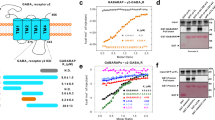
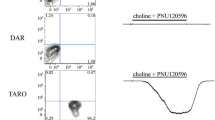
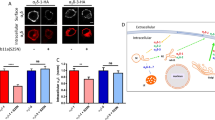
Abstract
Membrane trafficking processes regulate the G protein-coupled receptor activity. The muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) are highly pursued drug targets for neurological diseases, but the cellular machineries that control the trafficking of these receptors remain largely elusive. Here, we revealed the role of the small GTPase Rab10 as a negative regulator for the post-activation trafficking of M4 mAChR and the underlying mechanism. We show that constitutively active Rab10 arrests the receptor within Rab5-positive early endosomes and significantly hinders the resensitization of M4-mediated Ca2+ signaling. Mechanistically, M4 binds to Rab10-GTP, which requires the motif 386RKKRQMAA393 (R386-A393) within the third intracellular loop. Moreover, Rab10-GTP inactivates Arf6 by recruiting the Arf6 GTPase-activating protein, ACAP1. Strikingly, deletion of the motif R386-A393 causes M4 to bypass the control by Rab10 and switch to the Rab4-facilitated fast recycling pathway, thus reusing the receptor. Therefore, Rab10 couples the cargo sorting and membrane trafficking regulation through cycle between GTP-bound and GDP-bound state. Our findings suggest a model that Rab10 binds to the M4 like a molecular brake and controls the receptor’s transport through endosomes, thus modulating the signaling, and this regulation is specific among the mAChR subtypes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of dada and material
All plasmids and data generated in this study will be freely provided upon request to the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- A568-Tf:
-
Alexa568-labeled Transferrin
- Arf6:
-
ADP-ribosylation factor 6
- β1AR:
-
β1 Adrenoceptor
- CCh:
-
Carbachol
- CDE:
-
Clathrin-dependent endocytic
- CHC:
-
Clathrin heavy chain
- CHX:
-
Cycloheximide
- CIE:
-
Clathrin-independent endocytic
- Co-IP:
-
Co-immunoprecipitation
- DOPr:
-
δ-Opioid receptor
- EE:
-
Early endosome
- EHBP-1:
-
Effector EH domain binding protein 1
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- FI:
-
Fluorescence intensity
- GGA3:
-
Golgi-associated, gamma adaptin ear-containing, Arf-binding protein 3
- GIPC:
-
Gαi-interacting protein C terminus
- GPCR:
-
G protein-coupled receptor
- GST:
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- GST-GGA3-PBD:
-
Protein 3 binding domain (PBD) of GGA3 fused to glutathione S-transferase
- mAChRs:
-
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
- LHR:
-
Luteinizing hormone receptor
- PBD:
-
Protein 3 binding domain
- PDZ:
-
Postsynaptic density-95/Discs large/Zonula occludens 1
- PM:
-
Plasma membrane
- PTX:
-
Pertussis toxin
- RE:
-
Recycling endosome
- SNX27:
-
Sorting nexin 27
- TAC:
-
IL-2 receptor α-chain
- TfR:
-
Transferrin receptor
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Hauser AS, Attwood MM, Rask-Andersen M, Schioth HB, Gloriam DE (2017) Trends in GPCR drug discovery: new agents, targets and indications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16:829–842. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2017.178
Wei Z, Zhang M, Li C, Huang W, Fan Y, Guo J, Khater M, Fukuda M, Dong Z, Hu G, Wu G (2019) Specific TBC domain-containing proteins control the ER-Golgi-plasma membrane trafficking of GPCRs. Cell Rep 28:554–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.033. (e554)
Sposini S, Hanyaloglu AC (2017) Spatial encryption of G protein-coupled receptor signaling in endosomes; Mechanisms and applications. Biochem Pharmacol 143:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2017.04.028
Gupta MK, Mohan ML, Naga Prasad SV (2018) G Protein-coupled receptor resensitization paradigms. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 339:63–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ircmb.2018.03.002
Parent A, Hamelin E, Germain P, Parent JL (2009) Rab11 regulates the recycling of the β2-adrenergic receptor through a direct interaction. Biochem J 418:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20080867
Abdullah N, Beg M, Soares D, Dittman JS, McGraw TE (2016) Downregulation of a GPCR by β-arrestin2-mediated switch from an endosomal to a TGN recycling pathway. Cell Rep 17:2966–2978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.11.050
