Abstract
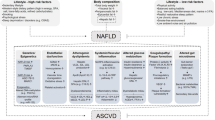
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is considered as the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome, which is characterised by obesity, insulin resistance, hypercholesterolemia and hypertension. NAFLD is the most frequent liver disease worldwide and more than 10% of NAFLD patients progress to the inflammatory and fibrotic stage of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can lead to end-stage liver disease including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most frequent primary malignant liver tumor. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSEC) are strategically positioned at the interface between blood and hepatic parenchyma. LSECs are highly specialized cells, characterised by the presence of transcellular pores, called fenestrae, and exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic characteristics under physiological conditions. However, during NAFLD development they undergo capillarisation and acquire a phenotype similar to vascular endothelial cells, actively promoting all pathophysiological aspects of NAFLD, including steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. LSEC dysfunction is critical for the progression to NASH and HCC while restoring LSEC homeostasis appears to be a promising approach to prevent NAFLD progression and its complications and even reverse tissue damage. In this review we present current information on the role of LSEC throughout the progressive phases of NAFLD, summarising in vitro and in vivo experimental evidence and data from human studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cotter TG, Rinella M (2020) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease 2020: the state of the disease. Gastroenterology 158:1851–1864
Byrne CD, Targher G (2015) NAFLD: a multisystem disease. J Hepatol 62:S47–S64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.012
Godoy-Matos AF, Silva Júnior WS, Valerio CM (2020) NAFLD as a continuum: from obesity to metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr 12:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-020-00570-y
Muzica CM et al (2020) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a bidirectional relationship. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020:6638306. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6638306
Katsarou A et al (2020) Metabolic inflammation as an instigator of fibrosis during nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 26:1993–2011. https://doi.org/10.3748/WJG.V26.I17.1993
Yu J, Shen J, Sun TT, Zhang X, Wong N (2013) Obesity, insulin resistance, NASH and hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol 23:483–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.07.003
Bertot LC, Adams LA (2019) Trends in hepatocellular carcinoma due to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:179–187
Marchesini G et al (2016) EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 64:1388–1402
Ramanathan R, Ali AH, Ibdah JA (2022) Mitochondrial dysfunction plays central role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci 23:7280
Mihm S (2018) Danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs): molecular triggers for sterile inflammation in the liver. Int J Mol Sci 19:3104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103104
Chatzigeorgiou A, Chavakis T (2015) Immune cells and metabolism. Handb Exp Pharmacol 233:221–249
Mendez-Sanchez N et al (2018) New aspects of lipotoxicity in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Int J Mol Sci 19:2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072034
Sørensen KK, Simon-Santamaria J, McCuskey RS, Smedsrød B (2015) Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Compr Physiol 5:1751–1774
Wilkinson AL, Qurashi M, Shetty S (2020) The role of sinusoidal endothelial cells in the axis of inflammation and cancer within the liver. Front Physiol 11:990. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00990
Nasiri-Ansari N et al (2022) Endothelial cell dysfunction and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a concise review. Cells 11:2511
Poisson J et al (2017) Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: physiology and role in liver diseases. J Hepatol 66:212–227
Xie G et al (2012) Role of differentiation of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in progression and regression of hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gastroenterology 142:918-927.e6
Deleve LD (2015) Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology 61:1740–1746
Cogger VC et al (2010) Three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrations. J Struct Biol 171:382–388
Braet F et al (2002) The new anti-actin agent dihydrohalichondramide reveals fenestrae-forming centers in hepatic endothelial cells. BMC Cell Biol 3:7
