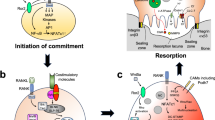
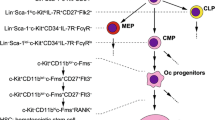
Abstract
Osteoclast-mediated bone resorption is responsible for bone metabolic diseases, negatively impacting people's health and life. It has been demonstrated that microRNA influences the differentiation of osteoclasts by regulating the signaling pathways during osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. So far, the involved mechanisms have not been fully elucidated. This review introduced the pathways involved in osteoclastogenesis and summarized the related microRNAs binding to their specific targets to mediate the downstream pathways in osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. We also discuss the clinical potential of targeting microRNAs to treat osteoclast-mediated bone resorption as well as the challenges of avoiding potential side effects and producing efficient delivery methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data relevant to this review is included in the text, references, and figures.
Abbreviations
- BMMs:
-
Bone marrow macrophages
- BMSCs:
-
Bone marrow stromal cells
- MMCs:
-
Multiple myeloma cells
- MSCs:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- CIA:
-
Collagen-induced arthritis
- OSM:
-
Oncostatin M
- EZH2:
-
Zeste homologue 2
- PBMCs:
-
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PMOP:
-
Postmenopausal hypoestrogenic women with osteoporosis
- OVX:
-
Ovariectomy
- AIA:
-
Adjuvant-induced arthritis
- BCX:
-
Breast cancer xenografted
- c-src:
-
Tyrosine-protein kinase src
- NFI-A:
-
Nuclear factor I-A
- NFIX:
-
Nuclear factor one X
- SIRT1:
-
Sirtuin-1
- CYLD:
-
Cylindromatosis
- MITF:
-
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- TNFRSF1B:
-
Tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 1B
- SOCS1:
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1
- PC:
-
Prostate cancer
- GCT:
-
Giant cell tumor
- HMSCs:
-
Human mesenchymal stem cell
- PTK:
-
Protein tyrosine kinase
- CALCR:
-
Calcitonin receptor
- SRGAP:
-
Slit-Robo GTPase-activating protein
- GPR65:
-
G protein-coupled receptor 65
- LEPR:
-
Leptin receptor
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- LGR:
-
G protein-coupled receptors
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- ONFH:
-
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head
- CCND1:
-
Cyclin D1
References
Inoue K, Nakano S, Zhao B (2019) Osteoclastic microRNAs and their translational potential in skeletal diseases. Semin Immunopathol 41(5):573–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-019-00761-4
Goldring SR, Purdue PE, Crotti TN et al (2013) Bone remodelling in inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202199
Sozen T, Ozisik L, Basaran NC (2017) An overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur J Rheumatol 4(1):46–56. https://doi.org/10.5152/eurjrheum.2016.048
Zhao H, Lu A, He X (2020) Roles of MicroRNAs in bone destruction of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:600867. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.600867
Boyce BF, Li J, Xing L et al (2018) Bone remodeling and the role of TRAF3 in osteoclastic bone resorption. Front Immunol 9:2263. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02263
Wang Y, Grainger DW (2012) RNA therapeutics targeting osteoclast-mediated excessive bone resorption. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64(12):1341–1357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2011.09.002
Javed A, Chen H, Ghori FY (2010) Genetic and transcriptional control of bone formation. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 22(3):283–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coms.2010.05.001
Nakashima T, Takayanagi H (2011) New regulation mechanisms of osteoclast differentiation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1240:E13–E18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06373.x
Nakashima T, Hayashi M, Takayanagi H (2012) New insights into osteoclastogenic signaling mechanisms. Trends Endocrinol Metab 23(11):582–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2012.05.005
Boyce BF (2013) Advances in the regulation of osteoclasts and osteoclast functions. J Dent Res 92(10):860–867. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034513500306
Lian JB, Stein GS, van Wijnen AJ et al (2012) MicroRNA control of bone formation and homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8(4):212–227. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2011.234
Iorio MV, Piovan C, Croce CM (2010) Interplay between microRNAs and the epigenetic machinery: an intricate network. Biochim Biophys Acta 1799(10–12):694–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.05.005
Ghildiyal M, Zamore PD (2009) Small silencing RNAs: an expanding universe. Nat Rev Genet 10(2):94–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2504
Mizoguchi F, Izu Y, Hayata T et al (2010) Osteoclast-specific Dicer gene deficiency suppresses osteoclastic bone resorption. J Cell Biochem 109(5):866–875. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.22228
Sugatani T, Hildreth BE 3rd, Toribio RE et al (2014) Expression of DGCR8-dependent microRNAs is indispensable for osteoclastic development and bone-resorbing activity. J Cell Biochem 115(6):1043–1047. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24759
Pi C, Li YP, Zhou X et al (2015) The expression and function of microRNAs in bone homeostasis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 20:119–138. https://doi.org/10.2741/4301
van der Eerden BC (2014) MicroRNAs in the skeleton: cell-restricted or potent intercellular communicators? Arch Biochem Biophys 561:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2014.04.016
Lozano C, Duroux-Richard I, Firat H et al (2019) MicroRNAs: key regulators to understand osteoclast differentiation? Front Immunol 10:375. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00375
Park JH, Lee NK, Lee SY (2017) Current understanding of RANK signaling in osteoclast differentiation and maturation. Mol Cells 40(10):706–713. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.0225
