Abstract
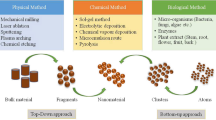
Chromium, mainly in the hexavalent form [Cr(VI)], has become a worldwide menace due to its extensive industrial applications and mining activities. According to the USEPA, it is one of 129 priority pollutants and 25 hazardous compounds, due to its higher toxicity, persistency, carcinogenicity, and mutagenic effects. Cr(VI) is hundred times more toxic than its trivalent form which is principally of geological origin. Cr(III) is generally insoluble and stable in the environment, primarily required for lipid and fat metabolism in human. In an aqueous solution, Cr(VI) is mostly found as the oxyanions HCrO4− (pH 2), Cr2O72− (pH 2–6), and CrO42− (pH > 6), which has very high mobility. Several figures show that Cr(VI) concentrations are significantly higher around the world, despite the fact that the acceptable limit for portable water is 0.05 mg/l and surface water discharge is 0.1 mg/L. Therefore, effective elimination of Cr(VI) from the water source requires long-term water management sustainable technology. Nano-remediation technology has gained a larger insight in the toxic contaminant removal due to its high surface area, non-toxic, vast reduction capacity, and cost-effective nature. It could be a state-of-the-art approach for the safe exclusion of heavy metals (Cr, As, Cd, Pb, and Hg) and organic compounds like pharmaceutical waste, organic solvents, phthalates, hydrocarbons, and persistent organic pollutants (POPs) from the wastewater. Carbon nanostructure, iron-based nanomaterials, metal organic framework, nano-photocatalyst, nanosensors, zeolites, and other methods are available for the reduction of Cr(VI) into Cr(III). Currently, iron-based nanomaterials are being investigated as a promising method for the effective reduction of Cr(VI) into Cr(III) from the aqueous solution, as its negative standard potential (E0(Fe2+/Fe0) = −0.44 V, favors reaction process. Despite all the advantages of iron particles, the pH dependency, agglomeration, and particle passivation limit the procedure. This chapter will discuss the occurrences, environmental cycle, health effects of chromium, as well as current developments in nanomaterial synthesis/modification via physico-chemical methods, probable reaction mechanisms, and the impact of various environmental conditions on Cr(VI) reduction capabilities in aqueous solution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdu N, Agbenin JO, Buerkert A (2011) Geochemical assessment, distribution, and dynamics of trace elements in urban agricultural soils under long-term wastewater irrigation in Kano, northern Nigeria. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174(3):447–458
Abid N, Khan AM, Shujait S, Chaudhary K, Ikram M, Imran M, Haider J, Khan M, Khan Q, Maqbool M (2021) Synthesis of nanomaterials using various top-down and bottom-up approaches, influencing factors, advantages, and disadvantages: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 102597
Adriano DC (2001) Trace elements in terrestrial environments: biogeochemistry, bioavailability, and risks of metals, vol 860. Springer, New York
Agency for Toxic Substance and Disease Registry (ATSDR) (2015) Toxicological profile for chromium. U.S. department of health and human services, public health services, ATSDR, Atlanta
Ali AS (2020) Application of nanomaterials in environmental improvement. Nanotechnol Environ
ATSDR U (2012) Toxicological profile for chromium. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service
Avudainayagam S, Megharaj M, Owens G, Kookana RS, Chittleborough D, Naidu R (2003) Chemistry of chromium in soils with emphasis on tannery waste sites. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 53–91
Babula P, Adam V, Opatrilova R, Zehnalek J, Havel L, Kizek R (2009) Uncommon heavy metals, metalloids and their plant toxicity: a review. Org Farming, Pest Control Rem Soil Pollutants 275–317
Bahador F, Foroutan R, Esmaeili H, Ramavandi B (2021) Enhancement of the chromium removal behavior of Moringa oleifera activated carbon by chitosan and iron oxide nanoparticles from water. Carbohyd Polym 251:117085
Bartlett RJ (1991) Chromium cycling in soils and water: links, gaps, and methods. Environ Health Perspect 92:17–24
Bhaumik M, Agarwal S, Gupta VK, Maity A (2016) Enhanced removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions using polypyrrole wrapped oxidized MWCNTs nanocomposites adsorbent. J Colloid Interface Sci 470:257–267
