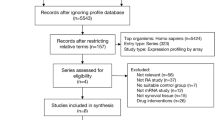
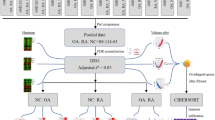
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term systemic inflammatory disease that primarily attacks synovial joints and ultimately leads to their destruction. The disease is characterized by series of processes such as inflammation in the joints, synovial hyperplasia, and cartilage destruction leading to bone erosion. Since RA being a chronic inflammatory complex disease, there is a constant need to develop novel and dynamic treatment to cure the disease. In the present research, network biology and gene expression profiling technology are integrated to predict novel key regulatory molecules, biological pathways, and functional network associated with RA. The microarray datasets of synovial fibroblast (SF) (GSE7669) and macrophages (GSE10500 and GSE8286), which are the primary cells in the synovium and reported as the key players in the pathophysiology of RA, were considered for identification of signature molecules related to RA. The statistical analysis was performed using false discovery rate (FDR), t-test, one-way anova, and Pearson correlation with favorable p-value. The K-core analysis depicted the change in network topology which consisted of up- and downregulated genes network, resulted in six novel meaningful networks with seed genes OAS2, VCAN, CPB1, ZNF516, ACP2, and OLFML2B. Hence, we propose that, differential gene expression network studies will be a standard step to elucidate novel expressed gene(s) globally.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anitua E, Sánchez M, Nurden AT, Zalduendo MM, De La Fuente M, Azofra J, Andía I (2007) Platelet-released growth factors enhance the secretion of hyaluronic acid and induce hepatocyte growth factor production by synovial fibroblasts from arthritic patients. Rheumatology 46(12):1769–1772
Athanasou NA (1995) Synovial macrophages. Ann Rheum Dis 54(5):392
Bauer JW, Bilgic H, Baechler EC (2009) Gene-expression profiling in rheumatic disease: tools and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Rheumatol 5(5):257–265
Begley TJ, Rosenbach AS, Ideker T, Samson LD (2002) Damage recovery pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae revealed by genomic phenotyping and interactome mapping1 1 NIH grants RO1-CA-55042 and P30-ES02109; NIH training grant ES07155 and National Research Service Award F32-ES11733 (to TJB). Mol Cancer Res 1(2):103–112
Chand Y, Alam MA (2012) Network biology approach for identifying key regulatory genes by expression based study of breast cancer. Bioinformation 8(23):1132
Cho CH, Koh YJ, Han J, Sung HK, Lee HJ, Morisada T, Koh GY (2007). Angiogenic role of LYVE-1-positive macrophages in adipose tissue. Circ Res 100(4):e47–e57
Du XY, Zabel BA, Myles T, Allen SJ, Handel TM, Lee PP, Leung LL (2009) Regulation of chemerin bioactivity by plasma carboxypeptidase N, carboxypeptidase B (activated thrombin-activable fibrinolysis inhibitor), and platelets. J Biol Chem 284(2):751–758
Fujimoto T, Kawashima H, Tanaka T, Hirose M, Toyama-Sorimachi N, Matsuzawa Y, Miyasaka M (2001) CD44 binds a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, aggrecan. Int Immunol 13(3):359–366
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA (2004) Affy—analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20(3):307–315
Geurts J, Vermeij EA, Pohlers D, Arntz OJ, Kinne RW, van den Berg WB, van de Loo FA (2011) A novel Saa3-promoter reporter distinguishes inflammatory subtypes in experimental arthritis and human synovial fibroblasts. Ann Rheum Dis 70(7):1311–1319
Han C, Robinson DW, Hackett MV, Paramore LC, Fraeman KH, Bala MV (2006) Cardiovascular disease and risk factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 33(11):2167–2172
Häupl T, Stuhlmüller B, Grützkau A, Radbruch A, Burmester GR (2010) Does gene expression analysis inform us in rheumatoid arthritis? Ann Rheum Dis 69(suppl 1):i37–i42
Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I, Gay RE, Gay S, Pap T (2006) Synovial fibroblasts: key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 45(6):669–675
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F, Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U, Speed TP (2003) Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics 4(2):249–264
Ito TK, Ishii G, Chiba H, Ochiai A (2007) The VEGF angiogenic switch of fibroblasts is regulated by MMP-7 from cancer cells. Oncogene 26(51):7194–7203
Jones JA, Chang DT, Meyerson H, Colton E, Kwon IK, Matsuda T, Anderson JM (2007) Proteomic analysis and quantification of cytokines and chemokines from biomaterial surface-adherent macrophages and foreign body giant cells. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 83(3):585–596
Kim TH, Choi SJ, Lee YH, Song GG, Ji JD (2014) Gene expression profile predicting the response to anti-TNF treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis; analysis of GEO datasets. Jt Bone Spine 81(4):325–330
Kobayashi H, Puri P, O’Briain DS, Surana R, Miyano T (1997) Hepatic overexpression of MHC class II antigens and macrophage-associated antigens (CD68) in patients with biliary atresia of poor prognosis. J Pediatr Surg 32(4):590–593
Kovar DR, Wu JQ, Pollard TD (2005) Profilin-mediated competition between capping protein and formin Cdc12p during cytokinesis in fission yeast. Mol Biol Cell 16(5):2313–2324
Lepus CM, Song JJ, Wang Q, Wagner CA, Lindstrom TM, Chu CR, Robinson WH (2014) Brief report: carboxypeptidase B serves as a protective mediator in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(1):101–106