Sposini S, Jean-Alphonse FG, Ayoub MA, Oqua A, West C, Lavery S, Brosens JJ, Reiter E, Hanyaloglu AC (2017) Integration of GPCR signaling and sorting from very early endosomes via opposing APPL1 mechanisms. Cell Rep 21:2855–2867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.023
Maxfield FR, McGraw TE (2004) Endocytic recycling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1315
Romero G, von Zastrow M, Friedman PA (2011) Role of PDZ proteins in regulating trafficking, signaling, and function of GPCRs: means, motif, and opportunity. Adv Pharmacol 62:279–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385952-5.00003-8
Hanyaloglu AC, von Zastrow M (2008) Regulation of GPCRs by endocytic membrane trafficking and its potential implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 48:537–568. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094830
Nooh MM, Mancarella S, Bahouth SW (2018) Novel paradigms governing β1-adrenergic receptor trafficking in primary adult rat cardiac myocytes. Mol Pharmacol 94:862–875. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.118.112045
Jean-Alphonse F, Bowersox S, Chen S, Beard G, Puthenveedu MA, Hanyaloglu AC (2014) Spatially restricted G protein-coupled receptor activity via divergent endocytic compartments. J Biol Chem 289:3960–3977. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.526350
Paquet M, Asay MJ, Fam SR, Inuzuka H, Castleberry AM, Oller H, Smith Y, Yun CC, Traynelis SF, Hall RA (2006) The PDZ scaffold NHERF-2 interacts with mGluR5 and regulates receptor activity. J Biol Chem 281:29949–29961. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M602262200
Temkin P, Lauffer B, Jager S, Cimermancic P, Krogan NJ, von Zastrow M (2011) SNX27 mediates retromer tubule entry and endosome-to-plasma membrane trafficking of signalling receptors. Nat Cell Biol 13:715–721. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2252
Hirakawa T, Galet C, Kishi M, Ascoli M (2003) GIPC binds to the human lutropin receptor (hLHR) through an unusual PDZ domain binding motif, and it regulates the sorting of the internalized human choriogonadotropin and the density of cell surface hLHR. J Biol Chem 278:49348–49357. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M306557200
Marchese A, Paing MM, Temple BR, Trejo J (2008) G protein-coupled receptor sorting to endosomes and lysosomes. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 48:601–629. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094646
Zenko D, Hislop JN (2018) Regulation and trafficking of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuropharmacology 136:374–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.11.017
van der Westhuizen ET, Choy KHC, Valant C, McKenzie-Nickson S, Bradley SJ, Tobin AB, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A (2020) Fine tuning muscarinic acetylcholine receptor signaling through allostery and bias. Front Pharmacol 11:606656. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.606656
Yohn SE, Conn PJ (2018) Positive allosteric modulation of M1 and M4 muscarinic receptors as potential therapeutic treatments for schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 136:438–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.09.012
Foster DJ, Choi DL, Conn PJ, Rook JM (2014) Activation of M1 and M4 muscarinic receptors as potential treatments for Alzheimer’s disease and schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 10:183–191. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S55104
Vogler O, Nolte B, Voss M, Schmidt M, Jakobs KH, van Koppen CJ (1999) Regulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor sequestration and function by beta-arrestin. J Biol Chem 274:12333–12338. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.18.12333
Volpicelli LA, Lah JJ, Fang G, Goldenring JR, Levey AI (2002) Rab11a and myosin Vb regulate recycling of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J Neurosci 22:9776–9784
Bao Z, Zhou S, Zhou H (2020) Sorting Nexin 27 as a potential target in G proteincoupled receptor recycling for cancer therapy (Review). Oncol Rep 44:1779–1786. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7766
Stenmark H (2009) Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:513–525. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2728
Chua CEL, Tang BL (2018) Rab 10-a traffic controller in multiple cellular pathways and locations. J Cell Physiol 233:6483–6494. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26503
