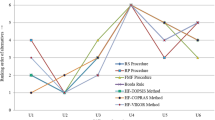
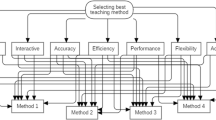
Abstract
Multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) method as an instrument has been applied in different fields. Deciding and recognizing the appropriate conditions is important due to adjust the present educational changes, and it is also significant in mathematics education. However, this idea is rarely used in academic discipline. This study tried to examine and categorize proper conditions for mathematics teaching as a real-life utilization with a multi-criteria decision analysis and fuzzy-decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (MCDA and F-DEMATEL) method. Specifically, adjusting to present educational changes, it is about flipped classroom combined with sustainable development and information, communication, and technology (ICT) in mathematics teaching. In this case, the principal criteria and sub-criteria were carefully chosen after the discussion of an association of specialists as decision-makers with the MCDA and F-DEMATEL methods. Later, the final analyses’ findings were measured with simple additive weighting (SAW) throughout their weight coefficients’ result and susceptibility study with the chosen criteria and sub-criteria. The findings showed that the most significant criteria and sub-criteria for variation to present educational changes had been revealed to be based on the above-cited evaluation methodologies. Thus, this approach could be used to certify the most important flipped and sustainable mathematics teaching for adjusting to present educational changes with resultant learning environments in more long-term education. Hence, it could be related to decision-making defects in private sectors, at government sectors and more educational areas, which continually requires constant actualization of knowledge and distribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyuz, E., Celik, E.: A fuzzy DEMATEL method to evaluate critical operational hazards during gas freeing process in crude oil tankers. J. Loss. Prevent. Proc. 38, 243–253 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2015.10.006
Arafat, S., Aljohani, N., Abbasi, R., Hussain, A., Lytras, M.: Connections between e-learning, web science, cognitive computation and social sensing, and their relevance to learning analytics: a preliminary study. Comput. Hum. Behav. 92, 478–486 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.02.026
Aunio, P., Heiskari, P., Van Luit, J.E., Vuorio, J.: The development of early numeracy skills in kindergarten in low, average and high performance groups. J. Early Child. Res. 13(1), 3–16 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1177/2F1476718X14538722
Azeiteiro, U.M., Bacelar-Nicolau, P., Caetano, F.J., Caeiro, S.: Education for sustainable development through e-learning in higher education: experiences from Portugal. J. Clean. Prod. 106, 308–319 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.11.056
Balana, B.B., Mathijs, E., Muys, B.: Assessing the sustainability of forest management: an application of multi-criteria decision analysis to community forests in northern Ethiopia. J. Environ. Manage. 91(6), 1294–1304 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.02.005
Butterworth, B., Varma, S., Laurillard, D.: Dyscalculia: from brain to education. Science 332, 1049–1053 (2011)
Büyüközkan, G., Çifçi, G.: A novel hybrid MCDM approach based on fuzzy DEMATEL, fuzzy ANP and fuzzy TOPSIS to evaluate green suppliers. Exp. Syst. Appl. 39, 3000–3011 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.08.162
Chen-Yi, H., Ke-Ting, C., Gwo-Hshiung, T.: FMCDM with fuzzy DEMATEL approach for customers’ choice behavior model. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 9(4), 236–246 (2007)
Chen, Y., Yu, J., Khan, S., Spatial sensitivity analysis of multi-criteria weights in GIS based land suitability evaluation. Environ. Model. Softw 25, 1582–1591 (2010).