Chen C, Liu YM, Fu BL et al (2021) MicroRNA-21: an emerging player in bone diseases. Front Pharmacol 12:722804. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.722804
Husain A, Jeffries MA (2017) Epigenetics and bone remodeling. Curr Osteoporos Rep 15(5):450–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-017-0391-y
Boyce BF, Rosenberg E, de Papp AE et al (2012) The osteoclast, bone remodelling and treatment of metabolic bone disease. Eur J Clin Invest 42(12):1332–1341. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2012.02717.x
Gennari L, Bianciardi S, Merlotti D (2017) MicroRNAs in bone diseases. Osteoporos Int 28(4):1191–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-016-3847-5
Tanaka S, Miyazaki T, Fukuda A et al (2006) Molecular mechanism of the life and death of the osteoclast. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1068:180–186. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1346.020
Boyce BF (2013) Advances in osteoclast biology reveal potential new drug targets and new roles for osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res 28(4):711–722. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.1885
Boyce BF, Yao Z, Xing L (2009) Osteoclasts have multiple roles in bone in addition to bone resorption. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 19(3):171–180. https://doi.org/10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v19.i3.10
Shalev M, Arman E, Stein M et al (2021) PTPRJ promotes osteoclast maturation and activity by inhibiting Cbl-mediated ubiquitination of NFATc1 in late osteoclastogenesis. FEBS J 288(15):4702–4723. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15778
Wagner EF, Karsenty G (2001) Genetic control of skeletal development. Curr Opin Genet Dev 11(5):527–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-437x(00)00228-8
Boyce BF, Xing L (2008) Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem Biophys 473(2):139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2008.03.018
Delgado-Calle J, Garmilla P, Riancho JA (2012) Do epigenetic marks govern bone mass and homeostasis? Curr Genomics 13(3):252–263. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920212800543129
Gordon JA, Montecino MA, Aqeilan RI et al (2014) Epigenetic pathways regulating bone homeostasis: potential targeting for intervention of skeletal disorders. Curr Osteoporos Rep 12(4):496–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-014-0240-1
Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC (2009) Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(2):126–139. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2632
Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W (2010) The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet 11(9):597–610. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2843
Sugatani T, Vacher J, Hruska KA (2011) A microRNA expression signature of osteoclastogenesis. Blood 117(13):3648–3657. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-10-311415
Tang P, Xiong Q, Ge W et al (2014) The role of microRNAs in osteoclasts and osteoporosis. RNA Biol 11(11):1355–1363. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2014.996462
Sayed D, Abdellatif M (2011) MicroRNAs in development and disease. Physiol Rev 91(3):827–887. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00006.2010
Michlewski G, Caceres JF (2019) Post-transcriptional control of miRNA biogenesis. RNA 25(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.068692.118
Feng Q, Zheng S, Zheng J (2018) The emerging role of microRNAs in bone remodeling and its therapeutic implications for osteoporosis. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20180453
Sugatani T, Hruska KA (2009) Impaired micro-RNA pathways diminish osteoclast differentiation and function. J Biol Chem 284(7):4667–4678. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M805777200
Franceschetti T, Dole NS, Kessler CB et al (2014) Pathway analysis of microRNA expression profile during murine osteoclastogenesis. PLoS One 9(9):e107262. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107262
Li H, Wang Z, Fu Q et al (2014) Plasma miRNA levels correlate with sensitivity to bone mineral density in postmenopausal osteoporosis patients. Biomarkers 19(7):553–556. https://doi.org/10.3109/1354750X.2014.935957
Rossi M, Pitari MR, Amodio N et al (2013) miR-29b negatively regulates human osteoclastic cell differentiation and function: implications for the treatment of multiple myeloma-related bone disease. J Cell Physiol 228(7):1506–1515. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24306
Zhao X, Xu D, Li Y et al (2014) MicroRNAs regulate bone metabolism. J Bone Miner Metab 32(3):221–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-013-0537-7
Kearns AE, Khosla S, Kostenuik PJ (2008) Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin regulation of bone remodeling in health and disease. Endocr Rev 29(2):155–192. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2007-0014
Xing L, Schwarz EM, Boyce BF (2005) Osteoclast precursors, RANKL/RANK, and immunology. Immunol Rev 208:19–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00336.x
Zhao B, Ivashkiv LB (2011) Negative regulation of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by cytokines and transcriptional repressors. Arthritis Res Ther 13(4):234. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3379
Chen C, Cheng P, Xie H et al (2014) MiR-503 regulates osteoclastogenesis via targeting RANK. J Bone Miner Res 29(2):338–347. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2032
Huang MZ, Zhuang Y, Ning X et al (2020) Artesunate inhibits osteoclastogenesis through the miR-503/RANK axis. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20194387
Wang C, He H, Wang L et al (2018) Reduced miR-144-3p expression in serum and bone mediates osteoporosis pathogenesis by targeting RANK. Biochem Cell Biol 96(5):627–635. https://doi.org/10.1139/bcb-2017-0243
Wang W, Qiao SC, Wu XB et al (2021) Circ_0008542 in osteoblast exosomes promotes osteoclast-induced bone resorption through m6A methylation. Cell Death Dis 12(7):628. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03915-1