Bilal M, Adeel M, Rasheed T, Zhao Y, Iqbal HM (2019) Emerging contaminants of high concern and their enzyme-assisted biodegradation—a review. Environ Int 124:336–353
Brumovský M, Filip J, Malina O, Oborná J, Sracek O, Reichenauer TG, Andryskova P, Zbořil R (2020) Core–shell Fe/FeS nanoparticles with controlled shell thickness for enhanced trichloroethylene removal. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(31):35424–35434
Burakov AE, Galunin EV, Burakova IV, Kucherova AE, Agarwal S, Tkachev AG, Gupta VK (2018) Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:702–712
Calderon B, Fullana A (2015) Heavy metal release due to aging effect during zero valent iron nanoparticles remediation. Water Res 83:1–9
Cao Y, Huang J, Li Y, Qiu S, Liu J, Khasanov A, Khan MA, Young DP, Peng F, Cao D, Peng X (2016) One-pot melamine derived nitrogen doped magnetic carbon nanoadsorbents with enhanced chromium removal. Carbon 109:640–649
Cao Y, Huang J, Peng X, Cao D, Galaska A, Qiu S, Liu J, Khan MA, Young DP, Ryu JE, Feng H (2017) Poly (vinylidene fluoride) derived fluorine-doped magnetic carbon nano adsorbents for enhanced chromium removal. Carbon 115:503–514
Cengiz MF, Kilic S, Yalcin F, Kilic M, Gurhan Yalcin M (2017) Evaluation of heavy metal risk potential in Bogacayi River water (Antalya, Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 189(6):1–12
Choppala G, Bolan N, Park JH (2013) Chromium contamination and its risk management in complex environmental settings. Adv Agron 120:129–172
Coetzee JJ, Bansal N, Chirwa E (2020) Chromium in environment, its toxic effect from chromite-mining and ferrochrome industries, and its possible bioremediation. Exposure Health 12(1):51–62
Das AP, Singh S (2011) Occupational health assessment of chromite toxicity among Indian miners. Indian J Occup Environ Med 15(1):6
De Miguel E, Iribarren I, Chacon E, Ordonez A, Charlesworth S (2007) Risk-based evaluation of the exposure of children to trace elements in playgrounds in Madrid (Spain). Chemosphere 66(3):505–513
Dehghani MH, Taher MM, Bajpai AK, Heibati B, Tyagi I, Asif M, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2015) Removal of noxious Cr (VI) ions using single-walled carbon nanotubes and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng J 279:344–352
Deng F, Li S, Zhou M, Zhu Y, Qiu S, Li K, Ma F, Jiang J (2019) A biochar modified nickel-foam cathode with iron-foam catalyst in electro-Fenton for sulfamerazine degradation. Appl Catal B 256:117796
Diao ZH, Chu W (2021) FeS2 assisted degradation of atrazine by bentonite-supported nZVI coupling with hydrogen peroxide process in water: performance and mechanism. Sci Total Environ 754:142155
Diao ZH, Du JJ, Jiang D, Kong LJ, Huo WY, Liu CM, Wu QH, Xu XR (2018) Insights into the simultaneous removal of Cr6+ and Pb2+ by a novel sewage sludge-derived biochar immobilized nanoscale zero valent iron: coexistence effect and mechanism. Sci Total Environ 642:505–515
Dinda D, Gupta A, Saha SK (2013) Removal of toxic Cr (VI) by UV-active functionalized graphene oxide for water purification. J Mater Chem A 1(37):11221–11228
Ding J, Pu L, Wang Y, Wu B, Yu A, Zhang X, Pan B, Zhang Q, Gao G (2018) Adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) together with Cr(III) sequestration by polyaniline confined in pores of polystyrene beads. Environ Sci Technol 52(21):12602–12611
Donadelli JA, Caram B, Kalaboka M, Kapsi M, Sakkas VA, Carlos L, Einschlag FSG (2020) Mechanisms of 4-phenylazophenol elimination in micro-and nano-ZVI assisted-Fenton systems. J Environ Chem Eng 8(1):103624
Dong H, Jiang Z, Deng J, Zhang C, Bila Y, Hou K, Zhang L, Tang L, Zeng G (2018) Physicochemical transformation of Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles during aging in simulated groundwater and the consequent effect on contaminant removal. Water Res 129:51–57
Duranoğlu D, Trochimczuk AW, Beker U (2012) Kinetics and thermodynamics of hexavalent chromium adsorption onto activated carbon derived from acrylonitrile-divinylbenzene copolymer. Chem Eng J 187:193–202
Endres SC, Ciacchi LC, Mädler L (2021) A review of contact force models between nanoparticles in agglomerates, aggregates, and films. J Aerosol Sci 153:105719
EPA U. Toxic and priority pollutants under the clean water act. US EPA available online: https://www.epa.gov/eg/toxic-and-priority-pollutants-under-clean-water-act. Accessed 24 Jan 2021