Çınar, M., Ekici, N., Demir, Ö.: A snapshot of the readiness for e-learning among in-service teachers prior to the pandemic-related transition to e-learning in Turkey. Teach. Teach. Educ. 107, 103478 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2021.103478
Delivand, M.K., Cammerino, A.R.B., Garofalo, P., Monteleone, M.: Optimal locations of bioenergy facilities, biomass spatial availability, logistics costs and GHG (greenhouse gas) emissions: a case study on electricity productions in South Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 99, 129–139 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.03.018
Dias, L., Mousseau, V., Figueira, J., Clímaco, J.: An aggregation/disaggregation approach to obtain robust conclusions with ELECTRE TRI. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 138(2), 332–348 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(01)00250-8
Eneroth, C.: E-learning for environment. Improving e-learning as a tool for cleaner production education. Dissertation, Lund University (2000)
European Commission: Science Education for Responsible Citizenship (2015). Available online http://goo.gl/Vm3pZ0. Accessed 14 November 2021
Fletcher, J.M., Lyon, G.R., Fuchs, L.S., Barnes, M.A.: Learning Disabilities: From Identification to Intervention. Guilford Press, New York (2007)
Gabus, A., Fontela, E.: World problems, an invitation to further thought within the framework of DEMATEL. Battelle Geneva Research Centre, Geneva (1972)
Garrison, R.: Theoretical challenges for distance education in the 21st century: a shift from structural to transactional issues. IRRODL 1(1), 1–17 (2000). https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v1i1.2
Gaudin, M., Tanguy, G., Plagne, M., Saussac, A., Hansmann, Y., Jaulhac, B., Kelly, M., Ouchchane, L., Lesens, O.: E-learning versus face-to-face training: comparison of two learning methods for Lyme borreliosis. Infect. Dis. Now. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idnow.2021.11.001
González-Gómez, D., Jeong, J.S.: The flipped learning model in general science: effects on students’ learning outcomes and affective dimensions. In: Mintzes, J., Walter, E. (eds.) Active Learning in College Science, pp. 541–549. Springer, Cham (2020)
González-Gómez, D., Airado, D., Cañada-Cañada, F., Jeong, J.S.: A comprehensive application to assist in acid-base titration self-learning: an approach for high school and undergraduate students. J. Chem. Educ. 92(5), 855–863 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/ed5005646
González-Gómez, D., Jeong, J.S., Airado, D., Cañada-Cañada, F.: Performance and perception in the flipped learning model: an initial approach to evaluate the effectiveness of a new teaching methodology in a general science classroom. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 25(3), 450–459 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-016-9605-9
Govindan, K., Khodaverdi, R., Vafadarnikjoo, A.: Intuitionistic fuzzy based DEMATEL method for developing green practices and performances in a green supply chain. Exp. Syst. Appl. 42, 7207–7220 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.04.030
Hansen, D.E.: Knowledge transfer in on-line learning environments. J. Mark. Educ. 30(2), 93–105 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1177/2F0273475308317702
Hill, H.C., Blunk, M., Charalambous, C., Lewis, J., Phelps, G., Sleep, L., Ball, D.L.: Mathematical knowledge for teaching and the mathematical quality of instruction: an exploratory study. Cogn. Instr. 26(4), 430–511 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/07370000802177235
Jeong, J.S.: Design of spatial PGIS-MCDA-based land assessment planning for identifying sustainable land-use adaptation priorities for climate change impacts. Agric. Syst. 167, 61–71 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2018.09.001
Jeong, J.S., González-Gómez, D.: Web-GIS MC-SDSS verification forming the perception of building arrangements in Extremadura landscapes. Investig. Reg.-J. Reg. Res. 41, 193–213 (2018)
Jeong, J.S., González-Gómez, D.: A web-based tool framing a collective method for optimizing the location of a renewable energy facility and its possible application to sustainable STEM education. J. Clean. Prod. 251, 119747 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119747
Jeong, J.S., González-Gómez, D.: A STEM course analysis during COVID-19: a comparison study in performance and affective domain of PSTs between F2F and F2S flipped classroom. Front. Psychol. 3352 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.669855