Gong M, Ma J, Guillemette R et al (2014) miR-335 inhibits small cell lung cancer bone metastases via IGF-IR and RANKL pathways. Mol Cancer Res 12(1):101–110. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0136
Wang T, Yin H, Wang J et al (2015) MicroRNA-106b inhibits osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis by targeting RANKL in giant cell tumor of bone. Oncotarget 6(22):18980–18996. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4223
Tao Y, Wang Z, Wang L et al (2017) Downregulation of miR-106b attenuates inflammatory responses and joint damage in collagen-induced arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 56(10):1804–1813. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kex233
Li W, Wang X, Chang L et al (2019) MiR-377 inhibits wear particle-induced osteolysis via targeting RANKL. Cell Biol Int 43(6):658–668. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11143
Gong N, Zhu W, Xu R et al (2020) Keratinocytes-derived exosomal miRNA regulates osteoclast differentiation in middle ear cholesteatoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 525(2):341–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.058
Li M, Zhang Z, Gu X et al (2020) MicroRNA-21 affects mechanical force-induced midpalatal suture remodelling. Cell Prolif 53(1):e12697. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12697
Pitari MR, Rossi M, Amodio N et al (2015) Inhibition of miR-21 restores RANKL/OPG ratio in multiple myeloma-derived bone marrow stromal cells and impairs the resorbing activity of mature osteoclasts. Oncotarget 6(29):27343–27358. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4398
Suarjana IN, Isbagio H, Soewondo P et al (2019) The role of serum expression levels of microrna-21 on bone mineral density in hypostrogenic postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: study on level of RANKL, OPG, TGFbeta-1, sclerostin, RANKL/OPG ratio, and physical activity. Acta Med Indones 51(3):245–252
Chen Y, Wang X, Yang M et al (2018) miR-145–5p increases osteoclast numbers in vitro and aggravates bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis by targeting osteoprotegerin. Med Sci Monit 24:5292–300. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.908219
Han Z, Zhan R, Chen S et al (2020) miR-181b/oncostatin m axis inhibits prostate cancer bone metastasis via modulating osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Biochem 121(2):1664–1674. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29401
Li G, Liu H, Zhang X et al (2020) The protective effects of microRNA-26a in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by repressing EZH2. Cell Cycle 19(5):551–566. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2020.1717043
Wang QSX, Chen Y, Chen J, Li Y (2021) Osteoblasts-derived exosomes regulate osteoclast differentiation through miR-503–3p/Hpse axis. Acta Histochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2021.151790
Guo S, Gu J, Ma J et al (2021) GATA4-driven miR-206-3p signatures control orofacial bone development by regulating osteogenic and osteoclastic activity. Theranostics 11(17):8379–8395. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.58052
Li J, Li Y, Wang S et al (2019) miR-101-3p/Rap1b signal pathway plays a key role in osteoclast differentiation after treatment with bisphosphonates. BMB Rep 52(9):572–576
Zhou L, Song HY, Gao LL et al (2019) MicroRNA1005p inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by regulating fibroblast growth factor 21. Int J Mol Med 43(2):727–738. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.4017
Chang Y, Yu D, Chu W et al (2020) LncRNA expression profiles and the negative regulation of lncRNA-NOMMUT037835.2 in osteoclastogenesis. Bone 130:115072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2019.115072
Liu ZZ, Zhang CY, Huang LL et al (2019) Elevated expression of lncRNA SNHG15 in spinal tuberculosis: preliminary results. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(20):9017–9024. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201910_19303
Ni J, Zhang X, Li J et al (2021) Tumour-derived exosomal lncRNA-SOX2OT promotes bone metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting the miRNA-194-5p/RAC1 signalling axis in osteoclasts. Cell Death Dis 12(7):662. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03928-w
Franzoso G, Carlson L, Xing L et al (1997) Requirement for NF-kappaB in osteoclast and B-cell development. Genes Dev 11(24):3482–3496. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.11.24.3482
Xing L, Carlson L, Story B et al (2003) Expression of either NF-kappaB p50 or p52 in osteoclast precursors is required for IL-1-induced bone resorption. J Bone Miner Res 18(2):260–269. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.2.260
Boyce BF, Xiu Y, Li J et al (2015) NF-kappaB-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 30(1):35–44. https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.35
Liu J, Li D, Dang L et al (2017) Osteoclastic miR-214 targets TRAF3 to contribute to osteolytic bone metastasis of breast cancer. Sci Rep 7:40487. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40487
Mao Y, Chen Y, Fu Y et al (2020) miR-346-3p promotes osteoclastogenesis via inhibiting TRAF3 gene. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 56(7):533–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-020-00479-w
Guo LJ, Liao L, Yang L et al (2014) MiR-125a TNF receptor-associated factor 6 to inhibit osteoclastogenesis. Exp Cell Res 321(2):142–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.12.001
Miao F, Yin BH, Zhang X et al (2020) CircRNA_009934 induces osteoclast bone resorption via silencing miR-5107. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(14):7580–7588. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202007_22256
Lee Y, Kim HJ, Park CK et al (2013) MicroRNA-124 regulates osteoclast differentiation. Bone 56(2):383–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2013.07.007
Nakamachi Y, Ohnuma K, Uto K et al (2016) MicroRNA-124 inhibits the progression of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Ann Rheum Dis 75(3):601–608. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206417