DeLeve LD, Maretti-Mira AC (2017) Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell: an update. Semin Liver Dis 37:377–387
Hammoutene A, Rautou PE (2019) Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 70:1278–1291
van Berkel TJC, de Rijke YB, Kruijt JK (1991) Different fate in vivo of oxidatively modified low density lipoprotein and acetylated low density lipoprotein in rats: recognition by various scavenger receptors on Kupffer and endothelial liver cells. J Biol Chem 266:2282–2289
Svistounov D et al (2012) The relationship between fenestrations, sieve plates and rafts in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. PLoS One 7:e46134
le Couteur DG, Fraser R, Cogger VC, McLean AJ (2002) Hepatic pseudocapillarisation and atherosclerosis in ageing. Lancet 359:1612–1615
Yokomori H et al (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factor increases fenestral permeability in hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells. Liver Int 23:467–475
Le Couteur DG et al (2001) Pseudocapillarization and associated energy limitation in the aged rat liver. Hepatology 33:537–543
Le Couteur DG, Fraser R, Hilmer S, Rivory LP, McLean AJ (2005) The hepatic sinusoid in aging and cirrhosis. Clin Pharmacokinet 44:187–200
Cogger VC et al (2004) The effects of oxidative stress on the liver sieve. J Hepatol 41:370–376
Qing Z et al (2021) Hypoxia maintains the fenestration of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and promotes their proliferation through the SENP1/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 540:42–50
Miyao M et al (2015) Pivotal role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in NAFLD/NASH progression. Lab Investig 95:1130–1144
Zhang Q et al (2019) High glucose/ox-LDL induced hepatic sinusoidal capillarization via αvβ5/FAK/ERK signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 513:1055–1062
Pasarín M et al (2012) Sinusoidal endothelial dysfunction precedes inflammation and fibrosis in a model of NAFLD. PLoS One 7:e32785
Mori T et al (1993) Defenestration of the sinusoidal endothelial cell in a rat model of cirrhosis. Hepatology 17:891–897
Jamieson HA et al (2007) Caloric restriction reduces age-related pseudocapillarization of the hepatic sinusoid. Exp Gerontol 42:374–378
Papadopoulos G et al (2023) Integrated omics analysis for characterization of the contribution of high fructose corn syrup to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obesity. Metabolism 144:155552
Cogger VC et al (2016) Dietary macronutrients and the aging liver sinusoidal endothelial cell. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 310:H1064–H1070
Zhang Q et al (2014) oxLDL induces injury and defenestration of human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells via LOX1. J Mol Endocrinol 53:281–293
O’Reilly JN, Cogger VC, Fraser R, Le Couteur DG (2010) The effect of feeding and fasting on fenestrations in the liver sinusoidal endothelial cell. Pathology 42:255–258
Herrnberger L et al (2014) Formation of fenestrae in murine liver sinusoids depends on plasmalemma vesicle-associated protein and is required for lipoprotein passage. PLoS One 9:1–26
Peng Q et al (2014) Protective effects of Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn against fatty liver disease induced by high fat diet in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 450:685–691
Soderborg TK et al (2018) The gut microbiota in infants of obese mothers increases inflammation and susceptibility to NAFLD. Nat Commun 9:1–12
Marra F, Svegliati-Baroni G (2018) Lipotoxicity and the gut-liver axis in NASH pathogenesis. J Hepatol 68:280–295
Dobbs BR, Rogers GWT, Xing HY, Fraser R (1994) Endotoxin-induced defenestration of the hepatic sinusoidal endothelium: a factor in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis? Liver 14:230–233
Xie G et al (2013) Hedgehog signalling regulates liver sinusoidal endothelial cell capillarisation. Gut 62:299–309
Witek RP et al (2009) Liver cell-derived microparticles activate hedgehog signaling and alter gene expression in hepatic endothelial cells. Gastroenterology 136:320-330.e2
Fang ZQ et al (2022) Notch-triggered maladaptation of liver sinusoidal endothelium aggravates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Hepatology 76:742–758
Pasarín M et al (2011) Insulin resistance and liver microcirculation in a rat model of early NAFLD. J Hepatol 55:1095–1102
Rockey DC, Chung JJ (1998) Reduced nitric oxide production by endothelial cells in cirrhotic rat liver: endothelial dysfunction in portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 114:344–351
DeLeve LD, Wang X, Guo Y (2008) Sinusoidal endothelial cells prevent rat stellate cell activation and promote reversion to quiescence. Hepatology 48:920–930
Dufton NP et al (2017) Dynamic regulation of canonical TGFβ signalling by endothelial transcription factor ERG protects from liver fibrogenesis. Nat Commun 8:895
