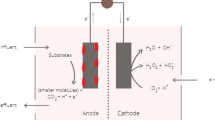
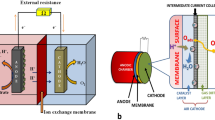
Abstract
This chapter provides a comprehensive overview of the potential application of microbial fuel cell (MFC) technology for the bioremediation of sewage sludge. The abundance of sewage sludge and its associated contaminants presents a significant challenge to environmental sustainability, necessitating the development of innovative approaches for its treatment. The implementation of MFC technology offers a promising alternative approach that can simultaneously provide bioremediation and power generation benefits. The chapter highlights current research and studies on the utilization of MFC for sewage sludge treatment, including an overview of the mechanisms involved in the adaptation of the technology to address environmental issues associated with sewage sludge pollution. The chapter also discusses parameters for enhancing MFC performance, such as the combination of inoculum, substrate pretreatment, sludge concentration, and the effect of nitrate and sulfate. The earliest applications of MFC technology for sludge treatment are also discussed, including the configuration of the system, the use of sludge as a substrate, and the adjustment of pH to suit the system. Early MFC research also focused on nutrient recovery. Overall, the chapter aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the potential contribution of MFC technology to sustainable wastewater management. By utilizing MFC technology for the bioremediation of sewage sludge, researchers can develop innovative solutions for addressing environmental challenges, thereby enhancing environmental sustainability.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zsirai I (2011) Sewage sludge as renewable energy. J Residuals Sci Technol 8(4):165–179. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.1939.0483
Grobelak A, Czerwińska K, Murtaś A (2019) General considerations on sludge disposal, industrial and municipal sludge. In: Industrial and municipal sludge: emerging concerns and scope for resource recovery. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, pp 135–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815907-1.00007-6
Kacprzak M et al (2017) Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development. Environ Res 156:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.03.010
Guangyin Z, Youcai Z (2017) Sewage sludge generation and characteristics. In: Pollution control and resource recovery: sewage sludge. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, pp 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811639-5.00001-2
RPA, WRC, and milieu (2008) Environmental, economic and social impacts of the use of sewage sludge on land final report Part II: report on options and impacts, p 158
Rorat A, Courtois P, Vandenbulcke F, Lemiere S (2019) Sanitary and environmental aspects of sewage sludge management. In: Industrial and municipal sludge: emerging concerns and scope for resource recovery. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, pp 155–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815907-1.00008-8
Tyagi VK, Lo SL (2013) Sludge: a waste or renewable source for energy and resources recovery? Renew Sustain Energ Rev 25(71):708–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.05.029
Fytili D, Zabaniotou A (2008) Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 12(1):116–140
Samolada MC, Zabaniotou AA (2014) Comparative assessment of municipal sewage sludge incineration, gasification and pyrolysis for a sustainable sludge-to-energy management in Greece. Waste Manage 34(2):411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2013.11.003
Siebielska I (2014) Comparison of changes in selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons concentrations during the composting and anaerobic digestion processes of municipal waste and sewage sludge mixtures. Water Sci Technol J Int Assoc Water Pollut Res 70(10):1617–1624. https://doi.org/10.2166/WST.2014.417
Fijalkowski KL, Kacprzak MJ, Rorat A (2014) Occurrence changes of Escherichia coli (including O157:H7 serotype) in wastewater and sewage sludge by quantitation method of (EMA) real time—PCR. New pub: Balaban 52(19–21):3965–3972. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.887499
Kacprzak M, Stan´czyk E, Stan´czyk-Mazanek S, (2003) Changes in the structure of fungal communities of soil treated with sewage sludge. Biol Fertil Soils 38:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-003-0633-2
Farzadkia M, Bazrafshan E (2014) Lime stabilization of waste activated sludge. Health Scope 3:1–5
Olszewski JM, Lozano N, Haines C, Rice CP, Ramirez M, Torrents A (2013) The effect of liming on antibacterial and hormone levels in wastewater biosolids. J Environ Sci Health. Part A, Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 48(8):862–870. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2013.761488
Dong K (2020) How renewable energy consumption lower global CO2 emissions? evidence from countries with different income levels, vol 2017, pp 1665–1698. https://doi.org/10.1111/twec.12898.