Esen AN, Haciyakupoglu S, Erenturk SA (2021) Assessment of different hazard indices around coal-fired power plants in Turkey. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 329(2):601–620
Fan Z, Zhang Q, Gao B, Li M, Liu C, Qiu Y (2019) Removal of hexavalent chromium by biochar supported nZVI composite: batch and fixed-bed column evaluations, mechanisms, and secondary contamination prevention. Chemosphere 217:85–94
Fang Y, Wen J, Zhang H, Wang Q, Hu X (2020) Enhancing Cr(VI) reduction and immobilization by magnetic core-shell structured NZVI@ MOF derivative hybrids. Environ Pollut 260:114021
Fang Y, Yang K, Zhang Y, Peng C, Robledo-Cabrera A, López-Valdivieso A (2021) Highly surface activated carbon to remove Cr (VI) from aqueous solution with adsorbent recycling. Environ Res 197:111151
Feng X, Long R, Wang L, Liu C, Bai Z, Liu X (2022) A review on heavy metal ions adsorption from water by layered double hydroxide and its composites. Sep Purif Technol 284:120099
Fu F, Dionysiou DD, Liu H (2014) The use of zero-valent iron for groundwater remediation and wastewater treatment: a review. J Hazard Mater 267:194–205
Gao G, Nie L, Yang S, Jin P, Chen R, Ding D, Wang XC, Wang W, Wu K, Zhang Q (2018) Well-defined strategy for development of adsorbent using metal organic frameworks (MOF) template for high performance removal of hexavalent chromium. Appl Surf Sci 457:1208–1217
Gauglhofer J, Bianchi V (1991) Chromium. In: Merian E (ed) Metals and their compounds in the environment. VCH Publisher, New York, pp 853–878
Gong Y, Gai L, Tang J, Fu J, Wang Q, Zeng EY (2017) Reduction of Cr(VI) in simulated groundwater by FeS-coated iron magnetic nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 595:743–751
Goutam SP, Saxena G, Roy D, Yadav AK, Bharagava RN (2020) Green synthesis of nanoparticles and their applications in water and wastewater treatment. In: Bioremediation of industrial waste for environmental safety, pp 349–379
Guertin J (2004) Toxicity and health effects of chromium (all oxidation states). Chromium (VI) handbook, pp 215–234
Herrero-Latorre C, Barciela-García J, García-Martín S, Pena-Crecente RM (2018) Graphene and carbon nanotubes as solid phase extraction sorbents for the speciation of chromium: a review. Anal Chim Acta 1002:1–17
Huang L, Zhou S, Jin F, Huang J, Bao N (2014) Characterization and mechanism analysis of activated carbon fiber felt-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron for the removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf, A 447:59–66
Huo SH, Yan XP (2012) Metal–organic framework MIL-100 (Fe) for the adsorption of malachite green from aqueous solution. J Mater Chem 22(15):7449–7455
IS-10500, B.I.S (2012) Indian standard drinking water–specification (second revision). Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), New Delhi
Jain M, Yadav M, Kohout T, Lahtinen M, Garg VK, Sillanpää M (2018) Development of iron oxide/activated carbon nanoparticle composite for the removal of Cr (VI), Cu (II) and Cd (II) ions from aqueous solution. Water Resour Ind 20:54–74
James BR, Petura JC, Vitale RJ, Mussoline GR (1995) Hexavalent chromium extraction from soils: a comparison of five methods. Environ Sci Technol 29(9):2377–2381
Jamkhande PG, Ghule NW, Bamer AH, Kalaskar MG (2019) Metal nanoparticles synthesis: an overview on methods of preparation, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol 53:101174
Jobby R, Jha P, Yadav AK, Desai N (2018) Biosorption and biotransformation of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)]: a comprehensive review. Chemosphere 207:255–266
Katz SA, Salem H (1993) The toxicology of chromium with respect to its chemical speciation: a review. J Appl Toxicol 13(3):217–224
Khan ST, Malik A (2019) Engineered nanomaterials for water decontamination and purification: from lab to products. J Hazard Mater 363:295–308
Khezami L, Capart R (2005) Removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution by activated carbons: kinetic and equilibrium studies. J Hazard Mater 123(1–3):223–231
Kieber RJ, Willey JD, Zvalaren SD (2002) Chromium speciation in rainwater: temporal variability and atmospheric deposition. Environ Sci Technol 36(24):5321–5327
Kimbrough DE, Cohen Y, Winer AM, Creelman L, Mabuni C (1999) A critical assessment of chromium in the environment. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 29(1):1–46
Kolahalam LA, Viswanath IK, Diwakar BS, Govindh B, Reddy V, Murthy YLN (2019) Review on nanomaterials: synthesis and applications. Mater Today: Proc 18:2182–2190