Dong C, Wu G (2013) G-protein-coupled receptor interaction with small GTPases. Methods Enzymol 522:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-407865-9.00006-6
Degrandmaison J, Abdallah K, Blais V, Genier S, Lalumiere MP, Bergeron F, Cahill CM, Boulter J, Lavoie CL, Parent JL, Gendron L (2020) In vivo mapping of a GPCR interactome using knockin mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:13105–13116. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1917906117
Wei Z, Xu X, Fang Y, Khater M, Naughton SX, Hu G, Terry AV Jr, Wu G (2021) Rab43 GTPase directs postsynaptic trafficking and neuron-specific sorting of G protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem 296:100517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100517
Jordan KL, Koss DJ, Outeiro TF, Giorgini F (2022) Therapeutic targeting of Rab GTPases: relevance for Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedicines. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051141
Brewer PD, Habtemichael EN, Romenskaia I, Mastick CC, Coster AC (2016) Glut4 is sorted from a Rab10 GTPase-independent constitutive recycling pathway into a highly insulin-responsive Rab10 GTPase-dependent sequestration pathway after adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 291:773–789. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.694919
Borchers AC, Langemeyer L, Ungermann C (2021) Who’s in control Principles of Rab GTPase activation in endolysosomal membrane trafficking and beyond. J Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202105120
Wang P, Liu H, Wang Y, Liu O, Zhang J, Gleason A, Yang Z, Wang H, Shi A, Grant BD (2016) RAB-10 promotes EHBP-1 bridging of filamentous actin and tubular recycling endosomes. PLoS Genet 12:e1006093. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006093
Wan M, Zhang W, Tian Y, Xu C, Xu T, Liu J, Zhang R (2015) Unraveling a molecular determinant for clathrin-independent internalization of the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Sci Rep 5:11408. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11408
Schuck S, Gerl MJ, Ang A, Manninen A, Keller P, Mellman I, Simons K (2007) Rab10 is involved in basolateral transport in polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Traffic 8:47–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2006.00506.x
Eguez L, Lee A, Chavez JA, Miinea CP, Kane S, Lienhard GE, McGraw TE (2005) Full intracellular retention of GLUT4 requires AS160 Rab GTPase activating protein. Cell Metab 2:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2005.09.005
Tian Y, Kang Q, Shi X, Wang Y, Zhang N, Ye H, Xu Q, Xu T, Zhang R (2021) SNX-3 mediates retromer-independent tubular endosomal recycling by opposing EEA-1-facilitated trafficking. PLoS Genet 17:e1009607. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1009607
Volpicelli LA, Lah JJ, Levey AI (2001) Rab5-dependent trafficking of the m4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor to the plasma membrane, early endosomes, and multivesicular bodies. J Biol Chem 276:47590–47598. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M106535200
Krudewig R, Langer B, Vogler O, Markschies N, Erl M, Jakobs KH, van Koppen CJ (2000) Distinct internalization of M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors confers selective and long-lasting desensitization of signaling to phospholipase C. J Neurochem 74:1721–1730. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0741721.x
Babbey CM, Ahktar N, Wang E, Chen CC, Grant BD, Dunn KW (2006) Rab10 regulates membrane transport through early endosomes of polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Mol Biol Cell 17:3156–3175. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e05-08-0799
Miinea CP, Sano H, Kane S, Sano E, Fukuda M, Peranen J, Lane WS, Lienhard GE (2005) AS160, the Akt substrate regulating GLUT4 translocation, has a functional Rab GTPase-activating protein domain. Biochem J 391:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20050887
Naslavsky N, Caplan S (2018) The enigmatic endosome—sorting the ins and outs of endocytic trafficking. J Cell Sci. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.216499
Hashimoto Y, Morisawa K, Saito H, Jojima E, Yoshida N, Haga T (2008) Muscarinic M4 receptor recycling requires a motif in the third intracellular loop. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325:947–953. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.107.135095