Ohnuma K, Kasagi S, Uto K et al (2019) MicroRNA-124 inhibits TNF-alpha- and IL-6-induced osteoclastogenesis. Rheumatol Int 39(4):689–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-018-4218-7
Zhao N, Han D, Liu Y et al (2016) DLX3 negatively regulates osteoclastic differentiation through microRNA-124. Exp Cell Res 341(2):166–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.01.018
Dinesh P, Kalaiselvan S, Sujitha S et al (2020) miR-506-3p alleviates uncontrolled osteoclastogenesis via repression of RANKL/NFATc1 signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 235(12):9497–9509. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29757
Ling L, Hu HL, Liu KY et al (2019) Long noncoding RNA MIRG induces osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in osteoporosis through negative regulation of miR-1897. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(23):10195–10203. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201912_19654
Zhang L, Lv Y, Xian G et al (2017) 25-hydroxycholesterol promotes RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through coordinating NFATc1 and Sp1 complex in the transcription of miR-139-5p. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 485(4):736–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.118
Takafuji Y, Tatsumi K, Kawao N et al (2021) MicroRNA-196a-5p in extracellular vesicles secreted from myoblasts suppresses osteoclast-like cell formation in mouse cells. Calcif Tissue Int 108(3):364–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-020-00772-6
Sun L, Lian JX, Meng S (2019) MiR-125a-5p promotes osteoclastogenesis by targeting TNFRSF1B. Cell Mol Biol Lett 24:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0146-0
Zhou Y, Zhu Y, Dong X et al (2021) Exosomes derived from pancreatic cancer cells induce osteoclast differentiation through the miR125a-5p/TNFRSF1B pathway. Onco Targets Ther 14:2727–2739. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S282319
Lee WS, Yasuda S, Kono M et al (2020) MicroRNA-9 ameliorates destructive arthritis through down-regulation of NF-kappaB1-RANKL pathway in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Clin Immunol 212:108348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2020.108348
Gao Y, Wang B, Shen C et al (2018) Overexpression of miR146a blocks the effect of LPS on RANKLinduced osteoclast differentiation. Mol Med Rep 18(6):5481–5488. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9610
Zhang J, Zhao H, Chen J et al (2012) Interferon-beta-induced miR-155 inhibits osteoclast differentiation by targeting SOCS1 and MITF. FEBS Lett 586(19):3255–3262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.06.047
Cheng P, Chen C, He HB et al (2013) miR-148a regulates osteoclastogenesis by targeting V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog B. J Bone Miner Res 28(5):1180–1190. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.1845
Guo K, Zhang D, Wu H et al (2018) MiRNA-199a-5p positively regulated RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by target Mafb protein. J Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27968
Ammari M, Presumey J, Ponsolles C et al (2018) Delivery of miR-146a to Ly6C(high) monocytes inhibits pathogenic bone erosion in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics 8(21):5972–5985. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.29313
Niu D, Gong Z, Sun X et al (2019) miR-338-3p regulates osteoclastogenesis via targeting IKKbeta gene. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 55(4):243–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-019-00325-8
Huang Y, Ren K, Yao T et al (2020) MicroRNA-25-3p regulates osteoclasts through nuclear factor I X. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 522(1):74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.11.043
Shen G, Ren H, Shang Q et al (2020) miR-128 plays a critical role in murine osteoclastogenesis and estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss. Theranostics 10(10):4334–4348. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.42982
Zhu J, Wang H, Liu H (2020) Osteoclastic miR-301-b knockout reduces ovariectomy (OVX)-induced bone loss by regulating CYDR/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 529(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.05.111
Liu Z, Li C, Huang P et al (2020) CircHmbox1 targeting miRNA-1247-5p is involved in the regulation of bone metabolism by TNF-alpha in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:594785. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.594785
Yao Z, Xing L, Boyce BF (2009) NF-kappaB p100 limits TNF-induced bone resorption in mice by a TRAF3-dependent mechanism. J Clin Invest 119(10):3024–3034. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI38716
Yang C, McCoy K, Davis JL et al (2010) NIK stabilization in osteoclasts results in osteoporosis and enhanced inflammatory osteolysis. PLoS One 5(11):e15383. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015383
Hu H, Brittain GC, Chang JH et al (2013) OTUD7B controls non-canonical NF-kappaB activation through deubiquitination of TRAF3. Nature 494(7437):371–374. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11831
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL (2003) Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 423(6937):337–342. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01658
Wada T, Nakashima T, Hiroshi N et al (2006) RANKL-RANK signaling in osteoclastogenesis and bone disease. Trends Mol Med 12(1):17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2005.11.007
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T et al (2002) Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell 3(6):889–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1534-5807(02)00369-6
Chen W, Zhu G, Hao L et al (2013) C/EBPalpha regulates osteoclast lineage commitment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(18):7294–7299. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1211383110
Liu C, Cao Z, Bai Y et al (2019) LncRNA AK077216 promotes RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via NFATc1 by inhibition of NIP45. J Cell Physiol 234(2):1606–1617. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27031