Kotaś J, Stasicka ZJEP (2000) Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation. Environ Pollut 107(3):263–283
Kumar M, Xiong X, Wan Z, Sun Y, Tsang DC, Gupta J, Gao B, Cao X, Tang J, Ok YS (2020) Ball milling as a mechanochemical technology for fabrication of novel biochar nanomaterials. Biores Technol 312:123613
Labied R, Benturki O, Eddine Hamitouche AY, Donnot A (2018) Adsorption of hexavalent chromium by activated carbon obtained from a waste lignocellulosic material (Ziziphus jujuba cores): kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic study. Adsorpt Sci Technol 36(3–4):1066–1099
Leonel AG, Mansur AA, Mansur HS (2021) Advanced functional nanostructures based on magnetic iron oxide nanomaterials for water remediation: a review. Water Res 190:116693
Li X, Gao X, Ai L, Jiang J (2015) Mechanistic insight into the interaction and adsorption of Cr (VI) with zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 microcrystals from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 274:238–324
Li X, Ai L, Jiang J (2016) Nanoscale zerovalent iron decorated on graphene nanosheets for Cr (VI) removal from aqueous solution: surface corrosion retard induced the enhanced performance. Chem Eng J 288:789–797
Li LL, Feng XQ, Han RP, Zang SQ, Yang G (2017) Cr (VI) removal via anion exchange on a silver-triazolate MOF. J Hazard Mater 321:622–628
Li Y, Xing B, Ding Y, Han X, Wang S (2020) A critical review of the production and advanced utilization of biochar via selective pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Biores Technol 312:123614
Liang J, Li X, Yu Z, Zeng G, Luo Y, Jiang L, Yang Z, Qian Y, Wu H (2017) Amorphous MnO2 modified biochar derived from aerobically composted swine manure for adsorption of Pb (II) and Cd (II). ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(6):5049–5058
Liu Y, Jin X, Chen Z (2018) The formation of iron nanoparticles by Eucalyptus leaf extract and used to remove Cr (VI). Sci Total Environ 627:470–479
Liu W, Jin L, Xu J, Liu J, Li Y, Zhou P, Wang C, Dahlgren RA, Wang X (2019) Insight into pH dependent Cr(VI) removal with magnetic Fe3S4. Chem Eng J 359:564–571
Liu B, Xu M, Wang J, Wang Z, Zhao L (2021) Ecological risk assessment and heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 163:111954
Loyaux-Lawniczak S, Lecomte P, Ehrhardt JJ (2001) Behavior of hexavalent chromium in a polluted groundwater: redox processes and immobilization in soils. Environ Sci Technol 35(7):1350–1357
Luo C, Tian Z, Yang B, Zhang L, Yan S (2013) Manganese dioxide/iron oxide/acid oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotube magnetic nanocomposite for enhanced hexavalent chromium removal. Chem Eng J 234:256–265
Luo M, Zhang Y, Li H, Hu W, Xiao K, Yu S, Zheng C, Wang X (2022) Pollution assessment and sources of dissolved heavy metals in coastal water of a highly urbanized coastal area: the role of groundwater discharge. Sci Total Environ 807:151070
Lv X, Hu Y, Tang J, Sheng T, Jiang G, Xu X (2013) Effects of co-existing ions and natural organic matter on removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI)-Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Chem Eng J 218:55–64
Lv D, Zhou J, Cao Z, Xu J, Liu Y, Li Y, Yang K, Lou Z, Lou L, Xu X (2019) Mechanism and influence factors of chromium (VI) removal by sulfide-modified nanoscale zerovalent iron. Chemosphere 224:306–315
Lyu H, Gao B, He F, Zimmerman AR, Ding C, Huang H, Tang J (2018) Effects of ball milling on the physicochemical and sorptive properties of biochar: experimental observations and governing mechanisms. Environ Pollut 233:54–63
Maitlo HA, Kim KH, Kumar V, Kim S, Park JW (2019) Nanomaterials-based treatment options for chromium in aqueous environments. Environ Int 130:104748
Maleki A, Hayati B, Naghizadeh M, Joo SW (2015) Adsorption of hexavalent chromium by metal organic frameworks from aqueous solution. J Ind Eng Chem 28:211–216
Markiewicz B, Komorowicz I, Sajnóg A, Belter M, Barałkiewicz D (2015) Chromium and its speciation in water samples by HPLC/ICP-MS–technique establishing metrological traceability: a review since 2000. Talanta 132:814–828
Mattox DM (2002) Physical vapor deposition (PVD) processes. Met Finish 100:394–408
Merian E, Anke M, Ihnat M, Stoeppler M (2004) Elements and their compounds in the environment: occurrence, analysis and biological relevance (No. Ed. 2). Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA
