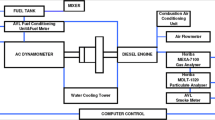
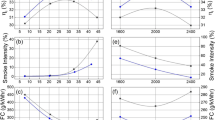
Abstract
Crude tire pyrolysis oil (CTPO) was refined using the principle of selective adsorption and preferential solubility using silica gel as an adsorbent and petroleum ether as a diluent and combusted in a single-cylinder diesel engine. Particulate analysis was conducted in a single-cylinder diesel engine to understand the carbonaceous deposition in piston crowns and surfaces using various analytical techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Further, lubricating oil analysis was performed using a combination of ICP-AES, viscosity, flash, and fire point tests. The results showed that carbon deposition from upgraded tire pyrolysis oil is observed to be higher than diesel due to its high aromatic content. The high amount of carbon deposits from upgraded tire pyrolysis oil was attributed to the high amount of oxygenates in StTPO, which leads to increased polymerization and subsequent condensation on piston crown surfaces, which was then carbonized.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams PT (2013) Pyrolysis of tires—a review. Waste Manage 33(8):1714–1728
Murugan S, Ramaswamy MC, Nagarajan G (2008) The use of tire pyrolysis oil in diesel engine. Waste Manage 28:2743–2749
Ilkilic C, Aydin H (2011) Fuel production from waste vehicle tire by catalytic pyrolysis and application in a diesel engine. Fuel Process Technol 92:1129–1135
Frigo S, Seggiani S, Puccini M, Vitolo S (2014) Liquid fuel production from waste tire pyrolysis and application in diesel engine. Fuel 116:399–408
Tudu K, Murugan S, Patel SK (2014) Light oil fraction from tire pyrolysis plant—an option for energy use. Energy Procedia 54:615–626
Vihar R, Seljak T, Opresnik SR, Katrasnik T (2015) Combustion characteristics of tire pyrolysis in turbocharged compression ignition engine. Fuel 150:226–235
Kumaravel ST, Murugesan A, Kumaravel A (2016) Tire pyrolysis oil as an alternative fuel for diesel engine—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:1678–1685
Sahir VK, Jawahar CP, Vinod V, Suresh PR (2018) J King Saud Univ Eng Sci (Article in press)
Bodisco TA, Rahman SMA, Hossain FM, Brown RJ (2019) On-road NOx emission of a modern commercial light-duty diesel vehicle using tire oil and diesel. Energy Rep 5:349–356
Verma P, Zare A, Jafari M, Bodisco TA, Rainey T, Ristovski ZD, Brown RJ (2019) Diesel engine performance and emissions with fuel derived from waste tires. Sci Rep 8:2457
Mohan A, Dutta S, Madav V (2019) Characterization and up-gradation of crude tire pyrolysis oil obtained from a rotating autoclave reactor. Fuel 250:339–351
Mohan A, Dutta S, Balusamy S, Madav V (2021) Liquid fuel from waste tires: novel refining, advanced characterization, and utilization in engine with ethyl levulinate as an additive. RSC Adv 11:9807–9826
La Rocca A, Di Liberto G, Shayler P, Parmenter C (2014) A novel diagnostics tool for measuring soot agglomerates size distribution in used automotive lubricating oil. SAE Int J Fuel Lubricants 7(1):301–306
Nanthagopal K, Ashok B, Saravanan B, Pathy MR, Sahil G, Ramesh A, Nahi MN, Rasul MG (2019) Study of decanol and Calophyllum Inophyllum biodiesel as ternary blend in compression ignition engine. Fuel 239:862–873
Vanderwal RL, Bryg VM, Hays MD (2010) Fingerprinting soot (towards source identification): physical structure and chemical composition. J Aerosol Sci 41(1):108–117
Lapuerta M, Fernandez JR, Agudelo JR (2009) Diesel particulate emission from used cooking oil biodiesel. Biores Technol 99(4):731–740
Jain A. Report on a compendium of technologies for the recovery of materials or energy from the end-of-life tires. Regional Resource Center for Asia and the Pacific
Islam MN (2016) Improvement of waste tire pyrolysis oil and performance test with diesel in compression ignition engine. J Renew Energy 2016, Article ID 5137247
Dimitriadis A, Natsios L, Dimaratos A, Katsaunis A, Samaras Z, Bezegianni S, Lehto K (2018) Evaluation of hydrotreated vegetable oil and its effects on passenger car diesel engine. Front Mech Eng 4
Zhang G, Chen F, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Chen J, Cao L, Gao J, Xu C (2021) Properties and utilization of waste tire oil: minireview. Fuel Process Technol 211:106–582
Banar M, Akyildiz V, Ozkan A, Cokaygil Z, Only O (2012) Characterization of pyrolytic oil obtained from pyrolysis of tire-derived fuel. Energy Convers Manage 62:22–30
Diesel fuel technical review. Chevron: https://www.chevron.com/-/media/chevron/operations/documents/diesel-fuel-tech-review.pdf
Murugan S, Ramaswamy MC, Nagarajan G (2008) Performance, emission, and combustion of direct-injected diesel engine using distilled tire pyrolysis oil-diesel blend. Fuel Process Technol 89:152–159
Murugan S, Ramaswamy MC, Nagarajan G (2008) The use of tire pyrolysis oil in diesel engine. Waste Manag 28:2743–2749
Umeki ER, Oliveira CF, Torres RB, Santos RG (2016) Physico-chemical properties of fuel blends composed of diesel and tire pyrolysis oil. Fuel 185:236–242
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the staff of the sophisticated analytical laboratory at IIT Bombay, Powai for the data analysis. The authors also like to thank NITK for microscopic examinations such as XRD and SEM. Akhil Mohan thanks IIT Bombay for providing infrastructure and PDF scholarship support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mohan, A., Madav, V. (2023). Capture and Characterization of Particulates from a Single-Cylinder Diesel Engine Fuelled with Refined Tire Pyrolysis Oil. In: Doolla, S., Rather, Z.H., Ramadesigan, V. (eds) Advances in Clean Energy and Sustainability. ICAER 2022. Green Energy and Technology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2279-6_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2279-6_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-2278-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-2279-6
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)