De Haan W et al (2020) Unraveling the transcriptional determinants of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell specialization. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 318:G803–G815
Gómez-Salinero JM et al (2022) Specification of fetal liver endothelial progenitors to functional zonated adult sinusoids requires c-Maf induction. Cell Stem Cell 29:593-609.e7
De Smedt J et al (2021) PU.1 drives specification of pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells to LSEC-like cells. Cell Death Dis 12:84
De Haan W et al (2022) Endothelial Zeb2 preserves the hepatic angioarchitecture and protects against liver fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res 118:1262–1275
Manicardi N et al (2021) Transcriptomic profiling of the liver sinusoidal endothelium during cirrhosis reveals stage-specific secretory signature. Cancers (Basel) 13:2688
Nagy D, Maude H, Birdsey GM, Randi AM, Cebola I (2023) RISING STARS: liver sinusoidal endothelial transcription factors in metabolic homeostasis and disease. J Mol Endocrinol 71:e230026
Ramachandran P et al (2019) Resolving the fibrotic niche of human liver cirrhosis at single-cell level. Nature 575:512–518
Su T et al (2021) Single-cell transcriptomics reveals zone-specific alterations of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in cirrhosis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:1139–1161
Bressan D, Battistoni G, Hannon GJ (2023) The dawn of spatial omics. Science 381:eabq4964
Lorenz L et al (2018) Mechanosensing by β1 integrin induces angiocrine signals for liver growth and survival. Nature 562:128–132
Mitten EK, Baffy G (2022) Mechanotransduction in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 77:1642–1656
Rabbany SY, Rafii S (2018) Blood flow forces liver growth. Nature 562:42–43
Kang N (2020) Mechanotransduction in liver diseases. Semin Liver Dis 40:84–90
Planas-Paz L et al (2012) Mechanoinduction of lymph vessel expansion. EMBO J 31:788–804
Hilscher MB et al (2019) Mechanical stretch increases expression of CXCL1 in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells to recruit neutrophils, generate sinusoidal microthombi, and promote portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 157:193-209.e9
Piera-Velazquez S, Li Z, Jimenez SA (2011) Role of endothelial–mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) in the pathogenesis of fibrotic disorders. Am J Pathol 179:1074–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.06.001
Smedsrød B et al (1994) Cell biology of liver endothelial and Kupffer cells. Gut 35:1509–1516
Wells RG (2008) Cellular sources of extracellular matrix in hepatic fibrosis. Clin Liver Dis 12:759–768
Neubauer K et al (1999) Transforming growth factor-beta1 stimulates the synthesis of basement membrane proteins laminin, collagen type IV and entactin in rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J Hepatol 31:692–702
Iwaisako K et al (2014) Origin of myofibroblasts in the fibrotic liver in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E3297–E3305
Mederacke I et al (2013) Fate tracing reveals hepatic stellate cells as dominant contributors to liver fibrosis independent of its aetiology. Nat Commun 4:2823
Dufton NP et al (2017) Dynamic regulation of canonical TGFβ signalling by endothelial transcription factor ERG protects from liver fibrogenesis. Nat Commun 8:1–14
Li Z et al (2019) MKL1 promotes endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and liver fibrosis by activating TWIST1 transcription. Cell Death Dis 10:899
Ribera J et al (2017) A small population of liver endothelial cells undergoes endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in response to chronic liver injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 313:G492–G504
Shetty S, Lalor PF, Adams DH (2018) Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells—gatekeepers of hepatic immunity. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:555–567
Bhandari S, Larsen AK, McCourt P, Smedsrød B, Sørensen KK (2021) The scavenger function of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in health and disease. Front Physiol 12:757469
Gracia-Sancho J, Caparrós E, Fernández-Iglesias A, Francés R (2021) Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver diseases. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:411–431. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-020-00411-3
Knolle PA et al (1999) Induction of cytokine production in naive CD4+ T cells by antigen- presenting murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells but failure to induce differentiation toward T(h1) cells. Gastroenterology 116:1428–1440
Neumann K et al (2015) Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells induce immunosuppressive IL-10-producing Th1 cells via the Notch pathway. Eur J Immunol 45:2008–2016
Diehl L et al (2008) Tolerogenic maturation of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells promotes B7-homolog 1-dependent CD8+ T cell tolerance. Hepatology 47:296–305