Lee CP, Huang YN, Nithiyanantham S et al (2019) LncRNA-Jak3:Jak3 coexpressed pattern regulates monosodium urate crystal-induced osteoclast differentiation through Nfatc1/Ctsk expression. Environ Toxicol 34(2):179–187. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22672
Zhang R, Li J, Li G et al (2020) LncRNA Nron regulates osteoclastogenesis during orthodontic bone resorption. Int J Oral Sci 12(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41368-020-0077-7
Li J, Jin F, Cai M et al (2022) LncRNA Nron inhibits bone resorption in periodontitis. J Dent Res 101(2):187–195. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345211019689
Ikeda F, Matsubara T, Tsurukai T et al (2008) JNK/c-Jun signaling mediates an anti-apoptotic effect of RANKL in osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res 23(6):907–914. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.080211
Huang H, Ryu J, Ha J et al (2006) Osteoclast differentiation requires TAK1 and MKK6 for NFATc1 induction and NF-kappaB transactivation by RANKL. Cell Death Differ 13(11):1879–1891. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401882
Qu B, Xia X, Yan M et al (2015) miR-218 is involved in the negative regulation of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by partial suppression of p38MAPK-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling: potential role for osteopenic diseases. Exp Cell Res 338(1):89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.07.023
Kong XH, Shi SF, Hu HJ et al (2021) MicroRNA-20a suppresses RANKL-modulated osteoclastogenesis and prevents bone erosion in mice with rheumatoid arthritis through the TLR4/p38 pathway. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 35(3):921–31. https://doi.org/10.23812/20-604-A
Ni X, Xia T, Zhao Y et al (2014) Downregulation of miR-106b induced breast cancer cell invasion and motility in association with overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase 2. Cancer Sci 105(1):18–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12309
Sang S, Zhang Z, Qin S et al (2017) MicroRNA-16-5p inhibits osteoclastogenesis in giant cell tumor of bone. Biomed Res Int 2017:3173547. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3173547
Guo J, Zeng X, Miao J et al (2019) MiRNA-218 regulates osteoclast differentiation and inflammation response in periodontitis rats through Mmp9. Cell Microbiol 21(4):e12979. https://doi.org/10.1111/cmi.12979
Wu Z, Yin H, Liu T et al (2014) MiR-126-5p regulates osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption in giant cell tumor through inhibition of MMP-13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443(3):944–949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.075
Ell B, Mercatali L, Ibrahim T et al (2013) Tumor-induced osteoclast miRNA changes as regulators and biomarkers of osteolytic bone metastasis. Cancer Cell 24(4):542–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2013.09.008
Zhao H, Zhang J, Shao H et al (2017) Transforming growth factor beta1/Smad4 signaling affects osteoclast differentiation via regulation of miR-155 expression. Mol Cells 40(3):211–21. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.2303
Zhao H, Zhang J, Shao H et al (2017) miRNA-340 inhibits osteoclast differentiation via repression of MITF. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20170302
Zhang Y, Ma C, Liu C et al (2020) NF-kappaB promotes osteoclast differentiation by overexpressing MITF via down regulating microRNA-1276 expression. Life Sci 258:118093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118093
Franceschetti T, Kessler CB, Lee SK et al (2013) miR-29 promotes murine osteoclastogenesis by regulating osteoclast commitment and migration. J Biol Chem 288(46):33347–33360. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.484568
Cui Y, Fu S, Sun D et al (2019) EPC-derived exosomes promote osteoclastogenesis through LncRNA-MALAT1. J Cell Mol Med 23(6):3843–3854. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14228
Zhang Y, Chen XF, Li J et al (2020) lncRNA Neat1 stimulates osteoclastogenesis via sponging miR-7. J Bone Miner Res 35(9):1772–1781. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.4039
Takigawa S, Chen A, Wan Q et al (2016) Role of miR-222-3p in c-Src-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 17(2):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020240
Huang Z, Chu L, Liang J et al (2021) H19 promotes HCC bone metastasis through reducing osteoprotegerin expression in a protein phosphatase 1 catalytic subunit alpha/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent manner and sponging microRNA 200b–3p. Hepatology 74(1):214–232. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31673
Chen L, Wang Y, Lu X et al (2021) miRNA-7062-5p promoting bone resorption after bone metastasis of colorectal cancer through inhibiting GPR65. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:681968. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.681968
Li HW, Zeng HS (2020) Regulation of JAK/STAT signal pathway by miR-21 in the pathogenesis of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. World J Pediatr 16(5):502–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-019-00268-w
Fordham JB, Guilfoyle K, Naqvi AR et al (2016) MiR-142-3p is a RANKL-dependent inducer of cell death in osteoclasts. Sci Rep 6:24980. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24980
Cong F, Wu N, Tian X et al (2017) MicroRNA-34c promotes osteoclast differentiation through targeting LGR4. Gene 610:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.01.028
Shin B, Hrdlicka HC, Delany AM et al (2021) Inhibition of miR-29 activity in the myeloid lineage increases response to calcitonin and trabecular bone volume in mice. Endocrinology. https://doi.org/10.1210/endocr/bqab135
Duan L, Liang Y, Xu X et al (2020) Noncoding RNAs in subchondral bone osteoclast function and their therapeutic potential for osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 22(1):279. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-020-02374-x
