-0486-6
Hwang, C., Kao, R., Cheng, C. C., Huang, J. F., Lee, C. W., & Sato, T. (2009). Results from parallel observations of superconducting and absolute gravimeters and GPS at the Hsinchu station of Global Geodynamics Project, Taiwan. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114, B07406. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JB006195
Imanishi, Y., Higashi, T., & Fukuda, Y. (2002). Calibration of the superconducting gravimeter T011 by parallel observation with the absolute gravimeter FG5#210-a Bayesian approach. Geophysical Journal International, 151(3), 867–878. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01806.x
Imanishi, Y., Sato, T., Higashi, T., Sun, W., & Okubo, S. (2004). A network of superconducting gravimeters detects submicrogal coseismic gravity changes. Science, 306(5695), 476–478. https://doi.org/10.1126/science1101875
Kao, R., Kabirzadeh, H., Kim, J. W., Neumeyer, J., & Sideris, M. G. (2014). Detecting small gravity change in field measurement: Simulations and experiments of the superconducting gravimeter-iGrav. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 11(4), 045004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-2132/11/4/045004
Kroner, C., & Jahr, T. (2006). Hydrological experiments around the superconducting gravimeter at Moxa observatory. Journal of Geodynamics, 41(1/3), 268–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2005.08.012
Kustowski, B., Ekström, G., & Dziewonski, A. M. (2008). Anisotropic shear-wave velocity structure of the Earth’s mantle: A global model. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 113, B06306. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JB005169
Loyer, S., Hinderer, J., & Boy, J. P. (1999). Determination of the gravimetric factor at the Chandler period from Earth orientation data and superconducting gravimetry observations. Geophysical Journal International, 136(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246X.1999.00646.x
Luan, W., Shen, W. B., Ding, H., & Zhang, T. X. (2019). Potential Slichter triplet detection using global superconducting gravimeter data. Surveys in Geophysics, 40(5), 1129–1150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-019-09561-9
Lyard, F., Lefevre, T., Letellier, F., & Francis, O. (2006). Modelling the global ocean tides: Modern insights from FES2004. Ocean Dynamics, 56(5), 394–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-006-0086-x
Marsland, S., Haak, H., Jungclaus, J. H., Latif, M., & Roske, F. (2003). The Max-Planck-Institute global ocean/sea ice model with orthogonal curvilinear coordinates. Ocean Modelling, 5(2), 91–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1463-5003(02)00015-X
Matsumoto, K., Takanezawa, T., & Ooe, M. (2000). Ocean tide models developed by assimilating TOPEX/POSEIDON altimeter data into hydrodynamical model: A global model and a regional model around Japan. Journal of Oceanography, 56(5), 567–581. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011157212596
Merriam, J. B. (1995). Non-linear tides observed with the superconducting gravimeter. Geophysical Journal International, 123(2), 529–540. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1995.tb06869.x
Meurers, B. (2012). Superconducting gravimeter calibration by colocated gravity observations: Results from GWR C025. International Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/954271
Naujoks, M., Kroner, C., Weise, A., Jahr, T., Krause, P., & Eisner, S. (2010). Evaluating local hydrological modelling by temporal gravity observations and a gravimetric three-dimensional model. Geophysical Journal International, 182(1), 233–249. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04615.x
Park, J., Song, T.-R.A., Tromp, J., Okal, E., Stein, S., Roult, G., Clevede, E., Laske, G., Kanamori, H., Davis, P., Berger, J., Braitenberg, C., van Camp, M., Lei, X., Sun, H., Xu, H., & Rosat, S. (2005). Earth’s free oscillations excited by the 26 December 2004 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake. Science, 308(5725), 1139–1144. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1112305
Ray, R. D. (2013). Precise comparisons of bottom-pressure and altimetric ocean tides. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 118(9), 4570–4584. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrc.20336.
