Abstract
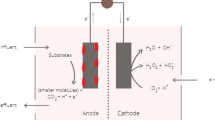
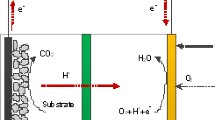
The microbial fuel cell (MFC) has emerged as an innovative and sustainable renewable energy technology, offering a potential alternative to address the global energy crisis. Operating through electrochemical processes, MFCs harness the power of electrogenic bacteria (EB) as biocatalysts to generate electricity. This chapter highlights the untapped potential of sewage sludge, derived from wastewater treatment, as a valuable fuel source within the MFC system. Extensive research has demonstrated the abundance of organic components present in sewage sludge, making it highly amenable to degradation through microbiological pathways within the MFC. Despite the lack of large-scale commercial utilization of MFC technology in wastewater treatment plants, the significant progress and promising findings indicate its effectiveness in addressing the challenges associated with sewage sludge management. The MFC system not only facilitates the simultaneous generation of energy but also contributes to bioremediation efforts. The redox potential inherent in MFCs enables this dual functionality, effectively integrating energy production with the treatment of sewage sludge. This chapter sheds light on the potential of MFC technology as an advanced approach for sewage sludge treatment. By harnessing the capabilities of electrogenic bacteria and capitalizing on the rich organic composition of sewage sludge, MFCs offer a sustainable solution that can simultaneously address energy needs and promote efficient waste management in wastewater treatment plants. The abundant and promising data accumulated thus far underscore the viability and potential of MFCs in mitigating the challenges associated with sewage sludge waste.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
To VHP, Nguyen TV, Vigneswaran S, Ngo HH (2016) A review on sludge dewatering indices. Water Sci Technol 74(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.102
Hanum F et al. (2019) Treatment of sewage sludge using anaerobic digestion in Malaysia: current state and challenges. Front Energy Res 7(MAR):1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2019.00019
Kasina M, Kowalski PR, Michalik M (2016) Metals accumulation during thermal processing of sewage sludge—characterization of fly ash and Air Pollution Control (APC) residues. Energy Procedia 97:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2016.10.012
Indah Water Konsortium (2013) Indah water cleaning the unseen
Wu B, Dai X, Chai X (2020) Critical review on dewatering of sewage sludge: influential mechanism, conditioning technologies and implications to sludge re-utilizations. Water Res 180:115912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115912
Duan N, Dong B, Wu B, Dai X (2012) High-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge under mesophilic conditions: feasibility study. Biores Technol 104:150–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.10.090
Dai X, Duan N, Dong B, Dai L (2013) High-solids anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste in comparison with mono digestions: stability and performance. Waste Manage 33(2):308–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.10.018
Tian K, Liu W-J, Qian T-T, Jiang H, Yu H-Q (Sep.2014) Investigation on the evolution of n-containing organic compounds during pyrolysis of sewage sludge. Environ Sci Technol 48(18):10888–10896. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5022137
Zhao M, Wang F, Fan Y, Raheem A, Zhou H (2019) Low-temperature alkaline pyrolysis of sewage sludge for enhanced H2 production with in-situ carbon capture. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44(16):8020–8027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.02.040
Yu G, Chen D, Arena U, Huang Z, Dai X (2018) Reforming sewage sludge pyrolysis volatile with Fe-embedded char: minimization of liquid product yield. Waste Manage 73:464–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.08.004
Baru PA, Hassan S (2018) Akademia Baru characterization of Malaysian sewage sludge dried using thermal dryer. J Adv Res Fluid Mech Therm Sci 5(January):24–29
Tambo N, Kobayashi M, Thebault P, Haubry A (1982) Sludge treatment and disposal. Water Supply 1(2/3). https://doi.org/10.1142/9781848160798_0015
Hii K, Baroutian S, Parthasarathy R, Gapes DJ, Eshtiaghi N (2014) Bioresource Technology: a review of wet air oxidation and thermal hydrolysis technologies in sludge treatment. Biores Technol 155:289–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.066
Technical EEA (2020) Horizon 2020 Mediterranean report, no. 6
Lou XF, Nair J (2009) The impact of landfilling and composting on greenhouse gas emissions—a review. Biores Technol 100(16):3792–3798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.12.006
Mancini G, Luciano A, Bolzonella D, Fatone F, Viotti P, Fino D (2021) A water-waste-energy nexus approach to bridge the sustainability gap in landfill-based waste management regions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 137(October 2020):110441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110441
