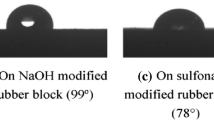
Abstract
Rational and sustainable disposing and recycling of waste rubber tyres (WRT) has become a challenge with their numbers increasing and accumulating. According to statistics, the cumulative annual generation of WRT is about 1.5 billion; they cannot be degraded and are difficult to recycle. WRT was generally buried in the landfills, stacked in open storage, or used as fuel; which not only pollutes the environment but also wastes resources. The application of waste rubber powder in concrete not only improves the ductility of concrete but provides a new solution to the problem of waste rubber pollution. However, the workability and mechanical properties of concrete are greatly affected due to the poor compatibility between rubber particles and the cement matrix. To improve these weaknesses, a novel method to modify WRP by combining the organic and inorganic mixed slurry coating and filling effect was proposed in this study. The particle size distribution of rubber particles before and after modification, the effect of rubber particles on hydration heat and rheology of cement mortar, and interfacial bonding between rubber particles and cement matrix were explored. The compressive strength and splitting tensile strength of concrete with WRP and modified WRP (MRA) were determined. The results demonstrate this modification method was very effective, and the structure and properties of WRP were significantly improved. Under the same volume replacement percentage, the compressive strength and splitting tensile of concrete increased by 70.0% and 46.1%, respectively. The cavitation phenomenon between rubber particle and cement matrix disappeared, and the interface bonding was significantly improved.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri, M., et al.: Evaluating the synergic effect of waste rubber powder and recycled concrete aggregate on mechanical properties and durability of concrete. Case. Stud. Const 15(2021), e00639 (2021)
Eldin, N., Senouci, B.: Rubber-tire particles as concrete aggregate. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 5(4), 478–496 (1993)
Eltayeb, E., et al.: Dynamic performance of rubberised concrete and its structural applications: an overview. Eng. Struct. 234, 111990 (2021)
Feng, L., et al.: Study of impact performance of rubber reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 36(8), 604–616 (2012)
Ferreira, L., et al.: Influence of curing conditions on the mechanical performance of concrete containing recycled plastic aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 36(9), 196–204 (2012)
Liu, C., et al.: Application of nanomaterials in ultra-high performance concrete: a review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 9(1), 1427–1444 (2020)
Liu, L., et al.: Evaluation of engineering properties and environmental effect of recycled waste tire-sand/soil in geotechnical engineering: a compressive review. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 126, 109831 (2020)
Liu, Y., et al.: The interaction of sodium citrate and polycarboxylate-based superplasticizer on the rheological properties and viscoelasticity of cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 293, 123466 (2021)
Malika, M., et al.: Fresh state properties of concrete incorporating scrap tire rubber. Period. Polytech.-Civ. 60(4), 611–617 (2016)
Mohajerani, A., et al.: Recycling waste rubber tyres in construction materials and associated environmental considerations: a review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 155, 104679 (2020)
Pereira, J.M., Lourenco, P.B.: Experimental characterization of masonry and masonry components at high strain rates. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 29(2), 04016223 (2017)
Pham, T.M., et al.: Effect of rubber aggregate size on static and dynamic compressive properties of rubberized concrete. Struct. Concr. 202100281 (2021)
Phiri, M.M., et al.: Chemical surface etching methods for ground tire rubber as sustainable approach for environmentally-friendly composites development—a review. Compos. Part B-Eng. 204, 108429 (2021)
Rana, A., et al.: Recycling of dimensional stone waste in concrete: a review. J. Clean. Prod. 135, 312–331 (2016)
Rashad, A.M.: A comprehensive overview about the effect of nano-SiO2 on some properties of traditional cementitious materials and alkali-activated fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 52, 437–464 (2014)
Richardson, A., et al.: Crumb rubber used in concrete to provide freeze-thaw protection (optimal particle size). J. Clean. Prod. 112(1), 599–606 (2016)
Roy, R., et al.: Encapsulation techniques and test methods of evaluating the bacteria-based self-healing efficiency of concrete: a literature review. Nord. Concr. Res. 62(1), 63–85 (2020)
Roychand, R., et al.: A comprehensive review on the mechanical properties of waste tire rubber concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 237, 117651 (2020)
Siddika, A., et al.: Properties and utilizations of waste tire rubber in concrete: a review. Constr. Build. Mater. 224, 711–731 (2019)
Sienkiewicz, M., et al.: Environmentally friendly polymer-rubber composites obtained from waste tyres: a review. J. Clean. Prod. 147, 560–571 (2017)
Sukontasukkul, P., Tiamlom, K.: Expansion under water and drying shrinkage of rubberized concrete mixed with crumb rubber with different size. Constr. Build. Mater. 29, 520–526 (2012)
Thomas, B.S., Gupta, R.C.: A comprehensive review on the applications of waste tire rubber in cement concrete. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 54, 1323–1333 (2016)
Toutanji, H.A.: The use of rubber tire particles in concrete to replace mineral aggregates. Cement Concr. Comp. 18(2), 135–139 (1996)
Wallevik, O.H., et al.: Avoiding inaccurate interpretations of rheological measurements for cement-based materials. Cement Concr. Res. 78(3), 100–109 (2015)
Xiong, Z., et al.: Review of dynamic behaviour of rubberised concrete at material and member levels. J. Build. Eng. 38, 102237 (2021)
Yu, Z., et al.: Fatigue deterioration of quasi-brittle materials. Int. J. Fatigue 118, 185–191 (2019)
Zhai, S., et al.: Investigation on preparation and multifunctionality of reduced graphene oxide cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 275, 122119 (2021)
Zhang, M., et al.: Further investigation on the dynamic compressive strength enhancement of concrete-like materials based on split Hopkinson pressure bar tests. Part I: Experiments. Int. J. Impact Eng. 36(12SI), 1327–1334 (2009)
Zhou, X.Q., Hao, H.: Modelling of compressive behaviour of concrete-like materials at high strain rate. Int. J. Solids Struct. 45(17), 4648–4661 (2008)
Zyka, K., Mohajerani, A.: Composite piles: a review. Constr. Build. Mater. 107, 394–410 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U21A20150 and No. 51978590).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhai, S., Zhang, Y., Liu, L. (2023). Investigation on Recycling Application of Waste Rubber Tyres in Concrete. In: Geng, G., Qian, X., Poh, L.H., Pang, S.D. (eds) Proceedings of The 17th East Asian-Pacific Conference on Structural Engineering and Construction, 2022. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 302. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7331-4_122
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7331-4_122
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-7330-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-7331-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)