BP, “BP Statistical Review of World Energy 2020,” 2020
NACWA (2010) Renewable energy resources: banking on biosolids, p 23
Gude VG (2018) Wastewater treatment in microbial fuel cells—an overview. J Clean Prod 122:287–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.02.022
Katuri KP, Scott K, Head IM, Picioreanu C, Curtis TP (2011) Microbial fuel cells meet with external resistance. Bioresour Technol 102(3):2758–2766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.147
Andreoli CV, von Sperling M, Fernandes F (2007) Sludge treatment and disposal, vol 1, IWA Publishing. https://doi.org/10.2166/9781780402130
Santoro C, Arbizzani C, Erable B, Ieropoulos I (2017) Microbial fuel cells: from fundamentals to applications: a review. J Power Sources 356:225–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.03.109
Gajda I, Greenman J, Ieropoulos IA (2018) Recent advancements in real-world microbial fuel cell applications. Curr Opin Electrochem 11:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2018.09.006
Ho NAD, Babel S, Sombatmankhong K (2018) Bio-electrochemical system for recovery of silver coupled with power generation and wastewater treatment from silver (I) diammine complex. J Water Process Eng 23:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2018.04.001
Fornero JJ, Rosenbaum M, Angenent T (2010) Electric power generation from municipal, food, and animal wastewaters using microbial fuel cells. Electroanalysis 22(7–8):832–843. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200980011
Omeroglu S, Sanin FD (2016) Bioelectricity generation from wastewater sludge using microbial fuel cells: a critical review. Clean Soil Air Water 44(9999):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201500829
Ucar D, Zhang Y, Angelidaki I, Franks AE (2007) An overview of electron acceptors in microbial fuel cells. Front Microbiol 8:643. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00643
Logan BE (ed) (2008). Wiley, Hoboken, NJ
Du Z, Li H, Gu T (2007) A state of the art review on microbial fuel cells: a promising technology for wastewater treatment and bioenergy. 25:464–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.05.004
Ahn Y, Zhang F, Logan BE (2014) Air humidity and water pressure effects on the performance of air-cathode microbial fuel cell cathodes. J Power Sour 247:655–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.08.084
Feng C, Huang L, Yu H, Yi X, Wei C (2015) Simultaneous phenol removal, nitrification and denitrification using microbial fuel cell technology. Water Res 76:160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2015.03.001
Jiang J, Zhao Q, Zhang J, Zhang G, Lee D (2009) Electricity generation from bio-treatment of sewage sludge with microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 100(23):5808–5812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.06.076
Logan BE, Wallack MJ, Kim K, He W, Feng Y, Saikaly PE (2015) Assessment of microbial fuel cell configurations and power densities. Environ Sci Technol Lett 2:206–214. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.5b00180
Fazal U et al (2021) Microbial fuel cell: study of bioresource potential of dairy effluent and Associated Process Limitations. Research Square, pp 1–17
Shamsudin NA, Sabri MNIM, Tajarudin HA, Mokhtar AMA, Makhtar MMZ (2022) The future promising alternative renewable energy from microbial fuel cell BT. In: Yaser AZ, Tajarudin HA, Embrandiri A (eds) Waste management, processing and valorisation. Springer, Singapore, pp 235–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7653-6_13
Seo Y, Kang H, Chang S, Lee Y, Cho K (2017) Toxic/hazardous substances and environmental engineering effects of nitrate and sulfate on the performance and bacterial community structure of membrane- less single-chamber air-cathode microbial fuel cells. J Environ Sci Health, Part A 53(1):13–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2017.1366242
Rajasulochana P, Preethy V (2016) Comparison on efficiency of various techniques in treatment of waste and sewage water—a comprehensive review. Resource-efficient Technol 2(4):175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.REFFIT.2016.09.004
Vu HT, Min B (2019) Integration of submersible microbial fuel cell in anaerobic digestion for enhanced production of methane and current at varying glucose levels. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44(14):7574–7582. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHYDENE.2019.01.091
Wang Z, Mei X, Ma J, Wu Z (2012) Recent advances in microbial fuel cells integrated with sludge treatment. Chem Eng Technol 35(10):1733–1743. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.201200132
Munoz-Cupa C, Hu Y, Xu C, Bassi A (2021) An overview of microbial fuel cell usage in wastewater treatment, resource recovery and energy production. Sci Total Environ 754:142429. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.142429
Das S, Mangwani N (2010) Recent developments in microbial fuel cells. J Sci Ind Res 69:727–731
Abourached C, Lesnik KL, Liu H (2014) Enhanced power generation and energy conversion of sewage sludge by CEA—microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 166:229–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.027
Ting CH, Lee DJ (2007) Production of hydrogen and methane from wastewater sludge using anaerobic fermentation. Int J Hydrogen Energy 32(6):677–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHYDENE.2006.06.063
Hu Z (2008) Electricity generation by a baffle-chamber membraneless microbial fuel cell. J Power Sour 179(1):27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.12.094
Dentel SK, Strogen B, Chiu P (2004) Direct generation of electricity from sludges and other liquid wastes. Water Sci Technol 50(9):161–168. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2004.0561
Liu Z et al (2009) Production of electricity from surplus sludge using a single chamber floating-cathode microbial fuel cell. Water Sci Technol 60(9):2399–2404. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2009.313