Carambia A et al (2014) TGF-β-dependent induction of CD4+CD25+Foxp3 + Tregs by liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J Hepatol 61:594–599
Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI, Nourshargh S (2007) Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol 7:678–689. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2156
Furuta K et al (2021) Lipid-induced endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 promotes nonalcoholic steatohepatitis pathogenesis. J Clin Investig 131:e143690
Ip E, Farrell G, Hall P, Robertson G, Leclercq I (2004) Administration of the potent PPARα agonist, Wy-14,643, reverses nutritional fibrosis and steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 39:1286–1296
Weston CJ et al (2015) Vascular adhesion protein-1 promotes liver inflammation and drives hepatic fibrosis. J Clin Investig 125:501–520
Guo Q et al (2022) Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell expressed vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 promotes liver fibrosis. Front Immunol 13:1–15
Carr RM (2021) VCAM-1: closing the gap between lipotoxicity and endothelial dysfunction in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Clin Investig 131:e147556
Chimen M et al (2017) Monocyte subsets coregulate inflammatory responses by integrated signaling through TNF and IL-6 at the endothelial cell interface. J Immunol 198:2834–2843
Seki E, Schwabe RF (2015) Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis: functional links and key pathways. Hepatology 61:1066–1079
Nati M et al (2016) The role of immune cells in metabolism-related liver inflammation and development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Rev Endocr Metab Disord 17:29–39
Hammoutene A et al (2020) A defect in endothelial autophagy occurs in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and promotes inflammation and fibrosis. J Hepatol 72:528–538
Flessa CM et al (2021) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): current evidence and perspectives. Curr Obes Rep 10:134–161
Duan JL et al (2023) Age-related liver endothelial zonation triggers steatohepatitis by inactivating pericentral endothelium-derived C-kit. Nat Aging 3:258–274
Papatheodoridi AM, Chrysavgis L, Koutsilieris M, Chatzigeorgiou A (2020) The role of senescence in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and progression to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 71:363–374
Moustakas II et al (2021) Hepatic senescence accompanies the development of NAFLD in non-aged mice independently of obesity. Int J Mol Sci 22:3446
Grosse L, Bulavin DV (2020) LSEC model of aging. Aging 12:11152–11160
Duan JL et al (2022) Shear stress-induced cellular senescence blunts liver regeneration through Notch-sirtuin 1–P21/P16 axis. Hepatology 75:584–599
Maeso-Díaz R et al (2018) Effects of aging on liver microcirculatory function and sinusoidal phenotype. Aging Cell 17:e12829
Wang D et al (2023) Assessing the effects of aging on the liver endothelial cell landscape using single-cell RNA sequencing. Hepatol Commun 7:e0021–e0021
Lei L, Mourabit HEI, Housset C, Cadoret A, Lemoinne S (2021) Role of angiogenesis in the pathogenesis of nafld. J Clin Med 10:1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071338
Carmeliet P (2003) Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med 9:653–660
Bocca C, Novo E, Miglietta A, Parola M (2015) Angiogenesis and fibrogenesis in chronic liver diseases. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:477–488
McCuskey RS, Reilly FD (1993) Hepatic microvasculature: dynamic structure and its regulation. Semin Liver Dis 13:1–12
Fernández M et al (2009) Angiogenesis in liver disease. J Hepatol 50:604–620
Hadjihambi A et al (2023) Novel in vivo micro-computed tomography imaging techniques for assessing the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/64838
Matsuda M, Seki E (2020) The liver fibrosis niche: Novel insights into the interplay between fibrosis-composing mesenchymal cells, immune cells, endothelial cells, and extracellular matrix. Food Chem Toxicol 143:111556
Granzow M et al (2014) Angiotensin-II type 1 receptor-mediated Janus kinase 2 activation induces liver fibrosis. Hepatology 60:334–348
Yoshiji H et al (2006) Angiotensin-II and vascular endothelial growth factor interaction plays an important role in rat liver fibrosis development. Hepatol Res 36:124–129
Coulon S et al (2012) Evaluation of inflammatory and angiogenic factors in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cytokine 59:442–449
Tarantino G et al (2009) Could inflammatory markers help diagnose nonalcoholic steatohepatitis? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21:504–511
Cayón A, Crespo J, Guerra AR, Pons-Romero F (2008) Gene expression in obese patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 100:212–218
