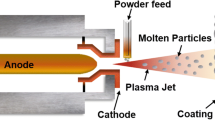
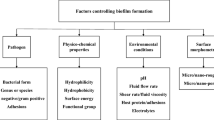
Abstract
Biomaterials refer to materials used in direct interaction with biological systems. Biocompatible and surface-modifiable metallic, polymeric, and ceramic biomaterials are currently used in various applications, allowing for adjustments to improve their performance while maintaining their bulk properties. Surface modification is done to enhance biocompatibility and come into contact as a bioactive substance for certain applications, such as protein surface modification on ceramics, polymers, metals, and composites. Surface modification techniques include calcium phosphate deposition, covalent binding of poly (ethylene glycol) and poly (heparin), and plasma polymerization. Analyzing the surface chemistry, structure, morphology, and topography of biomaterials is crucial in surface modification to improve interactions with blood, fight infection, interact with soft tissues, repair and regenerate nerve cells, manage stem cell growth and differentiation, and interact better with bone. Biomedical devices that can replace or repair damaged tissues and organs depend heavily on the usage of substances that can interact with people's bodies without triggering negative reactions. Although joint replacement surgery is a standard procedure, the inserted biomaterial may not last for a long time. Factors such as unfavorable immune system responses, the development of biofilms, or issues with the implants’ fabrication, biocompatibility, manufacturing processes, and their mechanical, chemical, or tri-biological processes may lead to their failure. Altering the surface of biomaterials can prevent these failures and improve the way the body responds to their implantation. Thus, the current chapter aims to show novel methodologies and applications of surface-modified biomaterials in the development of medical devices. It suggests novel studies on extending the lifespan of medical equipment and biomaterials.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CVD:
-
Chemical vapor deposition
- EPD:
-
Electrophoretic Deposition
- Co-Cr:
-
Cobalt-Chromium
- MRI:
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- CT:
-
Computer Tomography
- UHMWPE:
-
Ultra-High Molecular Polyethylene
- DDS:
-
Drug Delivery System
- PEG/PEO:
-
Polyethylene glycol/oxide
- PLA:
-
Polylactic acid
- PGA:
-
Polyglycolic acid
- TMC:
-
Tri-Methyl Carbonate
- PDS:
-
Polydioxanone
- PE:
-
Polyethylene
- PA:
-
Polyamide
- PMMA:
-
Polymethyl methacrylate
- PU:
-
Polyurethane
- PET:
-
Polyethylene terephthalate
- SR:
-
Synthetic Rubber
- PTFE:
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene
- PS:
-
Polystyrene
- PLA:
-
Polylactic acid
- PGA:
-
Polyglycolide
References
Patel, N.R., Gohil, P.P.: A review on biomaterials: scope, applications & human anatomy significance. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2(4), 91–101 (2012)
Ratner, B.D., Hoffman, A.S., Schoen, F.J., Lemons, J.E.: Biomaterials Science: An Introduction to Materials in Medicine. Elsevier (2004)
Kulinets, I.: Biomaterials and their applications in medicine. In: Regulatory Affairs for Biomaterials and Medical Devices, pp. 1–10. Woodhead Publishing (2015)
Martin, J.L., Norris, B.J., Murphy, E., Crowe, J.A.: Medical device development: the challenge for ergonomics. Appl. Ergon. 39(3), 271–283 (2008)
Madalina Mihai, M., Maria Holban, A., Giurcaneanu, C., Gabriela Popa, L., Mihaela Oanea, R., Lazar, V., Carmen Chifiriuc, M., Popa, M., Ioan, P.M.: Microbial biofilms: impact on the pathogenesis of periodontitis, cystic fibrosis, chronic wounds and medical device-related infections. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 15(16), 1552–1576 (2015)
Agarwal, R., García, A.J.: Surface modification of biomaterials. In: Principles of Regenerative Medicine, pp. 651–660). cademic Press (2019)
Fabbri, P., Messori, M.: Surface modification of polymers: chemical, physical, and biological routes. In: Modification of Polymer Properties, pp. 109–130. William Andrew Publishing (2017)
Merola, M., Affatato, S.: Materials for hip prostheses: a review of wear and loading considerations. Materials 12(3), 495 (2019)
Abraham, A.M., Venkatesan, S.: A review on application of biomaterials for medical and dental implants. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 237(2), 249–273 (2023)