Riccardi, U., Hinderer, J., Boy, J. P., & Rogister, Y. (2009). Tilt effects on GWR superconducting gravimeters. Journal of Geodynamics, 48(3–5), 316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2009.09.001
Riccardi, U., Rosat, S., & Hinderer, J. (2012). On the accuracy of the calibration of superconducting gravimeters using absolute and spring sensors: A critical comparison. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 169(8), 1343–1356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-011-0398-8
Rosat, S., Boy, J. P., Ferhat, G., Hinderer, J., Amalvict, M., Gegout, P., & Luck, B. (2009). Analysis of a 10-year (1997–2007) record of time-varying gravity in Strasbourg using absolute and superconducting gravimeters: New results on the calibration and comparison with GPS height changes and hydrology. Journal of Geodynamics, 48(3–5), 360–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0079-1946(98)00147-5
Rosat, S., Florsch, N., Hinderer, J., & Llubes, M. (2009). Estimation of the Free Core Nutation parameters from SG data: Sensitivity study and comparative analysis using linearized least-squares and Bayesian methods. Journal of Geodynamics, 48(3–5), 331–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2009.09.027
Rosat, S., & Hinderer, J. (2018). Limits of detection of gravimetric signals on Earth. Scientific Reports, 8, 15324. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-33717-z
Rosat, S., Lambert, S., Gattano, C., & Calvo, M. (2016). Earth’s core and inner-core resonances from analysis of VLBI nutation and superconducting gravimeter data. Geophysical Journal International, 208(1), 211–220. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggw378
Sato, T., Imanishi, Y., Fukuda, Y., Ikeda, H., Tamura, Y., Rosat, S., & Ohashi, T. (2005). Cooperative observation of superconducting gravimeters at Kamioka and Matsushiro in Japan. In: Geophysical Research Abstract, EGU, Vienna, Austria.
Savcenko, R., & Bosch, W. (2012). EOT11a-empirical ocean tide model from multimission satellite altimetry. DGFI Report No. 89.
Schüller, K. (2019). Program system for Earth tide analysis and prediction, Manual-01-ET34-X-V73. Surin, Thailand (April, 2019).
Shen, W. B., & Ding, H. (2014). Observation of spheroidal normal mode multiplets below 1 mHz using ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Geophysical Journal International, 196(3), 1631–1642. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggt468
Taguchi, E., Stammer, D., & Zahel, W. (2014). Inferring deep ocean tidal energy dissipation from the global high-resolution data-assimilative HAMTIDE model. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(7), 4573–4592. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JC009766
Tamura, Y., Sato, T., Fukuda, Y., & Higashi, T. (2005). Scale factor calibration of a superconducting gravimeter at Esashi Station, Japan, using absolute gravity measurements. Journal of Geodesy, 78(7–8), 481–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-004-0415-0
Van Camp, M., De Viron, O., Pajot-Métivier, G., Casenave, F., Watlet, A., Dassargues, A., & Vanclooster, M. (2016). Direct measurement of evapotranspiration from a forest using a superconducting gravimeter. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(19), 10225–10231. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL070534
Van Camp, M., Meurers, B., de Viron, O., & Forbriger, T. (2016). Optimized strategy for the calibration of superconducting gravimeters at the one per mille level. Journal of Geodesy, 90(1), 91–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0856-7
Van Camp, M., Vanclooster, M., Crommen, O., Petermans, T., Verbeeck, K., Meurers, B., van Dam, T., & Dassargues, A. (2006). Hydrogeological investigations at the Membach station, Belgium, and application to correct long periodic gravity variations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(B10), B10403. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JB004405
Van Camp, M., & Vauterin, P. (2005). Tsoft: Graphical and interactive software for the analysis of time series and Earth tides. Computers & Geosciences, 31(5), 631–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2004.11.015
Van Camp, M., Wiliams, S. D. P., & Francis, O. (2005). Uncertainty of absolute gravity measurements. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 110(B5), B05406. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JB003497
Widmer-Schnidrig, R. (2003). What can superconducting gravimeters contribute to normal-mode seismology? Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 93(3), 1370–1380. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120020149
Xu, J. Q., Sun, H. P., & Yang, X. F. (2004). A study of gravity variations caused by polar motion using superconducting gravimeter data from the GGP network. Journal of Geodesy, 78(3), 201–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-004-0386-1
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge M.S. Bos and H.-G. Scherneck for making the possible access to the free Ocean Tide Loading Provider (http://holt.oso.chalmers.se/loading/index.html). The atmospheric, non-tidal oceanic, and hydrological loading models are provided by the ESMGFZ product reposity (http://rz-vm115.gfz-potsdam.de:8080/repository). We thank the reviewers (D. Crossley and an anonymous reviewer) and the associate editor U. Riccardi for their very valuable comments and suggestions, all of which greatly improved the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41874032, 42030105, 41631072, 41721003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they do not have any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Adjusted tidal parameters for Kumming (iGrav-007 sensor), from June 2017 to September 2019.
