Abstract
Objective
Polymorphisms in ADAM33 gene have been implicated in susceptibility to the risk of childhood asthma. However, the results remain controversial. We performed meta-analyses to clarify the relationship between them.
Methods
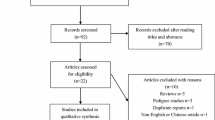
Relevant articles were searched in PubMed, Embase, Wanfang, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure. The Odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) was used to assess the strength of the associations.
Results
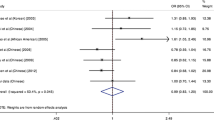
Fourteen studies with five ADAM33 polymorphisms (F + 1, T1, T2, S2, and V4) were identified, involving 2687 cases and 2996 controls. ADAM33 F + 1, T2, and T1 polymorphisms showed significant associations with asthma risks in the overall and Caucasian children, Asian children, and Caucasian and Chinese children, respectively; however, these significant results were unstable in sensitivity analysis. T1 revealed significant and stable associations with asthma risks among Asian children in the dominant (OR = 2.00, 95% CI = 1.40–2.87, P = 0.0002) and codominant (OR = 3.06, 95% CI = 1.71–5.50, P = 0.0002) models; in cumulative meta-analyses, these significant results were robust. Concerning S2 or V4 polymorphism, no significant associations were observed.
Conclusion
These findings demonstrate that ADAM33 T1 polymorphism might be a potential susceptible predictor of asthma for Asian children. Further functional studies between this polymorphism and asthma risks are warranted.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Y, Wicks J, Haitchi HM, Powell RM, Manuyakorn W, Howarth PH, et al. Regulation of a disintegrin and metalloprotease-33 expression by transforming growth factor-beta. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012;46(5):633–40.
Grotenboer NS, Ketelaar ME, Koppelman GH, Nawijn MC. Decoding asthma: translating genetic variation in IL33 and IL1RL1 into disease pathophysiology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131(3):856–65.
Pinto LA, Stein RT, Kabesch M. Impact of genetics in childhood asthma. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2008;84(4 Suppl):S68–75.
Ortiz RA, Barnes KC. Genetics of allergic diseases. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2015;35(1):19–44.
Van Eerdewegh P, Little RD, Dupuis J, Del Mastro RG, Falls K, Simon J, et al. Association of the ADAM33 gene with asthma and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Nature. 2002;418(6896):426–30.
Jie Z, Jin M, Cai Y, Bai C, Shen Y, Yuan Z, et al. The effects of Th2 cytokines on the expression of ADAM33 in allergen-induced chronic airway inflammation. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009;168(3):289–94.
Lee JY, Park SW, Chang HK, Kim HY, Rhim T, Lee JH, et al. A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 33 protein in patients with asthma: relevance to airflow limitation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173(7):729–35.
Foley SC, Mogas AK, Olivenstein R, Fiset PO, Chakir J, Bourbeau J, et al. Increased expression of ADAM33 and ADAM8 with disease progression in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119(4):863–71.
Ito I, Laporte JD, Fiset PO, Asai K, Yamauchi Y, Martin JG, et al. Downregulation of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 33 by IFN-gamma in human airway smooth muscle cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119(1):89–97.
Kavvoura FK, Ioannidis JP. Methods for meta-analysis in genetic association studies: a review of their potential and pitfalls. Hum Genet. 2008;123(1):1–14.
Blakey J, Halapi E, Bjornsdottir US, Wheatley A, Kristinsson S, Upmanyu R, et al. Contribution of ADAM33 polymorphisms to the population risk of asthma. Thorax. 2005;60(4):274–6.
Lee YH, Song GG. Association between ADAM33 T1 polymorphism and susceptibility to asthma in Asians. Inflamm Res. 2012;61(12):1355–62.
Song GG, Kim JH, Lee YH. Association between ADAM33 S2 and ST+ 4 polymorphisms and susceptibility to asthma: a meta-analysis. Gene. 2013;524(1):72–8.