Li, S., Wang, S., Liu, W., Zhang, C., Song, J.: Current strategies for enhancement of the bioactivity of artificial ligaments: a mini-review. J. Orthop. Transl. 1(36), 205–215 (2022)
Milinkovic, D.D., Zimmermann, F., Balcarek, P.: Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction using nonresorbable sutures yields comparable outcomes to reconstruction with a pedicled quadriceps tendon autograft when performed in addition to bony risk factor correction. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 31(1), 264–271 (2023)
Wang, Y., Li, G., Yang, L., Luo, R., Guo, G.: Development of innovative biomaterials and devices for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Adv. Mater. 34(46), 2201971 (2022)
Bui, H.T., Khair, N., Yeats, B., Gooden, S., James, S.P., Dasi, L.P.: Transcatheter heart valves: a biomaterials perspective. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 10(15), 2100115 (2021)
Raval, N., Kalyane, D., Maheshwari, R., Tekade, R.K.: Surface modifications of biomaterials and their implication on biocompatibility. In: Biomaterials and Bionanotechnology, pp. 639–674. Academic Press (2019)
Kurella, A., Dahotre, N.B.: Surface modification for bioimplants: the role of laser surface engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 20(1), 5 (2005)
Steckbeck, S.: Experimental Analysis of Interactions between Biomolecules and Inorganic Surfaces. Doctoral dissertation, Bremen, Universität Bremen, Diss. (2014)
Amani, H., Arzaghi, H., Bayandori, M., Dezfuli, A.S., Pazoki-Toroudi, H., Shafiee, A., Moradi, L.: Controlling cell behavior through the design of biomaterial surfaces: a focus on surface modification techniques. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 6(13), 1900572 (2019)
Bose, S., Robertson, S.F., Bandyopadhyay, A.: Surface modification of biomaterials and biomedical devices using additive manufacturing. Acta Biomater. 15(66), 6–22 (2018)
Brunette, D.M., Tengvall, P., Textor, M., Thomsen, P.: Titanium in Medicine: Material Science, Surface Science, Engineering, Biological Responses and Medical Applications. Springer, Berlin (2001)
Ahirwar, H., Zhou, Y., Mahapatra, C., Ramakrishna, S., Kumar, P., Nanda, H.S.: Materials for orthopedic bioimplants: modulating degradation and surface modification using integrated nanomaterials. Coatings 10(3), 264 (2020)
Ohmori, H., Katahira, K., Nagata, J., Mizutani, M., Komotori, J.: Improvement of corrosion resistance in metallic biomaterials using a new electrical grinding technique. CIRP Ann. 51(1), 491–494 (2002)
Callister, W.D.: Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering. Wiley, London (2000)
Priyadarshini, B., Rama, M., Chetan, V.U.: Bioactive coating as a surface modification technique for biocompatible metallic implants: a review. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 7(4), 397–406 (2019)
Gibson, I.R., Bonfield, W.: Preparation and characterization of magnesium/carbonate co-substituted hydroxyapatites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 13(7), 685–693 (2002)
Kulkarni, M., Mazare, A., Schmuki, P., Iglič, A., Seifalian, A.: Biomaterial surface modification of titanium and titanium alloys for medical applications. Nanomedicine 111(615), 111 (2014)
Festas, A.J., Ramos, A., Davim, J.P.: Medical devices biomaterials—a review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 234(1), 218–228 (2020)
Lara, N., Neto, A.F., da Mota, A.J., de Souza, A.E., Brito, A.G., Da Silva, A.C., Martinez, A.C., Nozaki, A.P., da Silva, A.A., de Vasconcelos Ferraz, A., Moraes, Â.M.: Engenharia de Materiais: materializando o futuro. Pimenta Cultural (2022)
Soni, R., Pande, S., Kumar, S., Salunkhe, S., Natu, H., Hussein, H.M.: Wear characterization of laser cladded Ti-Nb-Ta alloy for biomedical applications. Crystals 12(12), 1716 (2022)
Su, Y., Luo, C., Zhang, Z., Hermawan, H., Zhu, D., Huang, J., Liang, Y., Li, G., Ren, L.: Bioinspired surface functionalization of metallic biomaterials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 1(77), 90–105 (2018)
Devgan, S., Sidhu, S.S.: Evolution of surface modification trends in bone related biomaterials: a review. Mater. Chem. Phys. 15(233), 68–78 (2019)
Bandyopadhyay, A., Mitra, I., Shivaram, A., Dasgupta, N., Bose, S.: Direct comparison of additively manufactured porous titanium and tantalum implants towards in vivo osseointegration. Addit. Manuf. 1(28), 259–266 (2019)