Donaldson JG, Porat-Shliom N, Cohen LA (2009) Clathrin-independent endocytosis: a unique platform for cell signaling and PM remodeling. Cell Signal 21:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.06.020
D’Souza-Schorey C, Chavrier P (2006) ARF proteins: roles in membrane traffic and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:347–358. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1910
Houndolo T, Boulay PL, Claing A (2005) G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis in ADP-ribosylation factor 6-depleted cells. J Biol Chem 280:5598–5604. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M411456200
Reiner C, Nathanson NM (2008) The internalization of the M2 and M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors involves distinct subsets of small G-proteins. Life Sci 82:718–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2008.01.013
D’Souza-Schorey C, van Donselaar E, Hsu VW, Yang C, Stahl PD, Peters PJ (1998) ARF6 targets recycling vesicles to the plasma membrane: insights from an ultrastructural investigation. J Cell Biol 140:603–616. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.140.3.603
Donaldson JG (2003) Multiple roles for Arf6: sorting, structuring, and signaling at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 278:41573–41576. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R300026200
Sannerud R, Declerck I, Peric A, Raemaekers T, Menendez G, Zhou L, Veerle B, Coen K, Munck S, De Strooper B, Schiavo G, Annaert W (2011) ADP ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) controls amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing by mediating the endosomal sorting of BACE1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:E559-568. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1100745108
Van Acker T, Tavernier J, Peelman F (2019) The small GTPase Arf6: an overview of its mechanisms of action and of its role in host(–)pathogen interactions and innate immunity. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092209
Pfeffer SR (2012) Rab GTPase localization and Rab cascades in Golgi transport. Biochem Soc Trans 40:1373–1377. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20120168
Kobayashi H, Fukuda M (2012) Rab35 regulates Arf6 activity through centaurin-β2 (ACAP2) during neurite outgrowth. J Cell Sci 125:2235–2243. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.098657
Shi A, Liu O, Koenig S, Banerjee R, Chen CC, Eimer S, Grant BD (2012) RAB-10-GTPase-mediated regulation of endosomal phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:E2306-2315. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1205278109
Allaire PD, Seyed Sadr M, Chaineau M, Seyed Sadr E, Konefal S, Fotouhi M, Maret D, Ritter B, Del Maestro RF, McPherson PS (2013) Interplay between Rab35 and Arf6 controls cargo recycling to coordinate cell adhesion and migration. J Cell Sci 126:722–731. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.112375
Jackson TR, Brown FD, Nie Z, Miura K, Foroni L, Sun J, Hsu VW, Donaldson JG, Randazzo PA (2000) ACAPs are arf6 GTPase-activating proteins that function in the cell periphery. J Cell Biol 151:627–638. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.151.3.627
Dai J, Li J, Bos E, Porcionatto M, Premont RT, Bourgoin S, Peters PJ, Hsu VW (2004) ACAP1 promotes endocytic recycling by recognizing recycling sorting signals. Dev Cell 7:771–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2004.10.002
Takatsu H, Yoshino K, Toda K, Nakayama K (2002) GGA proteins associate with Golgi membranes through interaction between their GGAH domains and ADP-ribosylation factors. Biochem J 365:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20020428
Carroll RC, Morielli AD, Peralta EG (1995) Coincidence detection at the level of phospholipase C activation mediated by the m4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Curr Biol 5:536–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00106-0
Esseltine JL, Ribeiro FM, Ferguson SS (2012) Rab8 modulates metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 1 intracellular trafficking and signaling in a protein kinase C-dependent manner. J Neurosci 32:16933–16942a. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0625-12.2012
Richards MH, van Giersbergen PL (1995) Human muscarinic receptors expressed in A9L and CHO cells: activation by full and partial agonists. Br J Pharmacol 114:1241–1249. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13339.x