Oladejo J, Shi K, Luo X, Yang G, Wu T (2019) A review of sludge-to-energy recovery methods. Energies 12(1):1–38. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010060
Sharma M, Singh J, Baskar C, Kumar A (2018) A comprehensive review on biochar formation and its utilization for wastewater treatment. Pollut Res 37:1–18
Varjani S, Kumar G, Rene ER (2019) Developments in biochar application for pesticide remediation: current knowledge and future research directions. J Environ Manage 232:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.11.043
Bora AP, Gupta DP, Durbha KS (2020) Sewage sludge to bio-fuel: a review on the sustainable approach of transforming sewage waste to alternative fuel. Fuel 259:116262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116262
Vijayaraghavan K (Jan 2019) Recent advancements in biochar preparation, feedstocks, modification, characterization and future applications. Environ Tech Rev 8(1):47–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622515.2019.1631393
Agegnehu G, Srivastava AK, Bird MI (2017) The role of biochar and biochar-compost in improving soil quality and crop performance: a review. Appl Soil Ecol 119:156–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.06.008
Gubišová M et al (2020) Sewage sludge as a soil amendment for growing biomass plant Arundo donax L. Agronomy 10(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050678
Potter MC, Waller AD (Sep 1911) Electrical effects accompanying the decomposition of organic compounds. Proc R Soc London Ser B, Contain Pap Biol Character 84(571):260–276. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.1911.0073
Shamsuddin NA, Mohd Sabri MNI, Tajarudin HA, Shoparwe NF, Makhtar MMZ (May 2021) Effect of thermal pre-treatments method on sludge degradation process prior usage in membrane-less microbial fuel cell for electricity generation. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 76(1):012092. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/765/1/012092
Khoo KS, Chia WY, Tang DYY, Show PL, Chew KW, Chen WH (2020) Nanomaterials utilization in biomass for biofuel and bioenergy production. Energies 13(4):1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040892
Tamboli E, Eswari JS (2019) Chapter 3.2—microbial fuel cell configurations: an overview. Elsevier B.V. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64052-9.00016-9
Piccolino M (Jul 1998) Animal electricity and the birth of electrophysiology: the legacy of Luigi Galvani. Brain Res Bull 46(5):381–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0361-9230(98)00026-4
Bennetto HP, Stirling JL, Tanaka K, Vega CA (Feb1983) Anodic reactions in microbial fuel cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 25(2):559–568. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260250219
Rezaei F, Richard TL, Logan BE (2008) Enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose coupled with electricity generation in a microbial fuel cell. Biotechnol Bioeng 101(6):1163–1169. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22015
Khera J, Chandra A (2012) Microbial fuel cells: recent trends. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect A Phys Sci 82(1):31–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-012-0003-2
Logan BE (2012) Essential data and techniques for conducting microbial fuel cell and other types of bioelectrochemical system experiments. Chemsuschem 5(6):988–994. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201100604
Bullen RA, Arnot TC, Lakeman JB, Walsh FC (May 2006) Biofuel cells and their development. Biosens Bioelectron 21(11):2015–2045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2006.01.030
Shukla A, Suresh P, Berchmans S, Rajendran A (Aug 2004) Biological fuel cells and their applications. Curr Sci 87
Roller SD, Bennetto HP, Delaney GM, Mason JR, Stirling JL, Thurston CF (Mar 1984) Electron-transfer coupling in microbial fuel cells: 1. comparison of redox-mediator reduction rates and respiratory rates of bacteria. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. Biotechnol 34(1):3–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.280340103
Wilkinson S (2000) ‘Gastrobots’—benefits and challenges of microbial fuel cells in food powered robot applications. Auton Robot 9(2):99–111. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008984516499
Ieropoulos I, Melhuish C, Greenman J (2003) Artificial metabolism: towards true energetic autonomy in artificial life. Adv Artif Life: 792–799
Mohd Zaini Makhtar M, Tajarudin HA, Samsudin MDM, Vadivelu VM, Shoparwe NF, Izzah Zainuddin N (Jun 2021). Membrane-less microbial fuel cell: Monte Carlo simulation and sensitivity analysis for COD removal in dewatered sludge. AIP Adv 11(6):65016. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0039014
Logan BE et al (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40(17):5181–5192. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0605016
Pant D, Van Bogaert G, Diels L, Vanbroekhoven K (2010) A review of the substrates used in microbial fuel cells ( MFCs ) for sustainable energy production. Bioresour Technol 101(6):1533–1543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.017
