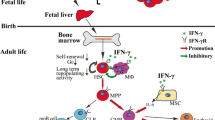
Abstract
Fli-1, a member of the ETS family of transcription factors, was discovered in 1991 through retroviral insertional mutagenesis as a driver of mouse erythroleukemias. In the past 30 years, nearly 2000 papers have defined its biology and impact on normal development and cancer. In the hematopoietic system, Fli-1 controls self-renewal of stem cells and their differentiation into diverse mature blood cells. Fli-1 also controls endothelial survival and vasculogenesis, and high and low levels of Fli-1 are implicated in the auto-immune diseases systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis, respectively. In addition, aberrant Fli-1 expression is observed in, and is essential for, the growth of multiple hematological malignancies and solid cancers. Here, we review the historical context and latest research on Fli-1, focusing on its role in hematopoiesis, immune response, and malignant transformation. The importance of identifying Fli-1 modulators (both agonists and antagonists) and their potential clinical applications is discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- F-MuLV:
-
Friend murine leukemia virus
- SFFV:
-
Spleen focus forming virus
- FV:
-
Friend virus
- Fli-1:
-
Friend virus leukemia integration 1
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
- ETS:
-
E26 transformation-specific
- ATA:
-
Amino-terminal transactivation
- CTA:
-
Carboxy-terminal transactivation
- HSCs:
-
Hematopoietic stem cells
- TME:
-
Tumor microenvironment
- hESCs:
-
Human embryonic stem cells
- TCGA:
-
The cancer genome atlas
- MEP:
-
Megakaryocyte erythroid progenitors
- TPO:
-
Thrombopoietin
- EPO:
-
Erythropoietin
- TPA:
-
Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
- LDBI:
-
LIM domain-binding protein 1
- ChIp:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- WAS:
-
Wiscott Aldrich syndrome
- KLF1:
-
Kruppel-like factor 1
- DN:
-
Double-negative
- DP:
-
Double-positive (DP)
- Treg:
-
Regulatory T
- Teff:
-
Effector T
- CTA:
-
Carboxy-terminal activation
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematous
- NKs:
-
Natural killer cells
- PKCδ:
-
Protein kinase C-delta
References
Friend C (1957) Cell-free transmission in adult Swiss mice of a disease having the character of a leukemia. J Exp Med 105:307–318. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.105.4.307
Howard JC, Yousefi S, Cheong G et al (1993) Temporal order and functional analysis of mutations within the Fli-1 and p53 genes during the erythroleukemias induced by F-MuLV. Oncogene 8:2721–2729
Ben-David Y, Giddens EB, Bernstein A (1990) Identification and mapping of a common proviral integration site Fli-1 in erythroleukemia cells induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1332–1336. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.87.4.1332
Ben-David Y, Giddens EB, Letwin K et al (1991) Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. Genes Dev 5:908–918. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.5.6.908
Truong AH, Ben-David Y (2000) The role of Fli-1 in normal cell function and malignant transformation. Oncogene 19(55):6482–6489. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204042
Ben-David Y, Prideaux VR, Chow V et al (1988) Inactivation of the p53 oncogene by internal deletion or retroviral integration in erythroleukemic cell lines induced by Friend leukemia virus. Oncogene 3:179–185
Delattre O, Zucman J, Plougastel B et al (1992) Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature 359:162–165. https://doi.org/10.1038/359162a0
May WA, Gishizky ML, Lessnick SL et al (1993) Ewing sarcoma 11;22 translocation produces a chimeric transcription factor that requires the DNA-binding domain encoded by FLI1 for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5752–5756. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.12.5752
Im YH, Kim HT, Lee C et al (2000) EWS-FLI1, EWS-ERG, and EWS-ETV1 oncoproteins of Ewing tumor family all suppress transcription of transforming growth factor beta type II receptor gene. Can Res 60:1536–1540
Li Y, Luo H, Liu T et al (2015) The ets transcription factor Fli-1 in development, cancer and disease. Oncogene 34:2022–2031. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.162
Orkin SH, Zon LI (2008) Hematopoiesis: an evolving paradigm for stem cell biology. Cell 132:631–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.025