fmin (cpd) | fmax (cpd) | Wave | Ath (nm/s2) | δ | δ error | κ (°) | κ error (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0.580000 | 0.791600 | SGM2Q1 | 0.29210 | 1.12911 | 0.59462 | 35.669 | 30.149 |
0.791601 | 0.810000 | 2SGM1 | 0.18122 | 0.53153 | 0.98048 | 81.597 | 105.630 |
0.810001 | 0.821300 | 3Q1 | 0.68057 | 1.31718 | 0.27191 | − 4.546 | 11.834 |
0.821301 | 0.842147 | SGMQ1 | 1.76311 | 1.17703 | 0.10148 | − 3.665 | 4.940 |
0.842148 | 0.860500 | 2Q1 | 6.05140 | 1.14530 | 0.03055 | 2.438 | 1.529 |
0.860501 | 0.878675 | SGM1 | 7.29747 | 1.18998 | 0.02507 | − 1.113 | 1.208 |
0.878676 | 0.896800 | Q1 | 45.72919 | 1.16396 | 0.00808 | − 0.452 | 0.398 |
0.896801 | 0.915000 | RO1 | 8.67999 | 1.18510 | 0.02065 | − 1.940 | 0.998 |
0.915001 | 0.933200 | O1 | 238.83795 | 1.15839 | 0.00185 | − 0.639 | 0.091 |
0.933201 | 0.947991 | TAU1 | 3.11325 | 1.23643 | 0.04684 | 3.307 | 2.171 |
0.947992 | 0.964460 | NTAU1 | 1.76125 | 1.30543 | 0.10628 | 3.494 | 4.665 |
0.964461 | 0.966853 | NO1 | 18.77436 | 1.12208 | 0.01045 | 0.085 | 0.534 |
0.966854 | 0.971667 | CHI1 | 3.59250 | 1.18039 | 0.05047 | 0.306 | 2.449 |
0.971668 | 0.996933 | PI1 | 6.49225 | 1.14241 | 0.02586 | 3.732 | 1.297 |
0.996934 | 0.998631 | P1 | 111.11307 | 1.15033 | 0.00151 | − 0.361 | 0.075 |
0.998632 | 1.002333 | S1 | 2.62542 | 2.39401 | 0.08979 | − 42.777 | 2.150 |
1.002334 | 1.004200 | K1 | 335.76870 | 1.12729 | 0.00088 | − 0.728 | 0.045 |
1.004201 | 1.006845 | PSI1 | 2.62664 | 1.13146 | 0.06429 | − 6.466 | 3.256 |
1.006846 | 1.023622 | PHI1 | 4.78026 | 1.18537 | 0.03502 | − 2.703 | 1.693 |
1.023623 | 1.035379 | TET1 | 3.59147 | 1.22358 | 0.05020 | 0.808 | 2.351 |
1.035380 | 1.055000 | J1 | 18.78093 | 1.15292 | 0.00963 | − 0.669 | 0.478 |
1.055001 | 1.075633 | SO1 | 3.11470 | 1.13650 | 0.05640 | − 0.610 | 2.844 |
1.075634 | 1.086000 | OO1 | 10.27093 | 1.14758 | 0.02336 | − 0.051 | 1.166 |
1.086001 | 1.112600 | NU1 | 1.96688 | 1.00750 | 0.11462 | 0.351 | 6.518 |
1.112601 | 1.470243 | 2(KM)P | 0.31408 | 1.13603 | 0.55572 | 3.169 | 28.041 |
1.470244 | 1.808000 | 2EPS2 | 0.75169 | 1.25113 | 0.07930 | − 8.952 | 3.632 |
1.808001 | 1.824458 | 3N2 | 1.75415 | 1.13590 | 0.04078 | − 0.567 | 2.058 |
1.824459 | 1.845944 | EPS2 | 4.54675 | 1.15721 | 0.01649 | 0.649 | 0.816 |
1.845945 | 1.863026 | 2N2 | 15.59133 | 1.16725 | 0.00479 | − 0.854 | 0.235 |
1.863027 | 1.880264 | MUE2 | 18.81743 | 1.16862 | 0.00423 | − 0.293 | 0.207 |