Xia TS, Wang GZ, Ding Q et al (2012) Bone metastasis in a novel breast cancer mouse model containing human breast and human bone. Breast Cancer Res Treat 132(2):471–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1496-0
Chiou WF, Huang YL, Liu YW (2014) (+)-Vitisin A inhibits osteoclast differentiation by preventing TRAF6 ubiquitination and TRAF6-TAK1 formation to suppress NFATc1 activation. PLoS One 9(2):e89159. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089159
Chen RS, Zhang XB, Zhu XT et al (2019) LncRNA Bmncr alleviates the progression of osteoporosis by inhibiting RANML-induced osteoclast differentiation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(21):9199–9206. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201911_19411
O’Shea JJ, Plenge R (2012) JAK and STAT signaling molecules in immunoregulation and immune-mediated disease. Immunity 36(4):542–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.014
Zhou S, Dai Q, Huang X et al (2021) STAT3 is critical for skeletal development and bone homeostasis by regulating osteogenesis. Nat Commun 12(1):6891. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27273-w
Salmena L, Carracedo A, Pandolfi PP (2008) Tenets of PTEN tumor suppression. Cell 133(3):403–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.013
Lee ZH, Kim HH (2003) Signal transduction by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B in osteoclasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305(2):211–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00695-8
Feng X (2005) Ranking intracellular signaling in osteoclasts. IUBMB Life 57(6):389–395. https://doi.org/10.1080/15216540500137669
Zhao C, Sun W, Zhang P et al (2015) miR-214 promotes osteoclastogenesis by targeting Pten/PI3k/Akt pathway. RNA Biol 12(3):343–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1017205
Wang C, Sun W, Ling S et al (2019) AAV-Anti-miR-214 prevents collapse of the femoral head in osteonecrosis by regulating osteoblast and osteoclast activities. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 18:841–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.09.030
Wang CG, Wang L, Yang T et al (2020) Pseudogene PTENP1 sponges miR-214 to regulate the expression of PTEN to modulate osteoclast differentiation and attenuate osteoporosis. Cytotherapy 22(8):412–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2020.04.090
Wang S, Liu Z, Wang J et al (2020) miR21 promotes osteoclastogenesis through activation of PI3K/Akt signaling by targeting Pten in RAW2647 cells. Mol Med Rep 21(3):1125–32. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.10938
Zhao Q, Liu C, Xie Y et al (2020) Lung cancer cells derived circulating miR-21 promotes differentiation of monocytes into osteoclasts. Onco Targets Ther 13:2643–2656. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S232876
Davis HM, Pacheco-Costa R, Atkinson EG et al (2017) Disruption of the Cx43/miR21 pathway leads to osteocyte apoptosis and increased osteoclastogenesis with aging. Aging Cell 16(3):551–563. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12586
Yu B, Bai J, Shi J et al (2020) MiR-106b inhibition suppresses inflammatory bone destruction of wear debris-induced periprosthetic osteolysis in rats. J Cell Mol Med 24(13):7490–7503. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15376
Li M, Luo R, Yang W et al (2019) miR-363-3p is activated by MYB and regulates osteoporosis pathogenesis via PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 55(5):376–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-019-00344-5
Lou Z, Peng Z, Wang B et al (2019) miR-142-5p promotes the osteoclast differentiation of bone marrow-derived macrophages via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway. J Bone Miner Metab 37(5):815–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-019-00997-y
Luo T, Zhou X, Jiang E et al (2021) Osteosarcoma cell-derived small extracellular vesicles enhance osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption through transferring MicroRNA-19a-3p. Front Oncol 11:618662. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.618662
Wu K, Feng J, Lyu F et al (2021) Exosomal miR-19a and IBSP cooperate to induce osteolytic bone metastasis of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Nat Commun 12(1):5196. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25473-y
Wang M, Zhao M, Guo Q et al (2021) Non-small cell lung cancer cell-derived exosomal miR-17-5p promotes osteoclast differentiation by targeting PTEN. Exp Cell Res 408(1):112834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112834
Hu CH, Sui BD, Du FY et al (2017) miR-21 deficiency inhibits osteoclast function and prevents bone loss in mice. Sci Rep 7:43191. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43191
Zhou Y, Liu Y, Cheng L (2012) miR-21 expression is related to particle-induced osteolysis pathogenesis. J Orthop Res 30(11):1837–1842. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.22128
Xu Z, Liu X, Wang H et al (2018) Lung adenocarcinoma cell-derived exosomal miR-21 facilitates osteoclastogenesis. Gene 666:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.008
Zhang Y, Tian Y, Yang X et al (2020) MicroRNA21 serves an important role during PAOO facilitated orthodontic tooth movement. Mol Med Rep 22(1):474–482. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11107
Madhyastha R, Madhyastha H, Pengjam Y et al (2019) The pivotal role of microRNA-21 in osteoclastogenesis inhibition by anthracycline glycoside aloin. J Nat Med 73(1):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-1237-3
Tian G, Hu K, Qiu S et al (2021) Exosomes derived from PC-3 cells suppress osteoclast differentiation by downregulating miR-148a and blocking the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Exp Ther Med 22(5):1304. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.10739
Ma Y, Yang H, Huang J (2018) Icariin ameliorates dexamethasoneinduced bone deterioration in an experimental mouse model via activation of microRNA186 inhibition of cathepsin K. Mol Med Rep 17(1):1633–1641. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.8065