De Graaf CA, Choi J, Baldwin TM et al (2016) Haemopedia: an expression atlas of murine hematopoietic cells. Stem Cell Rep 7:571–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.07.007
Choi J, Baldwin TM, Wong M et al (2019) Haemopedia RNA-seq: a database of gene expression during haematopoiesis in mice and humans. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D780–D785. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1020
Badwe CR, Lis R, Barcia Durán JG et al (2017) Fli1 is essential for the maintenance of hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis and function. Blood 130:3769. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V130.Suppl_1.3769.3769
Hart A, Melet F, Grossfeld P et al (2000) Fli-1 is required for murine vascular and megakaryocytic development and is hemizygously deleted in patients with thrombocytopenia. Immunity 13:167–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00017-0
Zhao H, Zhao Y, Li Z et al (2018) FLI1 and PKC co-activation promote highly efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into endothelial-like cells. Cell Death Dis 9:131. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0162-9
Liu T, Yao Y, Zhang G et al (2017) A screen for Fli-1 transcriptional modulators identifies PKC agonists that induce erythroid to megakaryocytic differentiation and suppress leukemogenesis. Oncotarget 8:16728–16743. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14377
Kruse EA, Loughran SJ, Baldwin TM et al (2009) Dual requirement for the ETS transcription factors Fli-1 and Erg in hematopoietic stem cells and the megakaryocyte lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13814–13819. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906556106
Ben-David Y, Bernstein A (1991) Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia and the multistage nature of cancer. Cell 66(5):831–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(91)90428-2
Ng AP, Loughran SJ, Metcalf D, Hyland CD, de Graaf CA, Hu Y et al (2011) Erg is required for self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells during stress hematopoiesis in mice. Blood 118(9):2454–2461. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-03-344739
Ma Y, Xu B, Yu J et al (2020) Fli-1 activation through targeted promoter activity regulation using a novel 3′, 5′-diprenylated chalcone inhibits growth and metastasis of prostate cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 21(6):2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062216
Deveaux S, Filipe A, Lemarchandel V et al (1996) Analysis of the thrombopoietin receptor (MPL) promoter implicates GATA and Ets proteins in the coregulation of megakaryocyte-specific genes. Blood 87:4678–4685
Athanasiou M, Clausen PA, Mavrothalassitis GJ et al (1996) Increased expression of the ETS-related transcription factor FLI-1/ERGB correlates with and can induce the megakaryocytic phenotype. Cell Growth Differ 7:1525–1534 (PMID: 8930402)
Bastian LS, Kwiatkowski BA, Breininger J et al (1999) Regulation of the megakaryocytic glycoprotein IX promoter by the oncogenic Ets transcription factor Fli-1. Blood 93:2637–2644 (PMID: 10194443)
Raslova H, Komura E, Le Couedic JP et al (2004) FLI1 monoallelic expression combined with its hemizygous loss underlies Paris-Trousseau/Jacobsen thrombopenia. J Clin Investig 114:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI21197
Stockley J, Morgan NV, Bem D et al (2013) Enrichment of FLI1 and RUNX1 mutations in families with excessive bleeding and platelet dense granule secretion defects. Blood 122:4090–4093. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-06-506873
Krishnamurti L, Neglia JP, Nagarajan R et al (2001) Paris-Trousseau syndrome platelets in a child with Jacobsen’s syndrome. Am J Hematol 66:295–299. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.1061
Klimchenko O, Mori M, Distefano A et al (2009) A common bipotent progenitor generates the erythroid and megakaryocyte lineages in embryonic stem cell-derived primitive hematopoiesis. Blood 114:1506–1517. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-09-178863
Siripin D, Kheolamai P, U-Pratya Y et al (2015) Transdifferentiation of erythroblasts to megakaryocytes using FLI1 and ERG transcription factors. Thromb Haemost 114:593–602. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH14-12-1090