Baselli GA et al (2020) Liver transcriptomics highlights interleukin-32 as novel NAFLD-related cytokine and candidate biomarker. Gut 69:1855–1866
Lefere S et al (2019) Angiopoietin-2 promotes pathological angiogenesis and is a therapeutic target in murine nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 69:1087–1104
Kitade M et al (2006) Leptin-mediated neovascularization is a prerequisite for progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. Hepatology 44:983–991
Coulon S et al (2013) Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the pathophysiology of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in two rodent models. Hepatology 57:1793–1805
Ding BS et al (2014) Divergent angiocrine signals from vascular niche balance liver regeneration and fibrosis. Nature 505:97–102
Marrone G et al (2013) The transcription factor KLF2 mediates hepatic endothelial protection and paracrine endothelial-stellate cell deactivation induced by statins. J Hepatol 58:98–103
Wang R et al (2015) Exosome adherence and internalization by hepatic stellate cells triggers sphingosine 1-phosphate-dependent migration. J Biol Chem 290:30684–30696
Winkler M et al (2021) Endothelial GATA4 controls liver fibrosis and regeneration by preventing a pathogenic switch in angiocrine signaling. J Hepatol 74:380–393
Hu J et al (2014) Endothelial cell-derived Angiopoietin-2 controls liver regeneration as a spatiotemporal rheostat. Science 343:416–419
Ding BS et al (2010) Inductive angiocrine signals from sinusoidal endothelium are required for liver regeneration. Nature 468:310–315
Duan JL et al (2018) Endothelial Notch activation reshapes the angiocrine of sinusoidal endothelia to aggravate liver fibrosis and blunt regeneration in mice. Hepatology 68:677–690
Shen Z et al (2023) Expansion of macrophage and liver sinusoidal endothelial cell subpopulations during non-alcoholic steatohepatitis progression. iScience 26:106572
Arner E et al (2015) Transcribed enhancers lead waves of coordinated transcription in transitioning mammalian cells. Science 347:1010–1014
Khachigian LM (2021) Early growth response-1, an integrative sensor in cardiovascular and inflammatory disease. J Am Heart Assoc 10:e023539
Fahmy RG, Dass CR, Sun LQ, Chesterman CN, Khachigian LM (2003) Transcription factor Egr-1 supports FGF-dependent angiogenesis during neovascularization and tumor growth. Nat Med 9:1026–1032
Shaulian E, Karin M (2002) AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol 4:E131–E136
Yoshitomi Y, Ikeda T, Saito-takatsuji H, Yonekura H (2021) Emerging role of AP-1 transcription factor JunB in angiogenesis and vascular development. Int J Mol Sci 22:1–14
Gerald D et al (2013) RhoB controls coordination of adult angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis following injury by regulating VEZF1-mediated transcription. Nat Commun 4:2824
Luna G, Paez J, Cardier JE (2004) Expression of the hematopoietic stem cell antigen Sca-1 (LY-6A/E) in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: possible function of Sca-1 in endothelial cells. Stem Cells Dev 13:528–535
Xiong X et al (2019) Landscape of intercellular crosstalk in healthy and NASH liver revealed by single-cell secretome gene analysis. Mol Cell 75:644-660.e5
Kalucka J et al (2020) Single-cell transcriptome atlas of murine endothelial cells. Cell 180:764-779.e20
Sakamoto M (2009) Early HCC: diagnosis and molecular markers. J Gastroenterol 44:108–111
Anstee QM, Reeves HL, Kotsiliti E, Govaere O, Heikenwalder M (2019) From NASH to HCC: current concepts and future challenges. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:411–428. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-019-0145-7
Massoud O, Charlton M (2018) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis 22:201–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2017.08.014
Paradis V et al (2009) Hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with metabolic syndrome often develop without significant liverfibrosis: a pathological analysis. Hepatology 49:851–859
Kanwal F et al (2018) Risk of hepatocellular cancer in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 155:1828–18372
Sung H et al (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249
Yang M, Zhang C (2021) The role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in cancer liver metastasis. Am J Cancer Res 11:1845–1860
Géraud C et al (2013) Endothelial transdifferentiation in hepatocellular carcinoma: loss of stabilin-2 expression in peri-tumourous liver correlates with increased survival. Liver Int 33:1428–1440
Hughes A, Dhoot GK (2018) Dysregulated cancer cell transdifferentiation into erythrocytes is an additional metabolic stress in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol 40:1010428318811467
Marfels C, Hoehn M, Wagner E, Günther M (2013) Characterization of in vivo chemoresistant human hepatocellular carcinoma cells with transendothelial differentiation capacities. BMC Cancer 13:176