Mertz W (1983) Chromium: an essential micronutrient. ASDC J Dent Child 50(2):142–144
Mitra S, Chakraborty AJ, Tareq AM, Emran TB, Nainu F, Khusro A, Idris AM, Khandaker MU, Osman H, Alhumaydhi FA, Simal-Gandara J (2022) Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J King Saud Univ-Sci 101865
Mohammadi AA, Alinejad A, Kamarehie B, Javan S, Ghaderpoury A, Ahmadpour M, Ghaderpoori M (2017) Metal-organic framework Uio-66 for adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14(9):1959–1968
Mohan D, Rajput S, Singh VK, Steele PH, Pittman CU Jr (2011) Modeling and evaluation of chromium remediation from water using low-cost bio-char, a green adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 188(1–3):319–333
Mohan D, Pittman Jr CU (2006) Activated carbons and low-cost adsorbents for remediation of tri- and hexavalent chromium from water. J Hazard Mater 137(2):762e811
Mondal NK, Chakraborty S (2020) Adsorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution on graphene oxide (GO) prepared from graphite: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Appl Water Sci 10(2):1–10
Montesinos VN, Quici N, Halac EB, Leyva AG, Custo G, Bengio S, Zampieri G, Litter MI (2014) Highly efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water with nanoparticulated zerovalent iron: understanding the Fe (III)–Cr (III) passive outer layer structure. Chem Eng J 244:569–575
Mortazavian S, An H, Chun D, Moon J (2018) Activated carbon impregnated by zero-valent iron nanoparticles (AC/nZVI) optimized for simultaneous adsorption and reduction of aqueous hexavalent chromium: material characterizations and kinetic studies. Chem Eng J 353:781–795
Motzer WE, Engineers T (2004) Chemistry, geochemistry, and geology of chromium and chromium compounds. Chromium (VI) handbook, pp 23–88
Mullet M, Boursiquot S, Ehrhardt JJ (2004) Removal of hexavalent chromium from solutions by mackinawite, tetragonal FeS. Colloids Surf, A 244(1–3):77–85
Neikov OD, Yefimov NA (2009) Handbook of non-ferrous metal powders: technologies and applications
Noraee Z, Jafari A, Ghaderpoori M, Kamarehie B, Ghaderpoury A (2019) Use of metal-organic framework to remove chromium (VI) from aqueous solutions. J Environ Health Sci Eng 17(2):701–709
Oze C, Bird DK, Fendorf S (2007) Genesis of hexavalent chromium from natural sources in soil and groundwater. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(16):6544–6549
Pellerin C, Booker SM (2000) Reflections on hexavalent chromium: health hazards of an industrial heavyweight. Environ Health Perspect 108(9):A402–A407
Peng Z, Xiong C, Wang W, Tan F, Xu Y, Wang X, Qiao X (2017a) Facile modification of nanoscale zero-valent iron with high stability for Cr (VI) remediation. Sci Total Environ 596:266–273
Peng W, Li H, Liu Y, Song S (2017b) A review on heavy metal ions adsorption from water by graphene oxide and its composites. J Mol Liq 230:496–504
Qu J, Zhang W, Bi F, Yan S, Miao X, Zhang B, Wang Y, Ge C, Zhang Y (2022b) Two-step ball milling-assisted synthesis of N-doped biochar loaded with ferrous sulfide for enhanced adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) and tetracycline from water. Environ Pollut 306:119398
Qu J, Wu Z, Liu Y, Li R, Wang D, Wang S, Wei S, Zhang J, Tao Y, Jiang Z, Zhang Y (2022a) Ball milling potassium ferrate activated biochar for efficient chromium and tetracycline decontamination: insights into activation and adsorption mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 127407
Qu J, Zhang W, Bi F, Yan S, Miao X, Zhang B, Wang Y, Ge C, Zhang Y (2022b) Two-step ball milling-assisted synthesis of N-doped biochar loaded with ferrous sulfide for enhanced adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) and tetracycline from water. Environ Pollut 306:119398
Qurie M, Khamis M, Manassra A, Ayyad I, Nir S, Scrano L, Bufo SA, Karaman R (2013) Removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous environments using micelle-clay adsorption. Sci World J
Rafiaee S, Samani MR, Toghraie D (2020) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous media using pomegranate peels modified by polymeric coatings: effects of various composite synthesis parameters. Synth Met 265:116416
Rajapaksha AU, Selvasembian R, Ashiq A, Gunarathne V, Ekanayake A, Perera VO, Wijesekera H, Mia S, Ahmad M, Vithanage M, Ok YS (2022) A systematic review on adsorptive removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions: recent advances. Sci Total Environ 809:152055