Moreau T, Evans AL, Vasquez L et al (2016) Corrigendum: Large-scale production of megakaryocytes from human pluripotent stem cells by chemically defined forward programming. Nat Commun 8:15076. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11208
Dalby A, Ballester-Beltran J, Lincetto C et al (2018) Transcription factor levels after forward programming of human pluripotent stem cells with GATA1, FLI1, and TAL1 determine megakaryocyte versus erythroid cell fate decision. Stem cell reports 11:1462–1478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.11.001
Huang H, Yu M, Akie TE et al (2009) Differentiation-dependent interactions between RUNX-1 and FLI-1 during megakaryocyte development. Mol Cell Biol 29:4103–4115. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00090-09
Tijssen MR, Cvejic A, Joshi A et al (2011) Genome-wide analysis of simultaneous GATA1/2, RUNX1, FLI1, and SCL binding in megakaryocytes identifies hematopoietic regulators. Dev Cell 20:597–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2011.04.008
Palii CG, Cheng Q, Gillespie MA et al (2019) Single-cell proteomics reveal that quantitative changes in co-expressed lineage-specific transcription factors determine cell fate. Cell Stem Cell 24:812-820.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2019.02.006
Soler E, Andrieu-Soler C, de Boer E et al (2010) The genome-wide dynamics of the binding of Ldb1 complexes during erythroid differentiation. Genes Dev 24(3):277–289. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.551810
Li L, Freudenberg J, Cui K et al (2013) Ldb1-nucleated transcription complexes function as primary mediators of global erythroid gene activation. Blood 121(22):4575–4585. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-01-479451
Giraud G, Kolovos P, Boltsis I et al (2021) Interplay between FLI-1 and the LDB1 complex in murine erythroleukemia cells and during megakaryopoiesis. iScience 24(3):102210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.102210
Shivdasani RA, Rosenblatt MF, Zucker-Franklin D et al (1995) Transcription factor NF-E2 is required for platelet formation independent of the actions of thrombopoietin/MGDF in megakaryocyte development. Cell 81:695–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(95)90531-6
Rost MS, Shestopalov I, Liu Y et al (2018) Nfe2 is dispensable for early but required for adult thrombocyte formation and function in zebrafish. Blood Adv 2:3418–3427. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2018021865
Wang C, Sample KM, Gajendran B, Kapranov P, Liu W, Hu A et al (2021) FLI1 induces megakaryopoiesis gene expression through WAS/WIP-dependent and independent mechanisms; implications for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Front Immunol 12:607836. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.607836
Bosticardo M, Marangoni F, Aiuti A, Villa A, Grazia RM (2009) Recent advances in understanding the pathophysiology of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Blood 113(25):6288–6295. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-12-115253
Pereira R, Quang CT, Lesault I et al (1999) FLI-1 inhibits differentiation and induces proliferation of primary erythroblasts. Oncogene 18:1597–1608. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202534
Tamir A, Howard J, Higgins RR et al (1999) Fli-1, an Ets-related transcription factor, regulates erythropoietin-induced erythroid proliferation and differentiation: evidence for direct transcriptional repression of the Rb gene during differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 19:4452–4464. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.19.6.4452
Minas TZ, Han J, Javaheri T, Hong SH, Schlederer M, Saygideğer-Kont Y et al (2015) YK-4-279 effectively antagonizes EWS-FLI1 induced leukemia in a transgenic mouse model. Oncotarget 6(35):37678–37694. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5520
Spyropoulos DD, Pharr PN, Lavenburg KR et al (2000) Hemorrhage, impaired hematopoiesis, and lethality in mouse embryos carrying a targeted disruption of the Fli1 transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 20:5643–5652. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.20.15.5643-5652.2000
Zhang XK, Moussa O, LaRue A et al (2008) The transcription factor Fli-1 modulates marginal zone and follicular B cell development in mice. J Immunol 181:1644–1654. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.181.3.1644