Yuan Y, Chen Q, Zhou S, Zhuang L, Hu P (2011) Improved electricity production from sewage sludge under alkaline conditions in an insert-type air-cathode microbial fuel cell. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 87(1):80–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2686
Fischer F, Bastian C, Happe M, Mabillard E, Schmidt N (2011) Microbial fuel cell enables phosphate recovery from digested sewage sludge as struvite. Bioresour Technol 102(10):5824–5830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.02.089
Ge Z, Zhang F, Grimaud J, Hurst J, He Z (2013) Long-term investigation of microbial fuel cells treating primary sludge or digested sludge. Bioresour Technol 136:509–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.016
Nandy A, Sharma M, Venkatesan SV, Taylor N, Gieg L, Thangadurai V (2019) Comparative evaluation of coated and non-coated carbon electrodes in a microbial fuel cell for treatment of municipal sludge. Energies 12(6):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12061034
Mohd Zaini Makhtar M, Tajarudin HA, Samsudin MDM, Vadivelu VM, Shoparwe NF, ‘Izzah Zainuddin N (2021) Membrane-less microbial fuel cell: Monte Carlo simulation and sensitivity analysis for COD removal in dewatered sludge. AIP Adv 11(6):65016. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0039014
Pant D, Van Bogaert G, Diels L, Vanbroekhoven K (2010) A review of the substrates used in microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for sustainable energy production. Bioresour Technol 101(6):1533–1543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.017
Liang P, Huang X, Fan MZ, Cao XX, Wang C (2007) Composition and distribution of internal resistance in three types of microbial fuel cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77(3):551–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1193-4
Liu Z, Liu J, Zhang S, Su Z (2009) Study of operational performance and electrical response on mediator-less microbial fuel cells fed with carbon-and protein-rich substrates. Biochem Eng J 45(3):185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2009.03.011
Chabert N, Amin Ali O, Achouak W (2015) All ecosystems potentially host electrogenic bacteria. Bioelectrochem 106:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2015.07.004
Logan BE, Regan JM (2006) Electricity-producing bacterial communities in microbial fuel cells. Trends in Microbiol 14(12):512–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2006.10.003
Wang H, Ren ZJ (2014) Bioelectrochemical metal recovery from wastewater: a review. Water Res 66:219–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2014.08.013
Mathuriya AS, Yakhmi JV (2014) Microbial fuel cells to recover heavy metals. Environ Chem Lett 12(4):483–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-014-0474-2/FIGURES/3
Li Z, Zhang X, Lei L (December 2008) Electricity production during the treatment of real electroplating wastewater containing Cr6+ using microbial fuel cell. Process Biochem 43(12):1352–1358. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2008.08.005
Choi C, Cui Y (March 2012) Recovery of silver from wastewater coupled with power generation using a microbial fuel cell. Biores Technol 107:522–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2011.12.058
Sun J, Hu Y, Bi Z, Cao Y (2009) Improved performance of air-cathode single-chamber microbial fuel cell for wastewater treatment using microfiltration membranes and multiple sludge inoculation. J Power Sour 187(2):471–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.11.022
Baranitharan E et al (2015) Enhanced power generation using controlled inoculum from palm oil mill effluent fed microbial fuel cell. Fuel 143:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.11.030
Xie B, Liu H, Yan Y (2009) Improvement of the activity of anaerobic sludge by low-intensity ultrasound. J Environ Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.09.004
Zhu H, Béland M (2006) Evaluation of alternative methods of preparing hydrogen producing seeds from digested wastewater sludge. Int J Hydrogen Energy 14(31):1980–1988. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHYDENE.2006.01.019
More TT, Ghangrekar MM (2010) Improving performance of microbial fuel cell with ultrasonication pre-treatment of mixed anaerobic inoculum sludge. Bioresour Technol 101(2):562–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.08.045
Khan MR, Amin MSA, Sarker S, Ferdaus K (2012) Design and fabrication of membrane less microbial fuel cell (ML-MFC) using food industries wastewater for power generation. J Chem Eng 27(2):55–59
Amin MSA, Haque T, Tarannum R, Khan MR (2014) Wastewater treatment and electricity generation by membrane less microbial fuel. Int J Environ Eng 6(3):314. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijee.2014.064306
Palanisamy G, Jung HY, Sadhasivam T, Kurkuri MD, Kim SC, Roh SH (2019) A comprehensive review on microbial fuel cell technologies: processes, utilization, and advanced developments in electrodes and membranes. J Clean Prod 221:598–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.172
Vavilin VA, Rytov SV, Lokshina LY (1996) A description of hydrolysis kinetics in anaerobic degradation of particulate organic matter. Bioresour Technol 56(2–3):229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-8524(96)00034-X
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Universiti Sains Malaysia for the financial support of this study via APEX Era grant (1001/PTEKIND/881004). The authors have declared no conflict of interest for the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mohamad Sobri, M.F., Mohd Zaini Makhtar, M. (2023). Application of Microbial Fuel Cell for Bioremediation of Sewage Sludge. In: Mohd Zaini Makhtar, M., Shukor, H., Yaser, A.Z. (eds) Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC) Applications for Sludge Valorization. Green Energy and Technology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1083-0_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1083-0_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-1082-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-1083-0
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)