Abstract
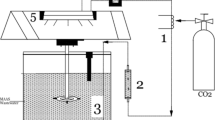
A chemical fertilizer plant in Kedah, Malaysia produced high Ammonia-nitrogen content in the discharge outlet, exceeding the allowable standard limit (Standard B). The standard is based on Environment Quality Act (EQA) 1974, to ensure the integrity of water is maintained. At the plant, current wastewater treatment used is reed bed system, which is incapable to treat the excessive amount of Ammonia-nitrogen. Feasibility of extended aeration activated sludge process (ASP) was then discovered in this study. Objective of this study is to determine the impact of treating wastewater generated from the chemical fertilizer plant using bench scale extended aeration activated sludge system at 20% of contamination, diluted with domestic wastewater of an average of 500 mg/L chemical oxygen demand concentration. Bench scale ASP was set up using 5000 mg/L initial biomass, a 20 L’ influent tank with a heavy-duty mixer, connected to a pump via 10 mm tube at 0.1 rpm which is equivalent to 5 L of water infused into the aeration tank for 24 h consistently, and finally discharged into an effluent tank. Influent and effluent samples were monitored for Total Suspended Solids (TSS), Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Nitrate (NO3–1), Ammonia (NH3), and Total Phosphorus (PO43−) while the mixed liquor sample was monitored for Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS) and Mixed Liquor Volatile Suspended Solids (MLVSS).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arashiro, L.T., Ferrer, I., Rousseau, D.P.L., Van Hulle, S.W.H., Garfi, M.: The effect of primary treatment of wastewater in high rate algal pond systems: biomass and bioenergy recovery. Bioresour Technol 280, 27–36 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.096
Karia, G.L., Christian, R.A.: Wastewater Treatment Concepts and Design Approach, 1st edn. Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi (2006)
Stott, R.: Fate and behaviour of parasites in wastewater treatment systems. In: Handbook of Water and Wastewater Microbiology, pp. 491–521 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-012470100-7/50032-7
Pepper, I.L., Gerba, C.P., Gentry, T.J.: Environmental Microbiology. Academic Press, San Diego, CA (2015)
Bitton, G.: Wastewater Microbiology. Wiley-Liss, Hoboken (2011)
Muralikrishna, I.V., Manickam, V.: Environmental Management: Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2017)
Berlicki, L., et al.: N-substituted aminomethanephosphonic and aminomethane-P-methylphosphinic acids as inhibitors of ureases. Amino Acids 42(5), 1937–1945 (2012)
Acknowledgment
To the greatest extent, intense gratitude goes to Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS for nurturing and guiding the respective researchers excellently throughout this study. The university has been generous in providing recherché insight in the aid to perform the project and environmental engineering illiteracy that will benefit mankind for the rest of time.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Md Hafiz, M.F.U.B., Mohamed Kutty, S.R.B., Hakmi, S.N.B.S.I. (2021). Impact of Treating Ammonia-Nitrogen Contamination from Chemical Fertilizer Plant Using Extended Aeration Activated Sludge System. In: Mohammed, B.S., Shafiq, N., Rahman M. Kutty, S., Mohamad, H., Balogun, AL. (eds) ICCOEE2020. ICCOEE 2021. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 132. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6311-3_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6311-3_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-33-6310-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-33-6311-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)