1.880265 | 1.899500 | N2 | 117.82104 | 1.16217 | 0.00155 | − 0.315 | 0.076 |
1.899501 | 1.915114 | NUE2 | 22.38086 | 1.16709 | 0.00360 | − 0.073 | 0.177 |
1.915115 | 1.928402 | GAM2 | 1.84740 | 1.16129 | 0.04058 | 0.599 | 2.002 |
1.928403 | 1.930667 | ALF2 | 2.11363 | 1.20579 | 0.03723 | − 1.964 | 1.769 |
1.930668 | 1.933790 | M2 | 615.36173 | 1.16063 | 0.00020 | − 0.323 | 0.010 |
1.933791 | 1.936152 | BET2 | 1.86198 | 1.24436 | 0.04382 | − 3.485 | 2.018 |
1.936153 | 1.950419 | DEL2 | 0.72135 | 1.30616 | 0.08591 | − 1.024 | 3.770 |
1.950420 | 1.964767 | LAM2 | 4.53766 | 1.13366 | 0.01773 | 0.152 | 0.896 |
1.964768 | 1.984282 | L2 | 17.39501 | 1.16273 | 0.00547 | − 1.012 | 0.269 |
1.984283 | 1.995500 | 2T2 | 0.67854 | 0.81121 | 0.12176 | − 5.557 | 8.603 |
1.995501 | 1.998996 | T2 | 16.72639 | 1.14759 | 0.00497 | 0.685 | 0.248 |
1.998997 | 2.001678 | S2 | 286.27319 | 1.15911 | 0.00029 | − 0.117 | 0.014 |
2.001679 | 2.004380 | R2 | 2.38853 | 1.21276 | 0.02802 | − 5.506 | 1.324 |
2.004381 | 2.010635 | K2 | 77.77178 | 1.15542 | 0.00124 | − 0.316 | 0.062 |
2.010636 | 2.022488 | KPHI2 | 0.52974 | 0.83991 | 0.15448 | − 1.263 | 10.538 |
2.022489 | 2.038400 | ZETA2 | 0.83174 | 1.39470 | 0.13359 | − 0.479 | 5.489 |
2.038401 | 2.056000 | ETA2 | 4.35033 | 1.19596 | 0.02123 | 0.403 | 1.017 |
2.056001 | 2.075800 | 2S2 | 0.72150 | 1.19121 | 0.14445 | − 7.991 | 6.949 |
2.075801 | 2.092667 | 2K2 | 1.13800 | 1.28363 | 0.12152 | 6.197 | 5.426 |
2.092668 | 2.396000 | 2KN2 | 0.21796 | 0.77336 | 0.48262 | − 21.652 | 35.768 |
2.580000 | 2.826600 | M2N3 | 0.51990 | 1.15411 | 0.11447 | − 7.906 | 5.684 |
2.826601 | 2.850000 | MMUE3 | 0.52263 | 1.16052 | 0.12748 | 5.295 | 6.294 |
2.850001 | 2.864300 | MN3 | 2.99898 | 1.04050 | 0.02177 | − 1.314 | 1.198 |
2.864301 | 2.880000 | MNUE3 | 0.56142 | 1.01662 | 0.11942 | 4.036 | 6.729 |
2.880001 | 2.915496 | M3 | 10.94282 | 1.05897 | 0.00617 | − 0.375 | 0.334 |
2.915497 | 2.953157 | ML3 | 0.61974 | 1.11906 | 0.10535 | 2.054 | 5.393 |
2.953158 | 3.340000 | MK3 | 1.42524 | 1.13764 | 0.05860 | 5.933 | 2.951 |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luan, W., Shen, W. & Jia, J. Analysis of iGrav Superconducting Gravity Measurements in Kunming, China, with Emphasis on Calibration, Tides, and Hydrology. Pure Appl. Geophys. 180, 643–660 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-022-03036-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-022-03036-6