Pham TH et al (2006) Microbial fuel cells in relation to conventional anaerobic digestion technology. Eng Life Sci 6(3):285–292. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.200620121
Li M et al (2018) Microbial fuel cell (MFC) power performance improvement through enhanced microbial electrogenicity. Biotechnol Adv 36(4):1316–1327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.04.010
Debabrata D (2018) Microbial fuel cell: a bioelectrochemical system that converts waste to watts. Springer International, Switzerland
Akiba T, Bennetto HP, Stirling JL, Tanaka K (1987) Electricity production from alkalophilic organisms. Biotech Lett 9(9):611–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01033196
Chabert N, Amin Ali O, Achouak W (2015) All ecosystems potentially host electrogenic bacteria. Bioelectrochemistry 106:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2015.07.004
Danish M et al (2021) Science of the total environment integrated air cathode microbial fuel cell-aerobic bioreactor set-up for enhanced bioelectrodegradation of azo dye Acid Blue 29. Sci Total Environ 756:0–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143752
Pous N, Koch C, Colprim J, Puig S, Harnisch F (2014) Extracellular electron transfer of biocathodes: revealing the potentials for nitrate and nitrite reduction of denitrifying microbiomes dominated by Thiobacillus sp. Electrochem Commun 49:93–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2014.10.011
Guang L, Koomson DA, Jingyu H, Ewusi-Mensah D, Miwornunyuie N (2020) Performance of exoelectrogenic bacteria used in microbial desalination cell technology. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(3):10–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031121
Xing D, Zuo Y, Cheng S, Regan JM, Logan BE (Jun.2008) Electricity generation by Rhodopseudomonas palustris DX-1. Environ Sci Technol 42(11):4146–4151. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800312v
Martínez ÁT et al (2005) Biodegradation of lignocellulosics: microbial, chemical, and enzymatic aspects of the fungal attack of lignin. Int Microbiol 8(3):195–204. https://doi.org/10.2436/im.v8i3.9526
Wesenberg D, Kyriakides I, Agathos SN (2003) White-rot fungi and their enzymes for the treatment of industrial dye effluents. Biotechnol Adv 22(1):161–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2003.08.011
Wilkinson S, Klar J, Applegarth S (Oct 2006) Optimizing biofuel cell performance using a targeted mixed mediator combination. Electroanalysis 18(19–20):2001–2007. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200603621
Sivasankar V, Mylsamy P, Omine K (2018) Microbial fuel cell technology for bioelectricity. Springer International Publishing, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92904-0
Lee Y-K (Nov 2003) Algal nutrition—heterotrophic carbon nutrition. Handb Microalgal Cult :116–124. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470995280.ch7
Kruzic AP, Kreissl JF (May2009) Natural treatment and onsite systems. Water Environ Res 81(10):1346–1360
Juang DF, Lee CH, Hsueh SC (2012) Comparison of electrogenic capabilities of microbial fuel cell with different light power on algae grown cathode. Biores Technol 123:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.07.041
Marsili E, Baron DB, Shikhare ID, Coursolle D, Gralnick JA, Bond DR (2008) Shewanella secretes flavins that mediate extracellular electron transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(10):3968–3973. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0710525105
Konovalova EY et al (May 2018) The microorganisms used for working in microbial fuel cells. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol 1952. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5031979
Logan BE (2009) Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat Rev Microbiol 7(5):375–381. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2113
Schröder U (2007) Anodic electron transfer mechanisms in microbial fuel cells and their energy efficiency. Phys Chem Chem Phys 9(21):2619–2629. https://doi.org/10.1039/b703627m
Feng C et al. (2014) Characterization of exoelectrogenic bacteria enterobacter strains isolated from a microbial fuel cell exposed to copper shock load. PLoS One 9(11). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113379
Wu Y et al (2020) Enhanced current production by exogenous electron mediators via synergy of promoting biofilm formation and the electron shuttling process. Environ Sci Technol 54(12):7217–7225. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00141
Miriam R, Federico Aulenta, Marianna V, Largus T Angenent (2011) Cathodes as electron donors for microbial metabolism: which extracellular electron transfer mechanisms are involved? Bioresour Technol 102(1):324–333, ISSN 0960-8524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.07.008
Bond D, Lovley D (2003) Electricity production by geobacter sulfurreducens attached to electrodes. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(3):1548–1555. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.3.1548
