Abstract
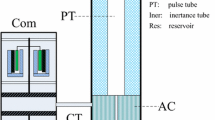
A new single-stage coaxial micro pulse tube cryocooler has been developed by Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, CAS. With the characteristics of long-life and low-mass, it could serve for infrared detectors in space and non-space applications. Driven by a high efficiency and lightweight linear compressor, it has a small cold finger with a diameter of 8 mm, and works at 175 Hz. Inertance tube and a reservoir is used as its phase shifter. At a reject temperature of 283 K, it can lift 0.79 W at 150 K with 10 W electrical input. This paper describes the key parameters of components, and presents test data in several working conditions of this pulse tube cryocooler in detail.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Radebaugh, R., O'Gallagher, A.: Regenerator operation at very high frequencies for microcryocoolers. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Cryogenic Engineering, pp. 1919–1928. Melville (2006)
Petach, M., Waterman, M., Tward, E.: Pulse tube microcooler for space applications. In: Proceedings of the ICC14, pp. 89–93 (2007)
Petach, M., Waterman, M., Pruitt, G., Tward, E.: High frequency coaxial pulse tube microcooler. In: Proceedings of the ICC15, pp. 97–103 (2009)
Vanapalli, S., Lewis, M., Gan, Z., Radebaugh, R.: 120 Hz pulse tube cryocooler for fast cooldown to 50K. Appl. Phys. Let. 90(7) (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2643073
Nast, T.C., Roth, E., Olson, J.R., Champagne, P., Frank, D.: Qualification of lockheed martin micro pulse tube Cryocooler to TRL6. In: Proceedings of the ICC18, pp. 51–57 (2014)
Li, J.Q., et al.: Modelling and experimental study of a 700 g micro coaxial Stirling-type pulse tube cryocooler operating at 100–190 Hz. In: 27th International Cryogenics Engineering Conference and International Cryogenic Materials Conference 2018, Iop Publishing Ltd, (2019)
Feng, T., et al.: A 598g Micro Pulse Tube Cryocooler’. In: Proceedings of the ICC21, pp. 157–161 (2020)
McKinley, I.M., Mok, M.A., Rodriguez, J.I.: Characterization testing of space-flight lockheed martin Micro 1-2 cryocooler for the Mapping Imaging Spectrometer for Europa (MISE). In: Proceedings of the ICC21, pp. 135–142 (2020)
McKinley, I.M., Hummel, C.D., Johnson, D.L., Rodriguez, J.I.: Characterization testing of Lockheed Martin high-power micro pulse tube cryocooler. In: Proceedings of the CEC2017
Acknowledgments
The project is supported by National Natural Science Foundation (Number 52106036), and National Key R&D Program of China under grant 2018YFB0504600, 2018YFB0504603.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Zhejiang University Press
About this paper
Cite this paper
Feng, T.S. et al. (2023). A 0.79 W/150 K Micro Pulse Tube Cryocooler. In: Qiu, L., Wang, K., Ma, Y. (eds) Proceedings of the 28th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and International Cryogenic Materials Conference 2022. ICEC28-ICMC 2022. Advanced Topics in Science and Technology in China, vol 70. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6128-3_101
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6128-3_101
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-6127-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-6128-3
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)