Abstract
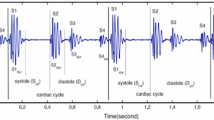
Phonocardiogram (PCG), one of the auscultation-based technique used as a diagnostic method of the heart condition, is a patient’s heart sound recording. The simplicity, non-invasive, and passive brings an advantage to implement this method as a diagnosis system. Nevertheless, PCG recordings are often interrupted by various sources, for instance, noise from the surrounding environment, respiratory or lung sounds, power disturbances, and movement of the surrounding skin, so inhibit the PCG implementation as a diagnosis method. Therefore, it requires an appropriate method to eliminate the noise that exists in the PCG signals. To get an appropriate method in the PCG system, we compare the Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD) and Double-Density Discrete Wavelet Transform (DD-DWT) method as a denoising system to minimize the noise effect in the PCG signal. Observation of the system performance used thirty data from the normal heart sound added by the additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN), and the performance parameter used signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and mean square error (MSE). Based on the result, we obtained the best SNR value of 25.55 dB for the EMD method and SNR value of 18.19 dB for DD-DWT. Also, we perceived the best MSE value of 0.01% for the EMD method, and 0.42% for the DD-DWT. The results obtained show that the denoising process using the EMD method is better than the DD-DWT to implement in the PCG signal.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali MN, El-Dahsan EA, Yahia AH (2017) Denoising of heart sound signals using discrete wavelet transform. J Circuits Syst Signal Process 36:4482
Dewangan N, Potdar RM (2014) Noise cancellation using adaptive filter for PCG signal. J Emerg Trend Tech Comput Sci 3:38
Low JX, Choo KW (2018) IoT-enabled heart monitoring device with signal denoising and segmentation using discrete wavelet transform. International conference on control, automation, robotic and vision, vol 15, p 119
Sahoo PK, Thakkar HK, Lee MY (2017) A cardiac early warning system with multi channel SCG and ECG monitoring for mobile health. J Sensors 17:1
Ri O et al (2015) Classification of heart sound signal using multi-modal features. J Eng Sci Tech 58:165
Swarup S, Makaryus AN (2018) Digital stethoscope: technology update. J Med Devices 18:29
Kumar P, Kumar A (2017) An adaptive thresholding method for the wavelet based denoising of phonocardiogram signal. J Biomed Signal Process Control 38:388
Soman KP, Ramachandran KI, Resmi NG (2010) Insight into wavelet from theory to practice, 3rd edn. Phi Learning Private Limited, New Delhi
Hahn SL (1996) Hilbert transforms in signal processing. Artech House, London
Mohguen W, Bekka RE (2017) New denoising method based on empirical mode decomposition and improved thresholding function. J Phys Conf Ser 787:012014
Boudaraa AO, Cexus JC, Saidi Z (2005) EMD-based signal noise reduction. J Inf Commun Eng 1:96
Viranda RS, Jusak J, Puspasari I (2017) Ektraksi ciri dan identifikasi sinyal suara jantung S1 dan S2 phonocardigram (PCG) menggunakan metode wavlet packet transform. J Control Netw Syst 6:187
Abdullah H, Cvetkovic D (2013) Double density wavelet for EEG signal denoising. International conference on machine learning and computer science, vol 2, p 51
Vimala C, Priya PA (2014) Noise reduction based on double density discrete wavelet transform. IEEE international conference on smart structure and systems, p 15
Liu C et al (2016) An open access database for the evaluation of heart sound algorithms. J Physiol Meas 12:2181
Goldberger A, Amaral L, Glass L, Hausdorff J, Ivanov PC, Mark R, Mietus JE, Moody B, Peng CK, Stanley HE (2001) PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals, Circulation 101:215
Selesnick IW (2001) The double density DWT. J Wavelet Signal Image Anal 39
Zulherman D, Hendry J, Adam IF (2020) Perbandingan real valued dan complex wavelet transform pada denoising sinyal fetal-phonocardiograms. J Nas Tek Elektro dan Teknol Inf 9:63
Ismail S, Siddiqi I, Akram U (2018) Localization and classification of heart beats in phonocardiography signals-a comprehensive review. EURASIP J Adv Sign Process 26:1
Salman AH, Ahmadi N, Mengko R, Langi AZR, Mengko TLR (2015) Performance comparison of denoising methods for heart sound signal. International symposium on intelligent signals processing and communication
Acknowledgements
Thank you to Lembaga Penelitian dan Pengabdian Masyarakat (LPPM) Institut Teknologi Telkom Purwokerto and Biomedical Engineering Program for funding this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fatmawati, T.Y., Yuliani, A., Afandi, M.A., Zulherman, D. (2021). Comparative Analysis of the Phonocardiogram Denoising System Based-on Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD) and Double-Density Discrete Wavelet Transform (DDDWT). In: Triwiyanto, Nugroho, H.A., Rizal, A., Caesarendra, W. (eds) Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Electronics, Biomedical Engineering, and Health Informatics. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 746. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6926-9_52
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6926-9_52
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-33-6925-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-33-6926-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)