Zochodne B, Truong AH, Stetler K et al (2000) Epo regulates erythroid proliferation and differentiation through distinct signaling pathways: implication for erythropoiesis and Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia. Oncogene 19:2296–2304. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203590
Starck J, Weiss-Gayet M, Gonnet C et al (2010) Inducible Fli-1 gene deletion in adult mice modifies several myeloid lineage commitment decisions and accelerates proliferation arrest and terminal erythrocytic differentiation. Blood 116:4795–4805. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-02-270405
Athanasiou M, Mavrothalassitis G, Sun-Hoffman L et al (2000) FLI-1 is a suppressor of erythroid differentiation in human hematopoietic cells. Leukemia 14:439–445. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401689
Rekhtman N, Radparvar F, Evans T et al (1999) Direct interaction of hematopoietic transcription factors PU.1 and GATA-1: functional antagonism in erythroid cells. Genes Dev 13:1398–1411. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.13.11.1398
Eisbacher M, Holmes ML, Newton A et al (2003) Protein-protein interaction between Fli-1 and GATA-1 mediates synergistic expression of megakaryocyte-specific genes through cooperative DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol 23:3427–3441. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.23.10.3427-3441.2003
Fujiwara Y, Browne CP, Cunniff K et al (1996) Arrested development of embryonic red cell precursors in mouse embryos lacking transcription factor GATA-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12355–12358. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.22.12355
Jagadeeswaran P, Lin S, Weinstein B et al (2010) Loss of GATA1 and gain of FLI1 expression during thrombocyte maturation. Blood Cells Mol Dis 44:175–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2009.12.012
Frontelo P, Manwani D, Galdass M et al (2007) Novel role for EKLF in megakaryocyte lineage commitment. Blood 110:3871–3880. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-03-082065
Perkins AC, Sharpe AH, Orkin SH (1995) Lethal beta-thalassaemia in mice lacking the erythroid CACCC-transcription factor EKLF. Nature 375:318–322. https://doi.org/10.1038/375318a0
Singleton BK, Burton NM, Green C et al (2008) Mutations in EKLF/KLF1 form the molecular basis of the rare blood group In(Lu) phenotype. Blood 112:2081–2088. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-03-145672
Tallack MR, Perkins AC (2010) Megakaryocyte-erythroid lineage promiscuity in EKLF null mouse blood. Haematologica 95:144–147. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2009.010017
Starck J, Cohet N, Gonnet C et al (2003) Functional cross-antagonism between transcription factors FLI-1 and EKLF. Mol Cell Biol 23:1390–1402. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.23.4.1390-1402.2003
Bouilloux F, Juban G, Cohet N et al (2008) EKLF restricts megakaryocytic differentiation at the benefit of erythrocytic differentiation. Blood 112:576–584. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-07-098996
Svenson JL, Chike-Harris K, Amria MY et al (2010) The mouse and human Fli1 genes are similarly regulated by Ets factors in T cells. Genes Immun 11(2):161–172. https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.73
Melet F, Motro B, Rossi DJ et al (1996) Generation of a novel Fli-1 protein by gene targeting leads to a defect in thymus development and a delay in Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia. Mol Cell Biol 16:2708–2718. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.16.6.2708
Zhang L, Eddy A, Teng YT et al (1995) An immunological renal disease in transgenic mice that overexpress Fli-1, a member of the ets family of transcription factor genes. Mol Cell Biol 15:6961–6970. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.15.12.6961
Smeets MF, Chan AC, Dagger S et al (2013) Fli-1 overexpression in hematopoietic progenitors deregulates T cell development and induces pre-T cell lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma. PLoS ONE 8:e62346. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0062346
Smeets MF, Wiest DL, Izon DJ (2014) Fli-1 regulates the DN2 to DN3 thymocyte transition and promotes gammadelta T-cell commitment by enhancing TCR signal strength. Eur J Immunol 44:2617–2624. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201444442