Wu LQ et al (2007) Phenotypic and functional differences between human liver cancer endothelial cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J Vasc Res 45:78–86
Zhuang PY et al (2015) Higher proliferation of peritumoral endothelial cells to IL-6/sIL-6R than tumoral endothelial cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 15:830
Olsavszky V et al (2021) Exploring the transcriptomic network of multi-ligand scavenger receptor Stabilin-1- and Stabilin-2-deficient liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Gene 768:145284
Hoshida Y et al (2008) Gene expression in fixed tissues and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359:1995–2004
Thompson KJ et al (2018) Altered fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4) expression and function in human and animal models of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 38:1074–1083
Laouirem S et al (2019) Endothelial fatty liver binding protein 4: a new targetable mediator in hepatocellular carcinoma related to metabolic syndrome. Oncogene 38:3033–3046
Milner KL et al (2009) Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein levels relate to inflammation and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 49:1926–1934
Chen KJ et al (2011) Selective recruitment of regulatory T cell through CCR6-CCL20 in hepatocellular carcinoma fosters tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS One 6:e24671
Fu J et al (2007) Increased regulatory T cells correlate with CD8 T-cell impairment and poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology 132:2328–2339
Mendt M, Cardier JE (2017) Activation of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor enhances biological functions associated with B16 melanoma liver metastasis. Melanoma Res 27:300–308
Arteta B et al (2010) Colon carcinoma cell interaction with liver sinusoidal endothelium inhibits organ-specific antitumor immunity through interleukin-1-induced mannose receptor in mice. Hepatology 51:2172–2182
Ma C et al (2018) Gut microbiome–mediated bile acid metabolism regulates liver cancer via NKT cells. Science 360:eaan5931
Zhang N et al (2011) Platelet adhesion and fusion to endothelial cell facilitate the metastasis of tumor cell in hypoxia-reoxygenation condition. Clin Exp Metastasis 28:1–12
Kitakata H et al (2002) Essential roles of tumor necrosis factor receptor p55 in liver metastasis of intrasplenic administration of colon 26 cells. Cancer Res 62:6682–6687
Medina J, Arroyo AG, Sánchez-Madrid F, Moreno-Otero R (2004) Angiogenesis in chronic inflammatory liver disease. Hepatology 39:1185–1195
Bergers G, Benjamin LE (2003) Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer 3:401–410
Semela D, Dufour JF (2004) Angiogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 41:864–880
Folkman J (2007) Angiogenesis: An organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:273–286
Chaparro Sánchez M, Sanz-Cameno P, Trapero-Marugán M, García-Buey L, Moreno-Otero R (2007) Mechanisms of angiogenesis in chronic inflammatory liver disease. Ann Hepatol 6:208–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1665-2681(19)31900-3
Mitsuhashi N et al (2003) Angiopoietins and Tie-2 expression in angiogenesis and proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 37:1105–1113
Semela D et al (2008) Platelet-derived growth factor signaling through ephrin-B2 regulates hepatic vascular structure and function. Gastroenterology 135:671–679
Yoshiji H et al (2014) Combination of sorafenib and angiotensin-II receptor blocker attenuates preneoplastic lesion development in a non-diabetic rat model of steatohepatitis. J Gastroenterol 49:1421–1429
Romero FA, Jones CT, Xu Y, Fenaux M, Halcomb RL (2020) The race to bash NASH: emerging targets and drug development in a complex liver disease. J Med Chem 63:5031–5073. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01701
Anstee QM et al (2023) Cenicriviroc lacked efficacy to treat liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: AURORA phase III randomized study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CGH.2023.04.003
Shojaie L, Ali M, Iorga A, Dara L (2021) Mechanisms of immune checkpoint inhibitor-mediated liver injury. Acta Pharm Sin B 11:3727–3739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.10.003
Llovet JM, Montal R, Sia D, Finn RS (2018) Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15:599–616. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-018-0073-4
Funding
Supported by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (HFRI #3222 to AC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Velliou, RI., Legaki, AI., Nikolakopoulou, P. et al. Liver endothelial cells in NAFLD and transition to NASH and HCC. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 80, 314 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-023-04966-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-023-04966-7