Abstract
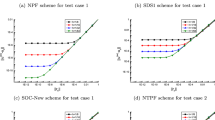
We present and study a parallel grad-div stabilized finite element discretization algorithm based on entire-overlapping domain decomposition for the numerical simulation of Navier–Stokes equations. The algorithm is easy to implement on top of existing sequential software, in which each subproblem used to calculate a local solution in its designated subregion is actually a global problem with vast of degrees of freedom coming from its own subregion, and hence, can be solved independently with other subproblems. We derive error bounds of the approximate solution by employing the technical tool of local a priori estimate, and investigate the effect of grad-div stabilization term on the approximation solutions. Numerical comparisons, with both inf-sup stable and unstable mixed finite elements pairs for the velocity and pressure, show that our present algorithm has an amazing superiority to its counterpart without stabilization in the sense that accuracy of the approximate velocities could be improved by two orders of magnitude when the viscosity \(\nu \) is small. While compared with the usual standard serial grad-div stabilized finite element method, our algorithm saves lots of CPU time in computing a solution with comparable accuracy.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Mu, L.: Pressure robust weak Galerkin finite element methods for Stokes problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 42, 608–629 (2020)
Mu, L., Ye, X., Zhang, S.Y.: A stablizer-free, pressure-robust, and superconvergence weak Galerkin finite element method for the Stokes equations on polytopal mesh. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 43, 2614–2637 (2021)
Ainsworth, M., Parker, C.: Mass conserving mixed \(hp\)-FEM approximations to Stokes flow. Part I: uniform stability. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 59, 1218–1244 (2021)
Ainsworth, M., Parker, C.: Mass conserving mixed \(hp\)-FEM approximations to Stokes flow. Part II: optimal convergence stability. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 59, 1245–1272 (2021)
Wei, H.Y., Huang, X.H., Li, A.: Piecewise divergence-free nonconforming virtual elements for Stokes problem in any dimensions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 59, 1835–1856 (2021)
Wang, G., Mu, L., Wang, Y., He, Y.N.: A pressure-robust virtual element method for the Stokes problem. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 382, 113879 (2021)
John, V., Linke, A., Merdon, C., Neilan, M., Rebholz, L.G.: On the divergence constraint in mixed finite element methods for incompressible flows. SIAM Rev. 42, 492–544 (2017)
John, V.: Finite Element Methods for Incompressible Flow Problems. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Franca, L.P., Hughes, T.J.R.: Two classes of mixed finite element methods. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 69, 89–129 (1988)
Olshanskii, M.A., Reusken, A.: Grad-div stabilization for Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 73, 1699–1718 (2004)
Olshanskii, M.A., Lube, G., Heister, T., Loewe, J.: Grad-div stabilization and subgrid pressure models for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 3975–3988 (2009)
De Frutos, J., Garcia-Archilla, B., John, V., Novo, J.: Grad-div stabilization for the evolutionary Oseen problem with inf-sup stable finite elements. J. Sci. Comput. 66, 991–1024 (2016)
Franz, S., Hohne, K., Matthies, G.: Grad-div stabilized discretizations on S-type meshes for the Oseen problem. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 38, 299–329 (2018)
Qin, Y., Hou, Y.R., Wang, Y.S.: Numerical analysis of two grad-div stabilization methods for the time-dependent Stokes/Darcy model. Comput. Math. Appl. 79, 817–832 (2020)
Jia, X.F., Tang, Z.Y., Feng, H.: Numerical analysis of CNLF modular grad-div stabilization method for time-dependent Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Math. Lett. 112, 106798 (2021)
Li, W., Fang, J.L., Huang, P.Z.: Rotational pressure-correction method for the Stokes/Darcy model based on the modular grad-div stabilization. Appl. Numer. Math. 160, 451–465 (2021)
Layton, W., Manica, C.C., Neda, M., Olshanskii, M.A., Rebholz, L.G.: On the accuracy of the rotation form in simulations of the Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 3433–3447 (2009)
Layton, W., Manica, C.C., Neda, M., Rebholz, L.G.: Numerical analysis and computational comparisons of the NS-alpha and NS-omega regularizations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199, 916–931 (2010)
Maxim, A., Olshanskii, M.A.: A low order Galerkin finite element method for the Navier–Stokes equations of steady incompressible flow: a stabilization issue and iterative method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 191, 5515–5536 (2002)
Codina, R.: Stabilized finite element approximation of transient incompressible flows using orthogonal subscales. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 191, 4295–4321 (2002)
Gravemeier, V., Wall, W.A., Ramm, E.: Large eddy simulation of turbulent incompressible flows by a three-level finite element method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 48, 1067–1099 (2005)