Chen Z, Arai E, Khan O, Zhang Z, Ngiow SF, He Y et al (2021) In vivo CD8+ T cell CRISPR screening reveals control by Fli1 in infection and cancer. Cell 184(5):1262-1280.e22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.019
Hodge DR, Li D, Qi SM, Farrar WL (2002) IL-6 induces expression of the Fli-1 proto-oncogene via STAT3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 292(1):287–291. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2002.6652
Lennard Richard ML, Nowling TK, Brandon D, Watson DK, Zhang XK (2015) Fli-1 controls transcription from the MCP-1 gene promoter, which may provide a novel mechanism for chemokine and cytokine activation. Mol Immunol 63(2):566–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2014.07.013
Lennard Richard ML, Sato S, Suzuki E, Williams S, Nowling TK, Zhang XK (2014) The Fli-1 transcription factor regulates the expression of CCL5/RANTES. J Immunol 193(6):2661–2668. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1302779
Lennard Richard ML, Brandon D, Lou N, Sato S, Caldwell T, Nowling TK et al (2016) Acetylation impacts Fli-1-driven regulation of granulocyte colony stimulating factor. Eur J Immunol 46(10):2322–2332. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201646315
Lou N, Lennard Richard ML, Yu J, Brandon M, Zhang XK (2017) The Fli-1 transcription factor is a critical regulator for controlling the expression of chemokine C-X-C motif ligand 2 (CXCL2). Mol Immunol 81:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2016.11.007
Li P, Goodwin AJ, Cook JA, Halushka PV, Zhang XK, Fan H (2019) Fli-1 transcription factor regulates the expression of caspase-1 in lung pericytes. Mol Immunol 108:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2019.02.003
Wang X, Lennard Richard M, Li P, Henry B, Schutt S, Yu XZ et al (2021) Expression of GM-CSF is regulated by Fli-1 transcription factor, a potential drug target. J Immunol 206(1):59–66. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.2000664
Wang X, Oates JC, Helke KL, Gilkeson GS, Zhang XK (2021) Camptothecin and topotecan, inhibitors of transcription factor Fli-1 and topoisomerase, markedly ameliorate lupus nephritis in NZBWF1 mice and reduce the production of inflammatory mediators in human renal cells. Arthritis Rheumatol 73(8):1478–1488. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41685
Suzuki E, Williams S, Sato S et al (2013) The transcription factor Fli-1 regulates monocyte, macrophage and dendritic cell development in mice. Immunology 139:318–327. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12070
Masuya M, Moussa O, Abe T et al (2005) Dysregulation of granulocyte, erythrocyte, and NK cell lineages in Fli-1 gene-targeted mice. Blood 105:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-12-4345
Starck J, Mouchiroud G, Gonnet C et al (1999) Unexpected and coordinated expression of Spi-1, Fli-1, and megakaryocytic genes in four Epo-dependent cell lines established from transgenic mice displaying erythroid-specific expression of a thermosensitive SV40 T antigen. Exp Hematol 27:630–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-472x(99)00006-5
Kennedy M, Firpo M, Choi K et al (1997) A common precursor for primitive erythropoiesis and definitive haematopoiesis. Nature 386(6624):488–493. https://doi.org/10.1038/386488a0
Huber TL, Kouskoff V, Fehling HJ et al (2004) Haemangioblast commitment is initiated in the primitive streak of the mouse embryo. Nature 432(7017):625–630. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03122
Iwafuchi-Doi M, Zaret KS (2016) Cell fate control by pioneer transcription factors. Development 143(11):1833–1837. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.133900
Wilson NK, Foster SD, Wang X et al (2010) Combinatorial transcriptional control in blood stem/progenitor cells: genome-wide analysis of ten major transcriptional regulators. Cell Stem Cell 7(4):532–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2010.07.016
Bergiers I, Andrews T, Vargel Bölükbaşı Ö et al (2018) Single-cell transcriptomics reveals a new dynamical function of transcription factors during embryonic hematopoiesis. Elife 7:e29312. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29312
