Abstract
Objective
Nafamostat mesilate (NM), a synthetic broad-spectrum serine protease inhibitor, has been commonly used for treating acute pancreatitis (AP) and other inflammatory-associated diseases in some East Asia countries. Although the potent inhibitory activity against inflammation-related proteases (such as thrombin, trypsin, kallikrein, plasmin, coagulation factors, and complement factors) is generally believed to be responsible for the anti-inflammatory effects of NM, the precise target and molecular mechanism underlying its anti-inflammatory activity in AP treatment remain largely unknown.
Methods
The protection of NM against pancreatic injury and inhibitory effect on the NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation were investigated in an experimental mouse model of AP. To decipher the molecular mechanism of NM, the effects of NM on nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activity and NF-κB mediated NLRP3 inflammasome priming were examined in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-primed THP-1 cells. Additionally, the potential of NM to block the activity of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) and disrupt the association between HDAC6 and NLRP3 was also evaluated.
Results
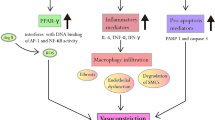
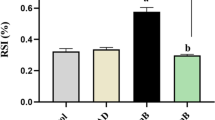
NM significantly suppressed NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the pancreas, leading to a reduction in pancreatic inflammation and prevention of pancreatic injury during AP. NM was found to interact with HDAC6 and effectively inhibit its function. This property allowed NM to influence HDAC6-dependent NF-κB transcriptional activity, thereby blocking NF-κB-driven transcriptional priming of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Furthermore, NM exhibited the potential to interfere the association between HDAC6 and NLRP3, impeding HDAC6-mediated intracellular transport of NLRP3 and ultimately preventing NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Conclusions
Our current work has provided valuable insight into the molecular mechanism underlying the immunomodulatory effect of NM in the treatment of AP, highlighting its promising application in the prevention of NLRP3 inflammasome-associated inflammatory pathological damage.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Becker V. Pathological anatomy and pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. World J Surg. 1981;5:303–13.
Liu R, Qi H, Wang J, Wang Y, Cui L, Wen Y, et al. Ulinastatin activates the renin-angiotensin system to ameliorate the pathophysiology of severe acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29:1328–37.
Ruud TE, Aasen AO, Stadaas JO, Aune S. Effects on peritoneal proteolysis and hemodynamics of prophylactic and therapeutic infusions of high doses of aprotinin in experimental acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986;21:1011–7.
Wisner JR Jr, Ozawa S, Renner IG. The effects of nafamostat mesilate (FUT-175) on caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in the rat. Int J Pancreatol. 1989;4:383–90.
Wisner JR Jr, Renner IG, Grendell JH, Niederau C, Ferrell LD. Gabexate mesilate (FOY) protects against ceruletide-induced acute pancreatitis in the rat. Pancreas. 1987;2:181–6.
Chen CC, Wang SS, Lee FY. Action of antiproteases on the inflammatory response in acute pancreatitis. JOP. 2007;8:488–94.
Sundaram S, Gikakis N, Hack CE, Niewiarowski S, Edmunds LH Jr, Koneti Rao A, et al. Nafamostat mesilate, a broad spectrum protease inhibitor, modulates platelet, neutrophil and contact activation in simulated extracorporeal circulation. Thromb Haemost. 1996;75:76–82.
Duan HQ, Wu QL, Yao X, Fan BY, Shi HY, Zhao CX, et al. Nafamostat mesilate attenuates inflammation and apoptosis and promotes locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018;24:429–38.
Yates AG, Weglinski CM, Ying Y, Dunstan IK, Strekalova T, Anthony DC. Nafamostat reduces systemic inflammation in TLR7-mediated virus-like illness. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19:8.
Hoque R, Sohail M, Malik A, Sarwar S, Luo Y, Shah A, et al. TLR9 and the NLRP3 inflammasome link acinar cell death with inflammation in acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:358–69.
Mangan MSJ, Olhava EJ, Roush WR, Seidel HM, Glick GD, Latz E. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17:588–606.
Luo ZL, Sun HY, Wu XB, Cheng L, Ren JD. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates acute pancreatitis induced lung injury by targeting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species triggered NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Food Funct. 2021;12:5658–67.
Pan X, Fang X, Wang F, Li H, Niu W, Liang W, et al. Butyrate ameliorates caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis and associated intestinal injury by tissue-specific mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol. 2019;176:4446–61.
Ren JD, Ma J, Hou J, Xiao WJ, Jin WH, Wu J, et al. Hydrogen-rich saline inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and attenuates experimental acute pancreatitis in mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014: 930894.
Wang L, Wang N, Shi G, Sun S. Follistatin-like 1 ameliorates severe acute pancreatitis associated lung injury via inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-kappaB pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14:4310–20.
Li C, Wang J, Fang Y, Liu Y, Chen T, Sun H, et al. Nafamostat mesilate improves function recovery after stroke by inhibiting neuroinflammation in rats. Brain Behav Immun. 2016;56:230–45.
Lin Y, Xu D, Gao F, Zheng X. Ulinastatin inhibits NLRP3-induced apoptosis in a PD cell model. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9:924.