Zheng W, Wang L, Su X, Hu XF. Association between V4 polymorphism in the ADAM33 gene and asthma risk: a meta-analysis. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(1):989–99.
Liu Y, Wang ZH, Zhen W, Lu SJ, Liu Z, Zou LY, et al. Association between genetic polymorphisms in the ADAM33 gene and asthma risk: a meta-analysis. DNA Cell Biol. 2014;33(11):793–801.
Liang S, Wei X, Gong C, Wei J, Chen Z, Deng J. A disintegrin and metalloprotease 33 (ADAM33) gene polymorphisms and the risk of asthma: a meta-analysis. Hum Immunol. 2013;74(5):648–57.
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Xiao Y, Huang J, Tian C, et al. Asthma susceptible genes in Chinese population: a meta-analysis. Respir Res. 2010;11:129.
Bora E, Arikan-Ayyildiz Z, Firinci F, Cankaya T, Giray-Bozkaya O, Uzuner N, et al. ADAM33 gene polymorphisms are not associated with asthma in turkish children. Ped Allergy Immunol Pulmonol. 2012;25(2):97–100.
Murk W, Walsh K, Hsu LI, Zhao L, Bracken MB, Dewan AT. Attempted replication of 50 reported asthma risk genes identifies a SNP in RAD50 as associated with childhood atopic asthma. Hum Hered. 2011;71(2):97–105.
Al-Khayyat AI, Al-Anazi M, Warsy A, Vazquez-Tello A, Alamri AM, Halwani R, et al. T1 and T2 ADAM33 single nucleotide polymorphisms and the risk of childhood asthma in a Saudi Arabian population: a pilot study. Ann Saudi Med. 2012;32(5):479–86.
El-Falaki MM, Wilson MM, Ezzat GM, Mokhtar DA, El Baz MS, Hamed DH. A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 33 (ADAM33) gene polymorphism association with asthma in Egyptian children. Egypt J Med Hum Genet. 2013;14(1):55–62.
Li H, Li Y, Zhang M, Xu G, Feng X, Xi J, et al. Associations of genetic variants in ADAM33 and TGF-beta1 genes with childhood asthma risk. Biomed Rep. 2014;2(4):533–8.
Fan JG, Wang ZA, Zhao HX. The ADAM33 S2 polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to pediatric asthma in the Chinese Han population. Genet Test Mol. Biomarkers. 2015;19(10):573–8.
Shalaby SM, Abdul-Maksoud RS, Abdelsalam SM, Abdelrahman HM, Abdelaziz Almalky MA. ADAM33 and ADAM12 genetic polymorphisms and their expression in Egyptian children with asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016;116(1):31–6.
Zihlif M, Zihlif N, Obeidat NM, Mahafza T, Froukh T, Ghanim MT, et al. Association between ADAM33 polymorphisms and susceptibility with adult and childhood asthma among Jordanians. Genet Test Mol Biomark. 2014;18(11):767–74.
Lau J, Antman EM, Jimenez-Silva J, Kupelnick B, Mosteller F, Chalmers TC. Cumulative meta-analysis of therapeutic trials for myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1992;327(4):248–54.
Rotondi MA, Bull SB. Cumulative meta-analysis for genetic association: when is a new study worthwhile? Hum Hered. 2012;74(2):61–70.
Zintzaras E, Lau J. Synthesis of genetic association studies for pertinent gene-disease associations requires appropriate methodological and statistical approaches. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(7):634–45.
Zhang J, Zeng XT, Lei JR, Tang YJ, Yang J. No association between XRCC1 gene Arg194Trp polymorphism and risk of lung cancer: evidence based on an updated cumulative meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(6):5629–35.
Mullen B, Muellerleile P, Bryant B. Cumulative meta-analysis: a consideration of indicators of sufficiency and stability. Personal Soc Psychol Bull. 2001;27(11):1450–62.