Hojjatzadeh, S.M., Parab, N.D., Yan, W., Guo, Q., Xiong, L., Zhao, C., Qu, M., Escano, L.I., Xiao, X., Fezzaa, K., Everhart, W.: Pore elimination mechanisms during 3D printing of metals. Nat. Commun. 10(1), 3088 (2019)
Ni, J., Ling, H., Zhang, S., Wang, Z., Peng, Z., Benyshek, C., Zan, R., Miri, A.K., Li, Z., Zhang, X., Lee, J.: Three-dimensional printing of metals for biomedical applications. Mater. Today Bio. 1(3), 100024 (2019)
Sing, S.L., Tey, C.F., Tan, J.H., Huang, S., Yeong, W.Y.: 3D printing of metals in rapid prototyping of biomaterials: techniques in additive manufacturing. In: Rapid Prototyping of Biomaterials, pp. 17–40. Woodhead Publishing (2020)
Liu, X., Chu, P.K., Ding, C.: Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. Rep. 47(3–4), 49–121 (2004)
Mondy, W.L., Cameron, D., Timmermans, J.P., De Clerck, N., Sasov, A., Casteleyn, C., Piegl, L.A.: Computer-aided design of microvasculature systems for use in vascular scaffold production. Biofabrication 1(3), 035002 (2009)
Setti, L., Fraleoni-Morgera, A., Ballarin, B., Filippini, A., Frascaro, D., Piana, C.: An amperometric glucose biosensor prototype fabricated by thermal inkjet printing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 20(10), 2019–2026 (2005)
Farahani, R.D., Dubé, M., Therriault, D.: Three-dimensional printing of multifunctional nanocomposites: manufacturing techniques and applications. Adv. Mater. 28(28), 5794–5821 (2016)
Stevens, M.M., George, J.H.: Exploring and engineering the cell surface interface. Science 310(5751), 1135–1138 (2005)
Elfick, A.P., Green, S.M., Krikler, S., Unsworth, A.: The nature and dissemination of UHMWPE wear debris retrieved from periprosthetic tissue of THR. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Japan. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 65(1), 95–108 (2003)
Roy, M., Balla, V.K., Bandyopadhyay, A., Bose, S.: MgO-doped tantalum coating on Ti: microstructural study and biocompatibility evaluation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4(2), 577–580 (2012)
Bai, L., Gong, C., Chen, X., Sun, Y., Zhang, J., Cai, L., Zhu, S., Xie, S.Q.: Additive manufacturing of customized metallic orthopedic implants: materials, structures, and surface modifications. Metals 9(9), 1004 (2019)
Darsell, J., Bose, S., Hosick, H.L., Bandyopadhyay, A.: From CT scan to ceramic bone graft. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 86(7), 1076–1080 (2003)
Bose, S., Fielding, G., Tarafder, S., Bandyopadhyay, A.: Understanding of dopant-induced osteogenesis and angiogenesis in calcium phosphate ceramics. Trends Biotechnol. 31(10), 594–605 (2013)
Tarafder, S., Bose, S.: Polycaprolactone-coated 3D printed tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: in vitro alendronate release behavior and local delivery effect on in vivo osteogenesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(13), 9955–9965 (2014)
Khaled, S.A., Burley, J.C., Alexander, M.R., Roberts, C.J.: Desktop 3D printing of controlled release pharmaceutical bilayer tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 461(1–2), 105–111 (2014)
Song, S.W., Hidajat, K., Kawi, S.: Functionalized SBA-15 materials as carriers for controlled drug delivery: influence of surface properties on matrix−drug interactions. Langmuir 21(21), 9568–9575 (2005)
Stallard, C.P., Solar, P., Biederman, H., Dowling, D.P.: Deposition of non-fouling PEO-like coatings using a low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma jet. Plasma Processes Polym. 13(2), 241–252 (2016)
Gloria, A., Causa, F., Russo, T., Battista, E., Della Moglie, R., Zeppetelli, S., De Santis, R., Netti, P.A., Ambrosio, L.: Three-dimensional poly (ε-caprolactone) bioactive scaffolds with controlled structural and surface properties. Biomacromol 13(11), 3510–3521 (2012)
Puppi, D., Chiellini, F., Piras, A.M., Chiellini, E.: Polymeric materials for bone and cartilage repair. Prog. Polym. Sci. 35(4), 403–440 (2010)
Kurtz, S.M., Devine, J.N.: PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants. Biomaterials 28(32), 4845–4869 (2007)
Dawson, J.I., Wahl, D.A., Lanham, S.A., Kanczler, J.M., Czernuszka, J.T., Oreffo, R.O.: Development of specific collagen scaffolds to support the osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials 29(21), 3105–3116 (2008)
