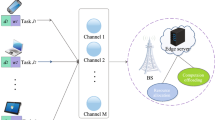
Abstract
Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) is used to enhance the data processing capability of low-power networks and has now become an efficient computing paradigm. In this paper, an edge-cloud collaborative system composed of multiple terminals (Mobile Terminal, MT) and its resource allocation strategy are considered. In order to reduce the total delay of MTs, a variety of offloading modes are adopted, and an edge-cloud collaborative task offloading algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning (DDPG) is proposed. The coordinated serial task dynamic allocation processing provides approximately optimal task allocation and offloading strategies for different user equipment applications. The simulation results show that compared with the Deep Q Neural Network (DQN) algorithm and the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm, the proposed algorithm significantly improves the maximum performance gain. Experiments show that the DDPG algorithm has better system performance than the traditional scheme, and improves the service quality of the application.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu, H., Jin, F., Lang, S.: Research review of computing offloading technology in mobile edge computing environment. Comput. Eng. Appl. 57(14), 60–74 (2021)
Lv, Z., Li, J., Dong, C., et al.: Deep learning in the COVID-19 epidemic: a deep model for urban traffic revitalization index. Data Knowl. Eng. 135, 101912 (2021)
Liang, G., Wang, Q., Xin, J., et al.: Overview of mobile edge computing resource allocation. J. Inf. Secur. 6(03), 227–256 (2021)
Lv, Z., Li, J., Dong, C., et al.: DeepSTF: a deep spatial–temporal forecast model of taxi flow. Comput. J. 66, 565–580 (2021)
Yu, B., Li, X., Pan, C., et al.: Edge-cloud collaborative resource allocation algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning. Comput. Sci. 49(07), 248–253 (2022)
Shi, J., Du, J., Wang, J., et al.: Priority-aware task offloading in vehicular fog computing based on deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(12), 16067–16081 (2020)
Zhang, L., Zhang, Z.Y., Min, L., et al.: Task offloading and trajectory control for UAV-assisted mobile edge computing using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Access 9, 53708–53719 (2021)
Chen, Y., Gu, W., Li, K.: Dynamic task offloading for internet of things in mobile edge computing via deep reinforcement learning. Int. J. Commun. Syst. e5154 (2022)
Cao, Z., Zhou, P., Li, R., et al.: Multiagent deep reinforcement learning for joint multichannel access and task offloading of mobile-edge computing in industry 4.0. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(7), 6201–6213 (2020)
Lv, Z., Li, J., Dong, C., et al.: DeepPTP: A deep pedestrian trajectory prediction model for traffic intersection. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. (TIIS) 15(7), 2321–2338 (2021)
Zhang, F., Zhao, J., Liu, D., et al.: Edge-cloud collaborative serial task offloading algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning. J. Univ. Electron. Sci. Technol. China 50(03), 398–404 (2021)
Xu, Z., Lv, Z., Li, J., et al.: A novel perspective on travel demand prediction considering natural environmental and socioeconomic factors. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 15, 136–159 (2022)
Liu, W., Huang, Y., Du, W., et al.: Resource-constrained serial task offloading strategy in mobile edge computing. J. Softw. 31(06), 1889–1908 (2020)
Xu, Z., Li, J., Lv, Z., et al.: A graph spatial-temporal model for predicting population density of key areas. Comput. Electr. Eng. 93, 107235 (2021)
Xu, Z., Li, J., Lv, Z., et al.: A classification method for urban functional regions based on the transfer rate of empty cars. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 16(2), 133–147 (2022)
Zhang, H., Li, H., Chen, S., et al.: Task offloading and resource optimization based on mobile edge computing in ultra-dense networks. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 41(05), 1194–1201 (2019)
Lv, Z., Wang, X., Cheng, Z., et al.: A new approach to COVID-19 data mining: a deep spatial–temporal prediction model based on tree structure for traffic revitalization index. Data Knowl. Eng. 146, 102193 (2023)
Li, H., Lv, Z., Li, J., et al.: Traffic flow forecasting in the COVID-19: a deep spatial-temporal model based on discrete wavelet transformation. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 17, 1–28 (2022)
Wang, Y., Fan, J., Wang, C.: A two-stage task migration strategy based on game theory in the cloud edge environment. Comput. Appl. 41(05), 1392–1398 (2021)
Zhao, H., Zhang, T., Chen, Y., et al.: Task distribution and offloading algorithm for in-vehicle edge network based on DQN. J. Commun. 41(10), 172–178 (2020)
Tang, M., Wong, V.W.S.: Deep reinforcement learning for task offloading in mobile edge computing systems. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 21(6), 1985–1997 (2020)
Shen, H., Jiang, Y., Deng, F., et al.: Task unloading strategy of multi UAV for transmission line inspection based on deep reinforcement learning. Electronics 11(14), 2188 (2022)
Wang, J., Hu, J., Min, G., et al.: Dependent task offloading for edge computing based on deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Comput. 71(10), 2449–2461 (2021)
Wang, J., Hu, J., Min, G., et al.: Fast adaptive task offloading in edge computing based on meta reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 32(1), 242–253 (2020)
Zhao, N., Ye, Z., Pei, Y., et al.: Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for task offloading in UAV-assisted mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 21(9), 6949–6960 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kong, Y., Li, Y., Wang, J., Yin, S. (2024). Edge Computing Task Unloading Decision Optimization Algorithm Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. In: Wang, L., Qiu, T., Lin, C., Wang, X. (eds) Wireless Sensor Networks. CWSN 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1994. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-1010-2_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-1010-2_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-1009-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-1010-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)