Ieropoulos IA, Greenman J, Melhuish C, Hart J (2005) Comparative study of three types of microbial fuel cell. Enzyme Microb Technol 37(2):238–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.03.006
Kumari S (2012) Studies on marine microbial fuel cell, Doctoral dissertation
Barton SC, Gallaway J, Atanassov P (2004) Enzymatic biofuel cells for implantable and microscale devices. Chem Rev 104(10):4867–4886. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr020719k
Zhao F, Slade RCT, Varcoe JR (2009) Techniques for the study and development of microbial fuel cells: an electrochemical perspective. Chem Soc Rev 38(7):1926–1939. https://doi.org/10.1039/b819866g
Sirinutsomboon B (2014) Modeling of a membraneless single-chamber microbial fuel cell with molasses as an energy source. Int J Energy Environ Eng 5(2–3):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-014-0093-5
Roy S, Marzorati S, Schievano A, Pant D (2017) Microbial fuel cells, vol 3. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409548-9.10122-8
Logan BE, Regan JM (2006) Electricity-producing bacterial communities in microbial fuel cells. Trends Microbiol 14(12):512–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2006.10.003
Du Z, Li H, Gu T (2007) A state of the art review on microbial fuel cells: a promising technology for wastewater treatment and bioenergy. Biotechnol Adv 25:464–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.05.004
Parkash A (2016 July) Microbial fuel cells: a source of bioenergy. Microbial and Biochemical Technology (July). https://doi.org/10.4172/1948-5948.1000293
He Z, Minteer SD, Angenent LT (2005) Electricity generation from artificial wastewater using an upflow microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 39(14):5262–5267. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0502876
Feng C, Tsai C-C, Ma C-Y, Yu C-P, Hou C-H (2017) Integrating cost-effective microbial fuel cells and energy-efficient capacitive deionization for advanced domestic wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 330:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.122
Feng Y, He W, Liu J, Wang X, Qu Y, Ren N (2014) A horizontal plug flow and stackable pilot microbial fuel cell for municipal wastewater treatment. Biores Technol 156:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.104
Santoro C et al. (2018 Feb) Ceramic microbial fuel cells stack: power generation in standard and supercapacitive mode. Sci Rep 8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21404-y
Min B, Logan BE (2004) Continuous electricity generation from domestic wastewater and organic substrates in a flat plate microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 38(21):5809–5814. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0491026
Helder M, Strik DP, Hamelers HVM, Buisman CJN (2012) The flat-plate plant-microbial fuel cell: the effect of a new design on internal resistances. Biotechnol Biofuels 5(1):70. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-5-70
Ding HH, Chang S, Liu Y (Nov 2017) Biological hydrolysis pretreatment on secondary sludge: enhancement of anaerobic digestion and mechanism study. Biores Technol 244(Pt 1):989–995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.064
Calderone L (2019) What is the future of non-renewable resources? Other Energy Topics.
Kumar A, Ogita S, Yau YY (2018) Biofuels: greenhouse gas mitigation and global warming. Springer, India. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-3763-1
IPCC (2014) Climate change 2014, mitigation of climate change. In: Contribution of working group III to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge, UK
IPCC (2014) Climate change. Synthesis report. Contribution of working groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Geneva
Kan S, Chen B, Chen G (2019) Worldwide energy use across global supply chains: Decoupled from economic growth? Appl Energy 250:1235–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.05.104
Ahmad T, Zhang D (2020) A critical review of comparative global historical energy consumption and future demand: the story told so far. Energy Rep 6:1973–1991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2020.07.020
Robert R (2020) Fossil fuels still supply 84 % of world energy—and other eye openers from BP’s annual review
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Universiti Sains Malaysia for the financial support of this study via APEX Era grant (1001/PTEKIND/881004) The authors have declared no conflict of interest for the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mohd Sabri, M.N.I., Mohd Abdul Rasik, N.A., Pusphanathan, K., Mohd Zaini Makhtar, M., Shukor, H. (2023). Microbial Fuel Cell Technology as Advanced Sewage Sludge Treatment. In: Mohd Zaini Makhtar, M., Shukor, H., Yaser, A.Z. (eds) Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC) Applications for Sludge Valorization. Green Energy and Technology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1083-0_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1083-0_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-1082-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-1083-0
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)