Azimi A, Tuominen R, Costa Svedman F, Caramuta S, Pernemalm M, Frostvik Stolt M et al (2017) Silencing FLI or targeting CD13/ANPEP lead to dephosphorylation of EPHA2, a mediator of BRAF inhibitor resistance, and induce growth arrest or apoptosis in melanoma cells. Cell Death Dis 8(8):e3029. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.406
Paulo P, Barros-Silva JD, Ribeiro FR et al (2012) FLI1 is a novel ETS transcription factor involved in gene fusions in prostate cancer. Genes Chromosom Cancer 51:240–249. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.20948
Golub TR, Barker GF, Bohlander SK, Hiebert SW, Ward DC, Bray-Ward P et al (1995) Fusion of the TEL gene on 12p13 to the AML1 gene on 21q22 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(11):4917–4921. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.11.4917
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW et al (2005) Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science 310(5748):644–648. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1117679
Tomlins SA, Mehra R, Rhodes DR, Smith LR, Roulston D, Helgeson BE et al (2006) TMPRSS2:ETV4 gene fusions define a third molecular subtype of prostate cancer. Cancer Res 66(7):3396–3400. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0168
Helgeson BE, Tomlins SA, Shah N, Laxman B, Cao Q, Prensner JR et al (2008) Characterization of TMPRSS2:ETV5 and SLC45A3:ETV5 gene fusions in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 68(1):73–80. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5352
Rickman DS, Pflueger D, Moss B, VanDoren VE, Chen CX, de la Taille A, Kuefer R, Tewari AK, Setlur SR, Demichelis F, Rubin MA (2009) SLC45A3-ELK4 is a novel and frequent erythroblast transformation-specific fusion transcript in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 69(7):2734–2738. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4926
Bonetti P, Testoni M, Scandurra M, Ponzoni M, Piva R, Mensah AA, Rinaldi A, Kwee I, Tibiletti MG, Iqbal J, Greiner TC, Chan WC et al (2013) Deregulation of ETS1 and FLI1 contributes to the pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 122(13):2233–2241. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-01-475772
Mesquita B, Lopes P, Rodrigues A, Pereira D, Afonso M, Leal C, Henrique R, Lind GE, Jerónimo C, Lothe RA, Teixeira MR (2013) Frequent copy number gains at 1q21 and 1q32 are associated with overexpression of the ETS transcription factors ETV3 and ELF3 in breast cancer irrespective of molecular subtypes. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138(1):37–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2408-2
Zhang J, McCastlain K, Yoshihara H, Xu B, Chang Y, Churchman ML, Wu G, Li Y, Wei L, Iacobucci I et al (2016) Deregulation of DUX4 and ERG in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet 48(12):1481–1489. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3691
Ando M, Kawazu M, Ueno T, Koinuma D, Ando K, Koya J, Kataoka K, Yasuda T, Yamaguchi H, Fukumura K et al (2016) Mutational landscape and antiproliferative functions of ELF transcription factors in human cancer. Cancer Res 76(7):1814–1824. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3816
Lilljebjörn H, Henningsson R, Hyrenius-Wittsten A, Olsson L, Orsmark-Pietras C, von Palffy S, Askmyr M, Rissler M, Schrappe M, Cario G et al (2016) Identification of ETV6-RUNX1-like and DUX4-rearranged subtypes in paediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat Commun 7:11790. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11790
Seki M, Kimura S, Isobe T, Yoshida K, Ueno H, Nakajima-Takagi Y, Wang C, Lin L, Kon A, Suzuki H et al (2017) Recurrent SPI1 (PU.1) fusions in high-risk pediatric T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet 49(8):1274–1281. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3900
Bose R, Karthaus WR, Armenia J, Abida W, Iaquinta PJ, Zhang Z, Wongvipat J, Wasmuth EV, Shah N, Sullivan PS et al (2017) ERF mutations reveal a balance of ETS factors controlling prostate oncogenesis. Nature 546(7660):671–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature22820
Budka JA, Ferris MW, Capone MJ, Hollenhorst PC (2018) Common ELF1 deletion in prostate cancer bolsters oncogenic ETS function, inhibits senescence and promotes docetaxel resistance. Genes Cancer 9(5–6):198–214. https://doi.org/10.18632/genesandck;ancer.182