Liu Z, Zhu X, Xu C, Min F, Yu G, Chen C. Ulinastatin ameliorates the malignant progression of prostate cancer cells by blocking the RhoA/ROCK/NLRP3 pathway. Drug Dev Res. 2023;84:36–44.
Qiu J, Xiao X, Gao X, Zhang Y. Ulinastatin protects against sepsis‑induced myocardial injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mol Med Rep 2021; 24.
Schmidt J, Rattner DW, Lewandrowski K, Compton CC, Mandavilli U, Knoefel WT, et al. A better model of acute pancreatitis for evaluating therapy. Ann Surg. 1992;215:44–56.
Bauernfeind FG, Horvath G, Stutz A, Alnemri ES, MacDonald K, Speert D, et al. Cutting edge: NF-kappaB activating pattern recognition and cytokine receptors license NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating NLRP3 expression. J Immunol. 2009;183:787–91.
Noguchi S, Nakatsuka M, Konishi H, Kamada Y, Chekir C, Kudo T. Nafamostat mesilate suppresses NF-kappaB activation and NO overproduction in LPS-treated macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 2003;3:1335–44.
Xu S, Chen H, Ni H, Dai Q. Targeting HDAC6 attenuates nicotine-induced macrophage pyroptosis via NF-kappaB/NLRP3 pathway. Atherosclerosis. 2021;317:1–9.
Yang Q, Li S, Zhou Z, Fu M, Yang X, Hao K, et al. HDAC6 inhibitor Cay10603 inhibits high glucose-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in retinal pigment epithelial cells via regulating NF-kappaB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2020;39:169–77.
Magupalli VG, Negro R, Tian Y, Hauenstein AV, Di Caprio G, Skillern W, et al. HDAC6 mediates an aggresome-like mechanism for NLRP3 and pyrin inflammasome activation. Science 2020; 369.
Hsu CW, Shou D, Huang R, Khuc T, Dai S, Zheng W, et al. Identification of HDAC Inhibitors Using a Cell-Based HDAC I/II Assay. J Biomol Screen. 2016;21:643–52.
Chang P, Li H, Hu H, Li Y, Wang T. The Role of HDAC6 in Autophagy and NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 763831.
Moreno-Gonzalo O, Ramirez-Huesca M, Blas-Rus N, Cibrian D, Saiz ML, Jorge I, et al. HDAC6 controls innate immune and autophagy responses to TLR-mediated signalling by the intracellular bacteria Listeria monocytogenes. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13: e1006799.
Liu L, Zhou X, Shetty S, Hou G, Wang Q, Fu J. HDAC6 inhibition blocks inflammatory signaling and caspase-1 activation in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019;370:178–83.
Youn GS, Lee KW, Choi SY, Park J. Overexpression of HDAC6 induces pro-inflammatory responses by regulating ROS-MAPK-NF-kappaB/AP-1 signaling pathways in macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;97:14–23.
Chen Q, Wang Y, Jiao F, Cao P, Shi C, Pei M, et al. HDAC6 inhibitor ACY1215 inhibits the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in acute liver failure by regulating the ATM/F-actin signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:7218–28.
Wang Y, Li X, Chen Q, Jiao F, Shi C, Pei M, et al. Histone Deacetylase 6 Regulates the Activation of M1 Macrophages by the Glycolytic Pathway During Acute Liver Failure. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:1473–85.
Yan S, Wei X, Jian W, Qin Y, Liu J, Zhu S, et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of HDAC6 Attenuates NLRP3 Inflammatory Response and Protects Dopaminergic Neurons in Experimental Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020;12:78.
Piippo N, Korhonen E, Hytti M, Skottman H, Kinnunen K, Josifovska N, et al. Hsp90 inhibition as a means to inhibit activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Sci Rep. 2018;8:6720.
Kovacs JJ, Murphy PJ, Gaillard S, Zhao X, Wu JT, Nicchitta CV, et al. HDAC6 regulates Hsp90 acetylation and chaperone-dependent activation of glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell. 2005;18:601–7.
Aoyagi S, Archer TK. Modulating molecular chaperone Hsp90 functions through reversible acetylation. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:565–7.
Hou Q, Kan S, Wang Z, Shi J, Zeng C, Yang D, et al. Inhibition of HDAC6 With CAY10603 Ameliorates Diabetic Kidney Disease by Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 938391.
Xu J, Zhao X, Jiang X, He L, Wu X, Wang J, et al. Tubastatin A Improves Post-Resuscitation Myocardial Dysfunction by Inhibiting NLRP3-Mediated Pyroptosis Through Enhancing Transcription Factor EB Signaling. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022;11: e024205.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82170660; 81570582) and Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province of China (No. 2022NSFSC0825).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J-DR secured the funding for the study. PC, L-JZ, and J-DR designed the experiments. PC, L-JZ, LH, W-QH, and Y-RT performed experiments and analyzed data. YL provided technical assistance in the experiments and revised the manuscript. J-DR drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The animal care and experimental protocols were approved by IACUC of the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, in accordance with NIH guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Zhao, LJ., Huang, L. et al. Nafamostat mesilate prevented caerulein-induced pancreatic injury by targeting HDAC6-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Inflamm. Res. 72, 1919–1932 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-023-01794-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-023-01794-0