Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to evaluate glycolysis inhibitor which can effectively ameliorate arthritis by inhibiting synoviocyte activation through AMPK/NF-кB pathway in AA rats.
Methods
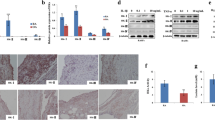
Adjuvant arthritis (AA) rats were treated with 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG), glycolysis inhibitor. HE staining and radiological Examination were used for histopathology analysis and evaluation of joint destruction. HKII expression was quantified by immunostaining. Proliferation and migration of synoviocytes were assessed by synovicyte scores of joint, CCK8 and transwell assay. Inflammatory factors and levels of AMPK, p65 and IκBα were quantified by ELISA analysis and WB.
Results
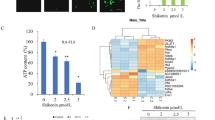
We observed that HKII expression was positively correlated with synovial hyperplasia, inflammatory cell infiltration, and cartilage destruction, and glycolysis inhibitor reduces the joint swelling degree, alleviates bone destruction, inhibits the proliferation and migration of synoviocyte, and reduces secretory function of synoviocytes in AA rats. In addition, we investigated that glycolysis inhibitor may inhibit activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway by activating the AMPK pathway.
Conclusion
This study suggests the involvement of energy metabolism in the pathological inflammation process in RA joints. Glycolysis inhibitors might, therefore, provide an opportunity for therapeutic intervention.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aletaha D, Smolen JS. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review. JAMA. 2018;320:1360–72.
Chen Z, Bozec A, Ramming A, Schett G. Anti-inflammatory and immune-regulatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15:9–17.
Garcia-Carbonell R, Divakaruni AS, Lodi A, Vicente-Suarez I, Saha A, Cheroutre H, et al. Critical role of glucose metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:1614–26.
McGarry T, Orr C, Wade S, Biniecka M, Wade S, Gallagher L, et al. JAK/STAT blockade alters synovial bioenergetics, mitochondrial function, and proinflammatory mediators in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70:1959–70.
Bustamante MF, Oliveira PG, Garcia-Carbonell R, Croft AP, Smith JM, Serrano RL, et al. Hexokinase 2 as a novel selective metabolic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:1636–43.
Korshunov DA, Klimov IA, Ivanov VV, Kondakova IV. Glycolysis Inhibitors monoiodoacetate and 2-deoxyglucose as antitumor agents: experimental study on lewis lung carcinoma model. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2018;165:695–7.
Schutt KL, Moseley JB. Transient activation of fission yeast AMPK is required for cell proliferation during osmotic stress. Mol Biol Cell. 2017;28:1804–14.
Noort AR, Tak PP, Tas SW. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling in rheumatoid arthritis: Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:15.
Taniguchi K, Karin M. NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18:309–24.
Chang Y, Wu Y, Wang D, Wei W, Qin Q, Xie G, et al. Therapeutic effects of TACI-Ig on rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis via attenuating inflammatory responses. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011;50:862–70.
Zhou J, Yu Y, Yang X, Wang Y, Song Y, Wang Q, et al. Berberine attenuates arthritis in adjuvant-induced arthritic rats associated with regulating polarization of macrophages through AMPK/NF-кB pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;852:179–88.
Liu Y, Zhang L, Wu Y, Tong T, Zhao W, Li P, et al. Therapeutic effects of TACI-Ig on collagen-induced arthritis by regulating T and B lymphocytes function in DBA/1 mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;654:304–14.
Zheng YQ, Wei W. Total glucosides of paeony suppresses adjuvant arthritis in rats and intervenes cytokine-signaling between different types of synoviocytes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2005;5:1560–73.
Bartok B, Firestein GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010;233:233–55.
Bordy R, Totoson P, Prati C, Marie C, Wendling D, Demougeot C. Microvascular endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018;14:404–20.
Fearon U, Canavan M, Biniecka M, Veale DJ. Hypoxia, mitochondrial dysfunction and synovial invasiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:385–97.
Biniecka M, Canavan M, McGarry T, Gao W, McCormick J, Cregan S, et al. Dysregulated bioenergetics: a key regulator of joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75:2192–200.
Bustamante MF, Garcia-Carbonell R, Whisenant KD, Guma M. Fibroblast-like synoviocyte metabolism in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19:110.
Tran CN, Davis MJ, Tesmer LA, Endres JL, Motyl CD, Smuda C, et al. Presentation of arthritogenic peptide to antigen-specific T cells by fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2007;56:1497–506.
Arend WP, Firestein GS. Pre-rheumatoid arthritis: predisposition and transition to clinical synovitis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8:573–86.
Ganesan R, Rasool M. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes-dependent effector molecules as a critical mediator for rheumatoid arthritis: Current status and future directions. Int Rev Immunol. 2017;36:20–30.
Choo YY, Tran PT, Min BS, Kim O, Nguyen HD, Kwon SH, et al. Sappanone A inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in BMMs and prevents inflammation-mediated bone loss. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;52:230–7.
Wen H, Liu Y, Li J, Wei D, Liu D, Zhao F. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 on RANKL expression in fibroblast-like synoviocytes and osteoclast-like cell formation induced by IL-22 in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018;36:798–805.
Sun L, Liu X, Fu H, Zhou W, Zhong D. 2-Deoxyglucose suppresses ERK phosphorylation in LKB1 and Ras wild-type non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0168793.
Zhao J, Ma Y, Zhang Y, Fu B, Wu X, Li Q, et al. Low-dose 2-deoxyglucose and metformin synergically inhibit proliferation of human polycystic kidney cells by modulating glucose metabolism. Cell Death Discov. 2019;5:76.
Xia ZB, Meng FR, Fang YX, Wu X, Zhang CW, Liu Y, et al. Inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation and angiogenesis of human fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e10920.
Tsubaki M, Takeda T, Tomonari Y, Koumoto YI, Imano M, Satou T, et al. Overexpression of HIF-1α contributes to melphalan resistance in multiple myeloma cells by activation of ERK1/2, Akt, and NF-κB. Lab Investig. 2019;99:72–84.
Liu G, Bi Y, Shen B, Yang H, Zhang Y, Wang X, et al. SIRT1 limits the function and fate of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumors by orchestrating HIF-1α-dependent glycolysis. Cancer Res. 2014;74:727–37.
Jin R, Yamashita H, Yu X, Wang J, Franco OE, Wang Y, et al. Inhibition of NF-kappa B signaling restores responsiveness of castrate-resistant prostate cancer cells to anti-androgen treatment by decreasing androgen receptor-variant expression. Oncogene. 2015;34:3700–10.
Zhu H, Chai Y, Dong D, Zhang N, Liu W, Ma T, et al. AICAR-induced AMPK activation inhibits the noncanonical NF-κB pathway to attenuate liver injury and fibrosis in BDL rats. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;2018:6181432.
Xiang HC, Lin LX, Hu XF, Zhu H, Li HP, Zhang RY, et al. AMPK activation attenuates inflammatory pain through inhibiting NF-κB activation and IL-1β expression. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16:34.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81903619, 81703529), Natural Science Research Key Project of Anhui Provincial Education Department (KJ2019A0304, KJ2018A0231), Anhui Province Natural Science Fund (1908085MH292), and the Science Fund of Bengbu Medical College (BYKC201904, BYYCX1812, BYKY1806ZD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors certify that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Xian, H., Qi, J. et al. Inhibition of glycolysis ameliorate arthritis in adjuvant arthritis rats by inhibiting synoviocyte activation through AMPK/NF-кB pathway. Inflamm. Res. 69, 569–578 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-020-01332-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-020-01332-2