Inoue K, Hu X, Zhao B (2020) Regulatory network mediated by RBP-J/NFATc1-miR182 controls inflammatory bone resorption. FASEB J 34(2):2392–2407. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201902227R
Miller CH, Smith SM, Elguindy M et al (2016) RBP-J-regulated miR-182 promotes TNF-alpha-induced osteoclastogenesis. J Immunol 196(12):4977–4986. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1502044
Tian Y, Gong Z, Zhao R et al (2021) Melatonin inhibits RANKL induced osteoclastogenesis through the miR882/Reverbalpha axis in Raw264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med 47(2):633–42. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2020.4820
Wang JZ, Zhao BH (2021) MiR-23b-3p functions as a positive factor for osteoporosis progression by targeting CCND1 in MC3T3-E1 cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 57(3):324–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-021-00544-y
Ghafouri-Fard S, Abak A, Shoorei H et al (2021) Regulatory role of microRNAs on PTEN signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 133:110986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110986
Sugatani T, Alvarez U, Hruska KA (2003) PTEN regulates RANKL- and osteopontin-stimulated signal transduction during osteoclast differentiation and cell motility. J Biol Chem 278(7):5001–5008. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M209299200
Tamura M, Gu J, Matsumoto K et al (1998) Inhibition of cell migration, spreading, and focal adhesions by tumor suppressor PTEN. Science 280(5369):1614–1617. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.280.5369.1614
Holliday LS, McHugh KP, Zuo J et al (2017) Exosomes: novel regulators of bone remodelling and potential therapeutic agents for orthodontics. Orthod Craniofac Res 20(Suppl 1):95–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/ocr.12165
Lu K, Chen Q, Li M et al (2020) Programmed cell death factor 4 (PDCD4), a novel therapy target for metabolic diseases besides cancer. Free Radic Biol Med 159:150–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.06.016
Dorrello NV, Peschiaroli A, Guardavaccaro D et al (2006) S6K1- and betaTRCP-mediated degradation of PDCD4 promotes protein translation and cell growth. Science 314(5798):467–471. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1130276
Sugatani T, Hruska KA (2013) Down-regulation of miR-21 biogenesis by estrogen action contributes to osteoclastic apoptosis. J Cell Biochem 114(6):1217–1222. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24471
Cong C, Tian J, Gao T et al (2020) lncRNA GAS5 is upregulated in osteoporosis and downregulates miR-21 to promote apoptosis of osteoclasts. Clin Interv Aging 15:1163–1169. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S235197
Shao B, Liao L, Yu Y et al (2015) Estrogen preserves Fas ligand levels by inhibiting microRNA-181a in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to maintain bone remodeling balance. FASEB J 29(9):3935–3944. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.15-272823
Li W, Zhu HM, Xu HD et al (2018) CRNDE impacts the proliferation of osteoclast by estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(18):5815–5821. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201809_15907
Kang H, Yang K, Xiao L et al (2017) Osteoblast hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha pathway activation restrains osteoclastogenesis via the interleukin-33-MicroRNA-34a-Notch1 pathway. Front Immunol 8:1312. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01312
Zhang X, Li Z, Zhao Z et al (2021) Runx1/miR-26a/Jagged1 signaling axis controls osteoclastogenesis and alleviates orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption. Int Immunopharmacol 100:107991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107991
Jiang ZY, Jiang JJ, Ma YS et al (2018) Downregulation of miR-223 and miR-19a induces differentiation and promotes recruitment of osteoclast cells in giant-cell tumor of the bone via the Runx2/TWIST-RANK/RANKL pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 505(4):1003–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.10.025
Hegewald AB, Breitwieser K, Ottinger SM et al (2020) Extracellular miR-574-5p induces osteoclast differentiation via TLR 7/8 in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol 11:585282. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.585282
Xie H, Cao L, Ye L et al (2021) The miR-1906 mimic attenuates bone loss in osteoporosis by down-regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathway. Physiol Int 107(4):469–478. https://doi.org/10.1556/2060.2020.00042
Wang WW, Yang L, Wu J et al (2017) The function of miR-218 and miR-618 in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21(24):5534–5541. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201712_13989
Croset M, Pantano F, Kan CWS et al (2018) miRNA-30 family members inhibit breast cancer invasion, osteomimicry, and bone destruction by directly targeting multiple bone metastasis-associated genes. Cancer Res 78(18):5259–5273. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3058
Yang S, Zhang W, Cai M et al (2018) Suppression of bone resorption by miR-141 in aged rhesus monkeys. J Bone Miner Res 33(10):1799–1812. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.3479
Li K, Chen S, Cai P et al (2020) MiRNA-483-5p is involved in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis by promoting osteoclast differentiation. Mol Cell Probes 49:101479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2019.101479
Kim K, Kim JH, Kim I et al (2015) MicroRNA-26a regulates RANKL-induced osteoclast formation. Mol Cells 38(1):75–80. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2015.2241
Yu FY, Xie CQ, Sun JT et al (2018) Overexpressed miR-145 inhibits osteoclastogenesis in RANKL-induced bone marrow-derived macrophages and ovariectomized mice by regulation of Smad3. Life Sci 202:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.03.042
Guo L, Chen K, Yuan J et al (2018) Estrogen inhibits osteoclasts formation and bone resorption via microRNA-27a targeting PPARgamma and APC. J Cell Physiol 234(1):581–594. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26788