Inzana, J.A., Olvera, D., Fuller, S.M., Kelly, J.P., Graeve, O.A., Schwarz, E.M., Kates, S.L., Awad, H.A.: 3D printing of composite calcium phosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomaterials 35(13), 4026–4034 (2014)
Yu, D.G., Branford-White, C., Ma, Z.H., Zhu, L.M., Li, X.Y., Yang, X.L.: Novel drug delivery devices for providing linear release profiles fabricated by 3DP. Int. J. Pharm. 370(1–2), 160–166 (2009)
Lee, K.Y., Mooney, D.J.: Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 37(1), 106–126 (2012)
Balamurugan, A., Balossier, G., Michel, J., Ferreira, J.M.: Electrochemical and structural evaluation of functionally graded bioglass-apatite composites electrophoretically deposited onto Ti6Al4V alloy. Electrochim. Acta 54(4), 1192–1198 (2009)
Stojanovic, D., Jokic, B., Veljovic, D., Petrovic, R., Uskokovic, P.S., Janackovic, D.: Bioactive glass–apatite composite coating for titanium implant synthesized by electrophoretic deposition. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27(2–3), 1595–1599 (2007)
Boccaccini, A.R., Peters, C., Roether, J.A., Eifler, D., Misra, S.K., Minay, E.J.: Electrophoretic deposition of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and PEEK/Bioglass® coatings on NiTi shape memory alloy wires. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 8152–8159 (2006)
Lerouge, S., Guignot, C., Tabrizian, M., Ferrier, D., Yagoubi, N., Yahia, L.H.: Plasma-based sterilization: effect on surface and bulk properties and hydrolytic stability of reprocessed polyurethane electrophysiology catheters. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 52(4), 774–782 (2000)
Hooper, K.A., Cox, J.D., Kohn, J.: Comparison of the effect of ethylene oxide and γ-irradiation on selected tyrosine-derived polycarbonates and poly (L-lactic acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 63(11), 1499–1510 (1997)
Simmons, A.: Future trends for the sterilisation of biomaterials and medical devices. In: Sterilisation of Biomaterials and Medical Devices, pp. 310–320. Woodhead Publishing (2012)
Srivastava, M., Rathee, S., Maheshwari, S., Kundra, T.K.: Additive Manufacturing: Fundamentals and Advancements. CRC Press (2019)
Guddati, S., Kiran, A.S., Leavy, M., Ramakrishna, S.: Recent advancements in additive manufacturing technologies for porous material applications. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 105, 193–215 (2019)
Morrison, R.J., Kashlan, K.N., Flanangan, C.L., Wright, J.K., Green, G.E., Hollister, S.J., Weatherwax, K.J.: Regulatory considerations in the design and manufacturing of implantable 3D-printed medical devices. Clin. Transl. Sci. 8(5), 594–600 (2015)
Schuh, J.C., Funk, K.A.: Compilation of international standards and regulatory guidance documents for evaluation of biomaterials, medical devices, and 3-D printed and regenerative medicine products. Toxicol. Pathol. 47(3), 344–357 (2019)
Harawaza, K., Cousins, B., Roach, P., Fernandez, A.: Modification of the surface nanotopography of implant devices: a translational perspective. Mater. Today Bio. 1(12), 100152 (2021)
Douglass, M., Garren, M., Devine, R., Mondal, A., Handa, H.: Bio-inspired hemocompatible surface modifications for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 17, 100997 (2022)
Zhang, D., Chen, Q., Shi, C., Chen, M., Ma, K., Wan, J., Liu, R.: Dealing with the foreign-body response to implanted biomaterials: strategies and applications of new materials. Adv. Func. Mater. 31(6), 2007226 (2021)
Punj, S., Singh, J., Singh, K.: Ceramic biomaterials: properties, state of the art and future prospectives. Ceram. Int. 47(20), 28059–28074 (2021)
Alghamdi, H.S., Jansen, J.A.: The development and future of dental implants. Dent. Mater. J. 39(2), 167–172 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Soni, B., Shivgotra, R., Kaur, M., Thakur, S. (2023). Surface-Modified Biomaterials in Medical Device Development. In: Malviya, R., Sundram, S. (eds) Engineered Biomaterials. Engineering Materials. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6698-1_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6698-1_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-6697-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-6698-1
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)