Li C, Wei Z, Fan Y, Huang W, Su Y, Li H, Dong Z, Fukuda M, Khater M, Wu G (2017) The GTPase Rab43 controls the anterograde ER-Golgi trafficking and sorting of GPCRs. Cell Rep 21:1089–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.011
Dong C, Yang L, Zhang X, Gu H, Lam ML, Claycomb WC, Xia H, Wu G (2010) Rab8 interacts with distinct motifs in alpha2B- and beta2-adrenergic receptors and differentially modulates their transport. J Biol Chem 285:20369–20380. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.081521
Seachrist JL, Laporte SA, Dale LB, Babwah AV, Caron MG, Anborgh PH, Ferguson SS (2002) Rab5 association with the angiotensin II type 1A receptor promotes Rab5 GTP binding and vesicular fusion. J Biol Chem 277:679–685. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109022200
Chen CC, Schweinsberg PJ, Vashist S, Mareiniss DP, Lambie EJ, Grant BD (2006) RAB-10 is required for endocytic recycling in the Caenorhabditis elegans intestine. Mol Biol Cell 17:1286–1297. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e05-08-0787
Chen S, Li L, Li J, Liu B, Zhu X, Zheng L, Zhang R, Xu T (2014) SEC-10 and RAB-10 coordinate basolateral recycling of clathrin-independent cargo through endosomal tubules in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:15432–15437. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1408327111
Mulvaney EP, O’Meara F, Khan AR, O’Connell DJ, Kinsella BT (2017) Identification of alpha-helix 4 (alpha4) of Rab11a as a novel Rab11-binding domain (RBD): interaction of Rab11a with the prostacyclin receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1864:1819–1832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.07.010
Tanna CE, Goss LB, Ludwig CG, Chen PW (2019) Arf GAPs as regulators of the actin cytoskeleton-an update. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020442
Pfeffer SR (2017) Rab GTPases: master regulators that establish the secretory and endocytic pathways. Mol Biol Cell 28:712–715. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E16-10-0737
Donaldson JG, Johnson DL, Dutta D (2016) Rab and Arf G proteins in endosomal trafficking and cell surface homeostasis. Small GTPases 7:247–251. https://doi.org/10.1080/21541248.2016.1212687
Fielding AB, Schonteich E, Matheson J, Wilson G, Yu X, Hickson GR, Srivastava S, Baldwin SA, Prekeris R, Gould GW (2005) Rab11-FIP3 and FIP4 interact with Arf6 and the exocyst to control membrane traffic in cytokinesis. EMBO J 24:3389–3399. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600803
Kiral FR, Kohrs FE, Jin EJ, Hiesinger PR (2018) Rab GTPases and membrane trafficking in neurodegeneration. Curr Biol 28:R471–R486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.010
Zhang X, Huang TY, Yancey J, Luo H, Zhang YW (2019) Role of Rab GTPases in Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:828–838. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00387
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Victor Hsu (Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA), Dr. Emmanuel Boucrot (Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology, University College London, London, UK), and Dr. Eli Song(Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China) for kindly donating material. This work was supported by the Major Research Plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91954107), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32270739, 31571468) to RZ.
Funding
This work was supported by the Major Research Plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91954107), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32270739, 31571468) to RZ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, RZ; Investigation, RX, MW, XS, SM, and LZ; Methodology, RX, PY, MW, XS, and RZ; Formal analysis, RX, and MW; Funding acquisition, RZ; Project administration, PY, RZ; Original draft, RZ; Writing and review and editing, RX, PY, MW, and RZ.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 70328 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 74340 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, R., Wan, M., Shi, X. et al. A Rab10–ACAP1–Arf6 GTPases cascade modulates M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor trafficking and signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 80, 87 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-023-04722-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-023-04722-x