Inoue K, Deng Z, Chen Y et al (2018) Bone protection by inhibition of microRNA-182. Nat Commun 9(1):4108. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06446-0
Liu W, Wang P, Xie Z et al (2019) Abnormal inhibition of osteoclastogenesis by mesenchymal stem cells through the miR-4284/CXCL5 axis in ankylosing spondylitis. Cell Death Dis 10(3):188. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1448-x
Jia D, Li Y, Han R et al (2019) miR146a5p expression is upregulated by the CXCR4 antagonist TN14003 and attenuates SDF1induced cartilage degradation. Mol Med Rep 19(5):4388–4400. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10076
Reziwan K, Sun D, Zhang B et al (2019) MicroRNA-1225 activates Keap1-Nrf2-HO-1 signalling to inhibit TNFalpha-induced osteoclastogenesis by mediating ROS generation. Cell Biochem Funct 37(4):256–265. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.3394
Chen X, Ouyang Z, Shen Y et al (2019) CircRNA_28313/miR-195a/CSF1 axis modulates osteoclast differentiation to affect OVX-induced bone absorption in mice. RNA Biol 16(9):1249–1262. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2019.1624470
Guo L, Zhu Y, Li L et al (2019) Breast cancer cell-derived exosomal miR-20a-5p promotes the proliferation and differentiation of osteoclasts by targeting SRCIN1. Cancer Med 8(12):5687–5701. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2454
Yan S, Miao L, Lu Y et al (2019) MicroRNA-506 upregulation contributes to sirtuin 1 inhibition of osteoclastogenesis in bone marrow stromal cells induced by TNF-alpha treatment. Cell Biochem Funct 37(8):598–607. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.3436
Wang H, Shen Y (2019) MicroRNA20a negatively regulates the growth and osteoclastogenesis of THP1 cells by downregulating PPARgamma. Mol Med Rep 20(5):4271–4276. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10676
Zhang Z, Xiang L, Wang Y et al (2020) Effect of diosgenin on the circulating MicroRNA profile of ovariectomized rats. Front Pharmacol 11:207. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00207
Liu S, Wang C, Bai J et al (2021) Involvement of circRNA_0007059 in the regulation of postmenopausal osteoporosis by promoting the microRNA-378/BMP-2 axis. Cell Biol Int 45(2):447–455. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11502
Qiao L, Li CG, Liu D (2020) CircRNA_0048211 protects postmenopausal osteoporosis through targeting miRNA-93-5p to regulate BMP2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(7):3459–3466. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202004_20804
Yu L, Liu Y (2019) circRNA_0016624 could sponge miR-98 to regulate BMP2 expression in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 516(2):546–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.06.087
Mao Z, Zhu Y, Hao W et al (2019) MicroRNA-155 inhibition up-regulates LEPR to inhibit osteoclast activation and bone resorption via activation of AMPK in alendronate-treated osteoporotic mice. IUBMB Life 71(12):1916–1928. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2131
Wang L, He Y, Ning W (2021) Role of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 in osteoclast formation and periodontitis development by downregulating microRNA-101-regulated VCAM-1. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 15(6):534–545. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.3187
Chengling L, Yulin Z, Xiaoyu X et al (2021) miR-325-3p, a novel regulator of osteoclastogenesis in osteolysis of colorectal cancer through targeting S100A4. Mol Med 27(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-021-00282-7
Huang Y, Yang Y, Wang J et al (2021) miR-21-5p targets SKP2 to reduce osteoclastogenesis in a mouse model of osteoporosis. J Biol Chem 296:100617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100617
Jiang H, Kitaura H, Liu L et al (2021) The miR-155-5p inhibits osteoclast differentiation through targeting CXCR2 in orthodontic root resorption. J Periodontal Res 56(4):761–773. https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12875
Guan J, Gan L, Jin D et al (2021) Overexpression of circ_0021739 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis is associated with reduced expression of microRNA-194–5p in osteoclasts. Med Sci Monit 27:e929170. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.929170
Charles JF, Aliprantis AO (2014) Osteoclasts: more than “bone eaters.” Trends Mol Med 20(8):449–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2014.06.001
Yang Y, Fang S (2017) Small non-coding RNAs-based bone regulation and targeting therapeutic strategies. Mol Cell Endocrinol 456:16–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2016.11.018
Vaananen K (2005) Mechanism of osteoclast mediated bone resorption–rationale for the design of new therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57(7):959–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2004.12.018
Taubmann J, Krishnacoumar B, Bohm C et al (2020) Metabolic reprogramming of osteoclasts represents a therapeutic target during the treatment of osteoporosis. Sci Rep 10(1):21020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77892-4
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP (2014) The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 505(7483):344–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12986
Acknowledgements
The figures were created with BioRender.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671021), Science and Technology Foundation of Sichuan Province, China (2022YFS0127).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LJ and XYL wrote the manuscript with feedback from all authors. SSH and SC gave their comments and suggestions to the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors approve the submission of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, L., Li, X., He, S. et al. Regulation of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption by microRNA. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 79, 287 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04298-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04298-y