Ramesha GK, Kumara AV, Muralidhara HB, Sampath S (2011) Graphene and graphene oxide as effective adsorbents toward anionic and cationic dyes. J Colloid Interface Sci 361(1):270–277
Richard FC, Bourg AC (1991) Aqueous geochemistry of chromium: a review. Water Res 25(7):807–816
Russell R, Beard JL, Cousins RJ, Dunn JT, Ferland G, Hambidge K, Lynch S, Penland JG, Ross AC, Stoecker BJ, Suttie JW (2001) Dietary reference intakes for vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc. A report of the panel on micronutrients, subcommittees on upper reference levels of nutrients and of interpretation and uses of dietary reference intakes, and the standing committee on the scientific evaluation of dietary reference intakes food and nutrition board institute of medicine, p 797
Saha R, Nandi R, Saha B (2011) Sources and toxicity of hexavalent chromium. J Coord Chem 64(10):1782–1806
Salem FY, Parkerton TF, Lewis RV, Huang JH, Dickson KL (1989) Kinetics of chromium transformations in the environment. Sci Total Environ 86(1–2):25–41
Saravanan A, Kumar PS, Jeevanantham S, Karishma S, Tajsabreen B, Yaashikaa PR, Reshma B (2021) Effective water/wastewater treatment methodologies for toxic pollutants removal: processes and applications towards sustainable development. Chemosphere 280:130595
Scaria J, Nidheesh PV, Kumar MS (2020) Synthesis and applications of various bimetallic nanomaterials in water and wastewater treatment. J Environ Manage 259:110011
Sepeur S (2008) Nanotechnology: technical basics and applications. Vincentz Network GmbH & Co KG
Shang J, Zong M, Yu Y, Kong X, Du Q, Liao Q (2017) Removal of chromium (VI) from water using nanoscale zerovalent iron particles supported on herb-residue biochar. J Environ Manage 197:331–337
Sharma P, Bihari V, Agarwal SK, Verma V, Kesavachandran CN, Pangtey BS, Mathur N, Singh KP, Srivastava M, Goel SK (2012) Groundwater contaminated with hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)]: a health survey and clinical examination of community inhabitants (Kanpur, India). PLoS ONE 7(10):e47877
Shen L, Liang S, Wu W, Liang R, Wu L (2013) Multifunctional NH 2-mediated zirconium metal–organic framework as an efficient visible-light-driven photocatalyst for selective oxidation of alcohols and reduction of aqueous Cr (vi). Dalton Trans 42(37):13649–13657
Shen W, Zhang J, Xiao M, Zhang X, Li J, Jiang W, Yan J, Zhang S, He W, He Y (2020) Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid induces surface erosion of zero-valent iron for enhanced hexavalent chromium removal. Appl Surf Sci 525:146593
Shyaa AA, Hasan OA, Abbas AM (2015) Synthesis and characterization of polyaniline/zeolite nanocomposite for the removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution. J Saudi Chem Soc 19(1):101–107
Singh KK, Singh A, Rai S (2022) A study on nanomaterials for water purification. Mater Today: Proc 51:1157–1163
Singh V, Yadav P, Mishra V (2020) Recent advances on classification, properties, synthesis, and characterization of nanomaterials. Green synthesis of nanomaterials for bioenergy applications, pp 83–97
Sinha R, Kumar R, Abhishek K, Shang J, Bhattacharya S, Sengupta S, Kumar N, Singh RK, Mallick J, Kar M, Sharma P (2022) Single-step synthesis of activated magnetic biochar derived from rice husk for hexavalent chromium adsorption: equilibrium mechanism, kinetics, and thermodynamics analysis. Groundwater Sustain Dev 100796
Srivastava V, Sarkar A, Singh S, Singh P, De Araujo AS, Singh RP (2017) Agroecological responses of heavy metal pollution with special emphasis on soil health and plant performances. Front Environ Sci 5:64
Su CC (2015) Heavy metal and cancer risk. J Public Health Epidemiol 1(4):1019–1021
Sutherland RA, Tack FM, Ziegler AD (2012) Road-deposited sediments in an urban environment: a first look at sequentially extracted element loads in grain size fractions. J Hazard Mater 225:54–62
Swaroop A, Bagchi M, Preuss HG, Zafra-Stone S, Ahmad T, Bagchi D (2019) Benefits of chromium (III) complexes in animal and human health. In: The nutritional biochemistry of chromium (III). Elsevier, pp 251–278
Tang J, Zhao B, Lyu H, Li D (2021) Development of a novel pyrite/biochar composite (BM-FeS2@ BC) by ball milling for aqueous Cr (VI) removal and its mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 413:125415
Thakur R, Sharma GD, Dwivedi BS, Khatik SK (2007) Chromium: as a pollutant. J Ind Pollut Control 23:197–203