Li X, Wu M, Kwoh CK, Ng SK (2010) Computational approaches for detecting protein complexes from protein interaction networks: a survey. BMC Genom 11(suppl 1):S3
Liu H, Shi B, Huang CC, Eksarko P, Pope RM (2008) Transcriptional diversity during monocyte to macrophage differentiation. Immunol Lett 117(1):70–80
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena P, Sica A (2002) Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol 23(11):549–555
Marcotte EM, Pellegrini M, Thompson MJ, Yeates TO, Eisenberg D (1999) A combined algorithm for genome-wide prediction of protein function. Nature 402(6757):83–86
Mor A, Abramson SB, Pillinger MH (2005) The fibroblast-like synovial cell in rheumatoid arthritis: a key player in inflammation and joint destruction. Clin Immunol 115(2):118–128
Nelson RH (2013) Hyperlipidemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Prim Care Clin Off Pract 40(1):195–211
Ng A, Bursteinas B, Gao Q, Mollison E, Zvelebil M (2006) pSTIING: a ‘systems’ approach towards integrating signalling pathways, interaction and transcriptional regulatory networks in inflammation and cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 34(suppl 1):D527–D534
Pantoja-Uceda D, Arolas JL, García P, López-Hernández E, Padró D, Aviles FX, Blanco FJ (2008) The NMR structure and dynamics of the two-domain tick carboxypeptidase inhibitor reveal flexibility in its free form and stiffness upon binding to human carboxypeptidase b†‡. Biochemistry 47(27):7066–7078
Perides G, Biviano F, Bignami A (1991) Interaction of a brain extracellular matrix protein with hyaluronic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) (General Subjects) 1075(3):248–258
Raman MP, Singh S, Devi PR, Velmurugan D (2012) Uncovering potential drug targets for tuberculosis using protein networks. Bioinformation 8(9):403
Rossol M, Schubert K, Meusch U, Schulz A, Biedermann B, Grosche J, Wagner U (2013) Tumor necrosis factor receptor type I expression of CD4+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis enables them to follow tumor necrosis factor gradients into the rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum 65(6):1468–1476
Sadler AJ, Williams BR (2008) Interferon-inducible antiviral effectors. Nat Rev Immunol 8(7):559–568
Sengupta U, Ukil S, Dimitrova N, Agrawal S (2009) Expression-based network biology identifies alteration in key regulatory pathways of type 2 diabetes and associated risk/complications. PLoS ONE 4(12):e8100
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504
Smith RS, Smith TJ, Blieden TM, Phipps RP (1997) Fibroblasts as sentinel cells. Synthesis of chemokines and regulation of inflammation. Am J Pathol 151(2):317
Snijesh VP, Singh S (2014) Molecular modeling and network based approach in explaining the medicinal properties of nyctanthes arbortristis, lippia nodiflora for rheumatoid arthritis. J Bioinform Intell Control 3(1):31–38
Song JJ, Hwang I, Cho KH, Garcia MA, Kim AJ, Wang TH, Robinson WH (2011) Plasma carboxypeptidase B downregulates inflammatory responses in autoimmune arthritis. J Clin Invest 121(9):3517–3527
Szekanecz Z, Koch AE (2007) Macrophages and their products in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 19(3):289–295
Tornow S, Mewes HW (2003) Functional modules by relating protein interaction networks and gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 31(21):6283–6289
van Baarsen LG, Wijbrandts CA, Rustenburg F, Cantaert T, van der Pouw TC (2010) Regulation of IFN response gene activity during infliximab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with clinical response to treatment. Arthritis Res Ther 12(1):11
van Oorschot RA, Birmingham V, Porter PA, Kammerer CM, VandeBerg JL (1993) Linkage between complement components 6 and 7 and glutamic pyruvate transaminase in the marsupialMonodelphis domestica. Biochem Genet 31(5–6):215–222
Varatharajan S, Karathedath S, Velayudhan SR, Srivastava A, Mathews V, Balasubramanian P (2013) Harnessing gene expression profiling in search of new candidate genes for Ara-C resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 122(21):1299
Westling J, Gottschall P, Thompson V, Cockburn A, Perides G, Zimmermann D, Sandy J (2004) ADAMTS4 (aggrecanase-1) cleaves human brain versican V2 at Glu405-Gln406 to generate glial hyaluronate binding protein. Biochem J 377:787–795
Yarilina A, Park-Min KH, Antoniv T, Hu X, Ivashkiv LB (2008) TNF activates an IRF1-dependent autocrine loop leading to sustained expression of chemokines and STAT1-dependent type I interferon–response genes. Nat Immunol 9(4):378–387
Acknowledgments
This research work was supported by Science Engineering and Research Board-Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi and Karunya University, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Singh, S., Snijesh, V.P., Jannet Vennila, J. (2015). Rheumatoid Arthritis Candidate Genes Identification by Investigating Core and Periphery Interaction Structures. In: Muppalaneni, N., Gunjan, V. (eds) Computational Intelligence in Medical Informatics. SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology(). Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-287-260-9_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-287-260-9_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-287-259-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-287-260-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)