Luk IY, Reehorst CM, Mariadason JM (2018) ELF3, ELF5, EHF and SPDEF transcription factors in tissue homeostasis and cancer. Molecules 23(9):2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092191
Zaliova M, Potuckova E, Hovorkova L et al (2019) ERG deletions in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia with DUX4 rearrangements are mostly polyclonal, prognostically relevant and their detection rate strongly depends on screening method sensitivity. Haematologica 104(7):1407–1416. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2018.204487
Yuan X, Dai M, Xu D (2020) TERT promoter mutations and GABP transcription factors in carcinogenesis: more foes than friends. Cancer Lett 493:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.07.003
Montgomery-Goecker C, Koduru P, Botten G, Xu J, Ghisoli M, Goldman SC et al (2021) Mixed phenotype acute leukemia, b/myeloid (bilineal and biphenotypic), with t(2;22)(q35;q12);EWSR1-FEV. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 43(3):e388–e394. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPH.0000000000001934
Suico MA, Shuto T, Kai H (2017) Roles and regulations of the ETS transcription factor ELF4/MEF. J Mol Cell Biol 9(3):168–177. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjw051
Erkizan HV, Kong Y, Merchant M et al (2009) A small molecule blocking oncogenic protein EWS-FLI1 interaction with RNA helicase A inhibits growth of Ewing’s sarcoma. Nat Med 15:750–756. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.1983
Grohar PJ, Griffin LB, Yeung C et al (2011) Ecteinascidin 743 interferes with the activity of EWS-FLI1 in Ewing sarcoma cells. Neoplasia (New York, N.Y.) 13:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.101202
Zöllner SK, Amatruda JF, Bauer S et al (2021) Ewing sarcoma-diagnosis, treatment, clinical challenges and future perspectives. J Clin Med 10(8):1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081685
Li YJ, Zhao X, Vecchiarelli-Federico LM et al (2012) Drug-mediated inhibition of Fli-1 for the treatment of leukemia. Blood Cancer J 2:e54. https://doi.org/10.1038/bcj.2011.52
Song J, Yuan C, Yang J et al (2018) Novel flavagline-like compounds with potent Fli-1 inhibitory activity suppress diverse types of leukemia. FEBS J 285:4631–4645. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14690
Liu T, Xia L, Yao Y et al (2019) Identification of diterpenoid compounds that interfere with Fli-1 DNA binding to suppress leukemogenesis. Cell Death Dis 10:117. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1363-1
Hou C, Mandal A, Rohr J, Tsodikov OV (2020) Allosteric interference in oncogenic FLI1 and ERG transactions by mithramycins. Structure 29(5):404-412.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2020.11.012
Rajesh Y, Biswas A, Kumar U, Banerjee I, Das S, Maji S, Das SK, Emdad L, Cavenee WK, Mandal M, Fisher PB (2020) Lumefantrine, an antimalarial drug, reverses radiation and temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117(22):12324–12331. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1921531117
Yao Y, Liu W, Gajendran B, Wang C, Zacksenhaus E, Sample KM, Varier KM, Hao X, Ben-David Y (2021) Ubash3b promotes TPA-mediated suppression of leukemogenesis through accelerated downregulation of PKCδ protein. Biochimie 184:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2021.02.001
Mora-Garcia P, Wei J, Sakamoto KM (2005) G-CSF induces stabilization of ETS protein Fli-1 during myeloid cell development. Pediatr Res 57(1):63–66. https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000147729.55592.2C
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank contribution of Chunlin Wang, Wuling Liu, and Analin Hu in preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by research grants from the Natural National Science Foundation of China (U1812403 and 21867009), the Science and Technology Department of Guizhou Province innovation and project grants (QKHPTRC[2019]5627), and the 100 Leading Talents of Guizhou Province to Y.B.-D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to writing this paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-David, Y., Gajendran, B., Sample, K.M. et al. Current insights into the role of Fli-1 in hematopoiesis and malignant transformation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 79, 163 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04160-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04160-1