United States (1989) Environmental protection agency. Office of emergency and remedial response: risk assessment guidance for superfund. office of emergency and remedial response, US environmental protection agency
Upadhyay S, Saha AK, Sinha A (2019) High carbon iron filings (HCIF) and metal reducing bacteria (Serratia sp.) co-assisted Cr (VI) reduction: kinetics, mechanism and longevity. J Environ Manage 236:388–395
USEPA (1989) Risk assessment guidance for superfund, vol I, human health evaluation manual (Part A). Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, Washington, DC
USEPA (2004) Risk assessment guidance for superfund volume i: human health evaluation manual (Part E). http://www.epa.gov/oswer/riskassessment/ragse/pdf/introduction.pdf
Vakili M, Deng S, Cagnetta G, Wang W, Meng P, Liu D, Yu G (2019) Regeneration of chitosan-based adsorbents used in heavy metal adsorption: a review. Sep Purif Technol 224:373–387
Vaseghi Z, Nematollahzadeh A (2020) Nanomaterials: types, synthesis, and characterization. Green synthesis of nanomaterials for bioenergy applications, pp 23–82
Wang SY, Tang YK, Li K, Mo YY, Li HF, Gu ZQ (2014) Combined performance of biochar sorption and magnetic separation processes for treatment of chromium-contained electroplating wastewater. Biores Technol 174:67–73
Wang Y, Yu L, Wang R, Wang Y, Zhang X (2020a) A novel cellulose hydrogel coating with nanoscale Fe0 for Cr (VI) adsorption and reduction. Sci Total Environ 726:138625
Wang K, Sun Y, Tang J, He J, Sun H (2020b) Aqueous Cr (VI) removal by a novel ball milled Fe0-biochar composite: role of biochar electron transfer capacity under high pyrolysis temperature. Chemosphere 241:125044
Wang W, Hu B, Wang C, Liang Z, Cui F, Zhao Z, Yang C (2020c) Cr (VI) removal by micron-scale iron-carbon composite induced by ball milling: the role of activated carbon. Chem Eng J 389:122633
Wang W, Gao P, Yang C, Zhao Z, Zhen S, Zhou Y, Zhang T (2022b) Separable and reactivated magnetic mZVAl/nFe3O4 composite induced by ball milling for efficient adsorption-reduction-sequestration of aqueous Cr (VI). Sep Purif Technol 288:120689
Wang M, Yang S, Liu J, Wu S, Xue Y (2022a) Enteromorpha prolifera biochar as a novel ball milling aid for enhancing the interfacial reaction activity of microscale zero-valent iron (mZVI) for Cr (VI) removal from water. J Water Process Eng 102844
Wu J, Cheng X, Yang G (2019) Preparation of nanochitin-contained magnetic chitosan microfibers via continuous injection gelation method for removal of Ni(II) ion from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 125:404–413
Wu Q, Hu W, Wang H, Liu P, Wang X, Huang B (2021) Spatial distribution, ecological risk and sources of heavy metals in soils from a typical economic development area, Southeastern China. Sci Total Environ 780:146557
Yang WM, Liu F, Jin YT, Dong ZM, Zhao GC (2022) Efficient reduction of Cr (VI) with carbon quantum dots. ACS Omega 7(27):23555–23565
Yavuz R, Orbak İ, Karatepe N (2006) Factors affecting the adsorption of chromium (VI) on activated carbon. J Environ Sci Health Part A 41(9):1967–1980
Ye J, Wang Y, Xu Q, Wu H, Tong J, Shi J (2021) Removal of hexavalent chromium from wastewater by Cu/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles. Sci Rep 11(1):1–11
Yin Y, Wang J (2017) Removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by nanoscale zero-valent iron. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 17(8):5864–5868
Yu G, Wang X, Liu J, Jiang P, You S, Ding N, Guo Q, Lin F (2021) Applications of nanomaterials for heavy metal removal from water and soil: a review. Sustainability 13(2):713
Zafra-Stone S, Bagchi M, Preuss HG, Bagchi D (2007) Benefits of chromium (III) complexes in animal and human health. In: The nutritional biochemistry of chromium (III), pp183–206
Zagho MM, Dawoud HD, Bensalah N, Altahtamouni TM (2019) A brief overview of RF sputtering deposition of boron carbon nitride (BCN) thin films. Emergent Mater 2(1):79–93
Zayed AM, Terry N (2003) Chromium in the environment: factors affecting biological remediation. Plant Soil 249(1):139–156
Zhang YC, Li J, Xu HY (2012) One-step in situ solvothermal synthesis of SnS2/TiO2 nanocomposites with high performance in visible light-driven photocatalytic reduction of aqueous Cr(VI). Appl Catal B 123:18–26
Zhang Y, Liu N, Yang Y, Li J, Wang S, Lv J, Tang R (2020) Novel carbothermal synthesis of Fe, N co-doped oak wood biochar (Fe/N-OB) for fast and effective Cr(VI) removal. Colloids Surf, A 600:124926