John, V., Kindl, A.: Numerical studies of finite element variational multiscale methods for turbulent flow simulations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199, 841–852 (2010)
John, V., Linke, A., Rebholz, L.G., Jenkins, E.W.: On the parameter choice in grad-div stabilization for Stokes equations. Adv. Comput. Math. 40, 491–516 (2014)
Ahmed, N.: On the grad-div stabilization for the steady Oseen and Navier–Stokes equations. Calcolo 54, 471–501 (2017)
Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations. Math. Comput. 69, 881–909 (2000)
Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations for nonlinear problems. Adv. Comput. Math. 14, 293–327 (2001)
He, Y.N., Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H., Li, J.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms for the Stokes problem. Numer. Math. 109, 415–434 (2008)
Jiang, Y., Zheng, B., Shang, Y.Q.: A parallel grad-div stabilized finite element algorithm for the Stokes equations with damping. Comput. Math. Appl. 135, 171–192 (2023)
He, Y.N., Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms for the Navier–Stokes problem. J. Comput. Math. 24, 227–238 (2006)
Shang, Y.Q., He, Y.N.: Parallel iterative finite element algorithms based on full domain partition for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 60, 719–737 (2010)
Shang, Y.Q.: A parallel subgrid stabilized finite element method based on fully overlapping domain decomposition for the Navier–Stokes equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 403, 667–679 (2013)
Shang, Y.Q., Qin, J.: A two-parameter stabilized finite element method for incompressible flows. Numer. Methods PDEs 33, 425–444 (2016)
Tang, Q.L., Huang, Y.Q.: Analysis of parallel finite element algorithm based on three linearization methods for the steady incompressible MHD flow. Comput. Math. Appl. 78, 35–54 (2019)
Zheng, B., Shang, Y.Q.: A parallel finite element method based on fully overlapping domain decomposition for the steady-state Smagorinsky model. Comput. Math. Appl. 147, 76–91 (2023)
Evans, C.L.: Partial Differential Equations, 2nd edn. Department of Mathmatics University of California, Springer, Berkeley (2010)
Raviart, P.A., Girault, V.: Finite Element Methods for Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Algorithms. Springer, Berlin (1996)
Rannacher, R., Heywood, J.G.: Finite element approximation of the nonstationary Navier–Stokes problems: regularity of solutions and second-order error estimates for spatial discretization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 19, 275–311 (1982)
Temam, R.: Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Numerical Analysis. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1984)
Hecht, F.: New development in FreeFem++. J. Numer. Math. 20, 251–265 (2012)
He, Y.N., Li, J.: Convergence of three iterative methods based on the finite element discretization for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 1351–1359 (2009)
Quarteroni, A., Valli, A.: Numerical Approximation of Partial Differential Equations. Springer, Berlin (1994)
Zheng, B., Shang, Y.Q.: A two-level stabilized quadratic equal-order finite element variational multiscale method for incompressible flows. Appl. Math. Comput. 384, 12537 (2020)
Zheng, H.B., Shan, L., Hou, Y.R.: A quadratic equal-order stabilized method for Stokes problem based on two local Gauss integrations. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 26, 1180–1190 (2010)
Becker, R., Braack, M.: A finite elements pressure gradent stabilization for the Stokes equations based on local projections. Cacolo 38, 173–199 (2001)
Bruneau, C.H., Saad, M.: The 2D lid-driven cavity problem revisited. Comput. Fluids 35, 326–348 (2006)
Ghia, U., Ghia, K.N., Shin, C.T.: High-Re solutions for incompressible flow using the Navier–Stokes equations and a multigrid method. J. Comput. Phys. 48, 387–441 (1982)
Gartling, D.K.: A test problem for outflow boundary conditions-flow over a backward-facing step. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 11, 953–967 (1990)
Tuann, S.Y., Olson, M.D.: Numerical studies of the flow around a circular cylinder by a finite element method. Comput. Fluids 6, 219–240 (1978)
Ding, H., Shu, C., Yeo, K.S., Xu, D.: Simulation of incompressible viscous flows past a circular cylinder by hybrid FD scheme and meshless least square-based finite difference method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 193, 727–744 (2004)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their deep gratitude to the anonymous referees who made valuable suggestions for revision and improvement of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that this work does not have any competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Turek.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing Municipality, China (No. cstc2021jcyj-msxmX1044).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, Y., Zhu, J. & Zheng, B. A Parallel Finite Element Discretization Algorithm Based on Grad-Div Stabilization for the Navier–Stokes Equations. J. Math. Fluid Mech. 26, 42 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00021-024-00868-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00021-024-00868-1