Awasthi S, Tripathi P, Ganesh S, Husain N. Association of ADAM33 gene polymorphisms with asthma in Indian children. J Hum Genet. 2011;56(3):188–95.
Qu S, Sun D, Wang Y, Zhang C, Lv Y, Yao L. Association of ADAM33 polymorphisms with childhood asthma in a northern Chinese population. Exp Mol Pathol. 2011;91(3):775–9.
Yu HC, Chen GQ, Li YQ, Wang LJ, Jiang CS, Meng LS. Association of T1 polymorphism in disintegrin and metalloprotease 33 gene with asthma. J Clin Pediatr. 2011; 29 (9):852–855 (in Chinese).
Xiong JY, He QQ, Jiang ZQ, Li JF. Association of polymorphism of T1 locus allele in ADAM33 gene with bronchial asthma. J Appl Clin Pediatr. 2009;24(16):1241–3. (Chinese).
Godava M, Kopriva F, Bohmova J, Vodicka R, Dusek L, Cvanova M, et al. Association of STAT6 and ADAM33 single nucleotide polymorphisms with asthma bronchiale and IgE level and its possible epigenetic background. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2012;156(3):236–47.
Schedel M, Depner M, Schoen C, Weiland SK, Vogelberg C, Niggemann B, et al. The role of polymorphisms in ADAM33, a disintegrin and metalloprotease 33, in childhood asthma and lung function in two German populations. Respir Res. 2006;7:91.
Puxeddu I, Pang YY, Harvey A, Haitchi HM, Nicholas B, Yoshisue H, et al. The soluble form of a disintegrin and metalloprotease 33 promotes angiogenesis: implications for airway remodeling in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;1400–1406(6):1406.e1401-1404.
Simpson A, Maniatis N, Jury F, Cakebread JA, Lowe LA, Holgate ST, et al. Polymorphisms in a disintegrin and metalloprotease 33 (ADAM33) predict impaired early-life lung function. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172(1):55–60.
Reijmerink NE, Kerkhof M, Koppelman GH, Gerritsen J, de Jongste JC, Smit HA, et al. Smoke exposure interacts with ADAM33 polymorphisms in the development of lung function and hyperresponsiveness. Allergy. 2009;64(6):898–904.
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Huang J, Li X, He C, Tian C, et al. Polymorphisms in the transforming growth factor-beta1 gene and the risk of asthma: a meta-analysis. Respirology. 2010;15(4):643–50.
Wang X, Li W, Huang K, Kang X, Li Z, Yang C, et al. Genetic variants in ADAM33 are associated with airway inflammation and lung function in COPD. BMC Pulm Med. 2014;14:173.
Tripathi P, Awasthi S, Gao P. ADAM metallopeptidase domain 33 (ADAM33): a promising target for asthma. Mediat Inflamm. 2014;2014:572025.
Bukvic BK, Blekic M, Simpson A, Marinho S, Curtin JA, Hankinson J, et al. Asthma severity, polymorphisms in 20p13 and their interaction with tobacco smoke exposure. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2013;24(1):10–8.
Chiang CH, Lin MW, Chung MY, Yang UC. The association between the IL-4, ADRβ2 and ADAM 33 gene polymorphisms and asthma in the Taiwanese population. J Chin Med Assoc. 2012;75(12):635–43.
Zheng XY, Guan WJ, Mao C, Chen HF, Ding H, Zheng JP, et al. Interleukin-10 promoter 1082/-819/-592 polymorphisms are associated with asthma susceptibility in Asians and atopic asthma: a meta-analysis. Lung. 2014;192(1):65–73.
Acknowledgements
This research received no specific grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, R., Zhao, F. & Zhong, X. T1 polymorphism in a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 33 (ADAM33) gene may contribute to the risk of childhood asthma in Asians. Inflamm. Res. 66, 413–424 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-017-1024-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-017-1024-8