Zhang P, Xue B, Jiao L, Meng X, Zhang L, Li B, Sun H (2022a) Preparation of ball-milled phosphorus-loaded biochar and its highly effective remediation for Cd-and Pb-contaminated alkaline soil. Sci Total Environ 813:152648
Zhang Q, Ye X, Chen D, Xiao W, Zhao S, Li J, Li H (2022b) Chromium (VI) removal from synthetic solution using novel zero-valent iron biochar composites derived from iron-rich sludge via one-pot synthesis. J Water Process Eng 47:102720
Zhao R, Zhou Z, Zhao X, Jing G (2019) Enhanced Cr(VI) removal from simulated electroplating rinse wastewater by amino-functionalized vermiculite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 218:458–467
Zhao N, Zhao C, Tsang DC, Liu K, Zhu L, Zhang W, Zhang J, Tang Y, Qiu R (2021) Microscopic mechanism about the selective adsorption of Cr (VI) from salt solution on O-rich and N-rich biochars. J Hazard Mater 404:124162
Zheng C, Yang Z, Si M, Zhu F, Yang W, Zhao F, Shi Y (2021) Application of biochars in the remediation of chromium contamination: fabrication, mechanisms, and interfering species. J Hazard Mater 407:124376
Zhou M, Wu YN, Qiao J, Zhang J, McDonald A, Li G, Li F (2013) The removal of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions by MIL-53 (Al) and mesostructured MIL-53 (Al). J Colloid Interface Sci 405:157–163
Zhou X, Lv B, Zhou Z, Li W, Jing G (2015) Evaluation of highly active nanoscale zero-valent iron coupled with ultrasound for chromium (VI) removal. Chem Eng J 281:155–163
Zhou Q, Huang J, Zhang X, Gao Y (2018) Assembling polypyrrole coated sepiolite fiber as efficient particle adsorbent for chromium (VI) removal with the feature of convenient recycling. Appl Clay Sci 166:307–317
Zhou H, Ye M, Zhao Y, Baig SA, Huang N, Ma M (2022) Sodium citrate and biochar synergistic improvement of nanoscale zero-valent iron composite for the removal of chromium (VI) in aqueous solutions. J Environ Sci 115:227–239
Zhu F, Li L, Ma S, Shang Z (2016) Effect factors, kinetics and thermodynamics of remediation in the chromium contaminated soils by nanoscale zero valent Fe/Cu bimetallic particles. Chem Eng J 302:663–669
Zhu F, He S, Liu T (2018a) Effect of pH, temperature and co-existing anions on the removal of Cr(VI) in groundwater by green synthesized nZVI/Ni. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:544–550
Zhu S, Huang X, Wang D, Wang L, Ma F (2018b) Enhanced hexavalent chromium removal performance and stabilization by magnetic iron nanoparticles assisted biochar in aqueous solution: mechanisms and application potential. Chemosphere 207:50–59
Zhu F, Ma S, Liu T, Deng X (2018c) Green synthesis of nano zero-valent iron/Cu by green tea to remove hexavalent chromium from groundwater. J Clean Prod 174:184–190
Zhuang L, Li Q, Chen J, Ma B, Chen S (2014) Carbothermal preparation of porous carbon-encapsulated iron composite for the removal of trace hexavalent chromium. Chem Eng J 253:24–33
Zissimos AM, Christoforou IC, Christofi C, Rigas M, Georgiadou EC, Christou A (2021) Occurrence and distribution of hexavalent chromium in ground and surface waters in Cyprus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106(3):428–434
Zou Y, Wang X, Khan A, Wang P, Liu Y, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Wang X (2016) Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: a review. Environ Sci Technol 50(14):7290–7304
Zou H, Zhao J, He F, Zhong Z, Huang J, Zheng Y, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Yu F, Bashir MA, Gao B (2021) Ball milling biochar iron oxide composites for the removal of chromium (Cr(VI)) from water: performance and mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 413:125252
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, Indian School of Mines (IIT), Dhanbad and CSIR-Central Institute of Mining and Fuel Research for their sincere support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kumari, A., Sinha, A., Singh, D.B. (2023). Iron-Based Modified Nanomaterials for the Efficacious Treatment of Cr(VI) Containing Wastewater: A Review. In: Sinha, A., Singh, S.P., Gupta, A.B. (eds) Persistent Pollutants in Water and Advanced Treatment Technology. Energy, Environment, and Sustainability. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2062-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2062-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-2061-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-2062-4
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)