Jeong, J.S., Ramírez-Gómez, A.: A multicriteria GIS-based assessment to optimize biomass facility sites with parallel environment—a case study in Spain. Energies 10(12), 2095 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122095
Jeong, J.S., García-Moruno, L., Hernández-Blanco, J.: A site planning approach for rural buildings into a landscape using a spatial multi-criteria decision analysis methodology. Land Use Policy 32, 108–118 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.09.018
Jeong, J.S., García-Moruno, L., Hernández-Blanco, J., Jaraíz-Cabanillas, F.J.: An operational method to supporting siting decisions for sustainable rural second home planning in ecotourism sites. Land Use Policy 41, 550–560 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2014.04.012
Jeong, J.S., González-Gómez, D., Cañada-Cañada, F.: Prioritizing elements of science education for sustainable development with the MCDA-FDEMATEL method using the flipped e-learning scheme. Sustainability 11(11), 3079 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113079
Jeong, J.S., González-Gómez, D., Conde-Núñez, M.C., Gallego-Picó, A.: Examination of students’ engagement with R-SPQ-2F of learning approach in flipped sustainable science course. J. Balt. Sci. Educ. 18(6), 880–891 (2019b). https://doi.org/10.33225/jbse/19.18.880
Kablan, M.M.: Decision support for energy conservation promotion: an analytic hierarchy process approach. Energ. Policy 32, 1151–1158 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(03)00078-8
Lee, J., Lee, W.: The relationship of e-learner’s self-regulatory efficacy and perception of e-learning environmental quality. Comput. Hum. Behav. 24(1), 32–47 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2006.12.001
Leonelli, M., Görgen, C., Smith, J.Q.: Sensitivity analysis in multilinear probabilistic models. Inf. Sci. 411, 84–97 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.05.010
Lim, C.P., Chai, C.S.: An activity theoretical approach to research of ICT integration in Singapore schools: orienting activities and learner autonomy. Comput. Educ. 43(3), 215–236 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2003.10.005
Lin, R.J.: Using fuzzy DEMATEL to evaluate the green supply chain management practices. J. Clean. Prod. 40, 32–39 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.06.010
Lin, C.L., Tzeng, G.H.: A value-created system of science (technology) park by using DEMETEL. Exp. Syst. Appl. 36, 9683–9697 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.11.040
Liou, J.J., Yen, L., Tzeng, G.H.: Building an effective safety management system for airlines. J. Air Transp. Manag. 14(1), 20–26 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jairtraman.2007.10.002
Maaß, K., Artigue, M.: Implementation of inquiry-based learning in day-to-day teaching: a synthesis. ZDM Math. Educ. 45, 779–795 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-013-0528-0
Malczewski, J.: GIS and Multicriteria Decision Analysis. Wiley, New York (1999)
Malczewski, J., Jackson, M.: Multicriteria spatial allocation of educational resources: an overview. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 34, 219–235 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0121(99)00025-7
Martínez-Montero, J., Sánchez, C.: Resolución de Problemas Y Método ABN. Wolters Kluwer Educación, The Netherlands (2013)
McVey, M.: E-learning and education for sustainability. Int. Rev. Educ. 62(1), 117–121 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11159-016-9533-1
Meszaros, C., Rapcsak, T.: On sensitivity analysis for a class of decision systems. Decis. Supp. Syst. 16, 231–240 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-9236(95)00012-7
Naccarato, E., Karakok, G.: Expectations and implementations of the flipped classroom model in undergraduate mathematics courses. IJEMST 46(7), 968–978 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2015.1071440
OECD Library: Global Teaching Insights (2021). https://www.globalteachinginsights.org. Accessed 23 October 2021
Parkes, M., Stein, S., Reading, C.: Student preparedness for university e-learning environments. Internet High. Educ. 25, 1–10 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2014.10.002
Pavlova, M.: Teaching and learning for sustainable development: ESD research in technology education. Int. J. Technol. Des. Educ. 23, 733–748 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-012-9213-9
Pereira, A., Mendes, A.Q., Morgado, L., Amante, L., Bidarra, J.: Universidade Aberta’s Pedagogical Model for Distance Education. Universidade Aberta, Lisbon (2008)
Perpina, C., Martínez-Llario, J.C., Pérez-Navarro, Á.: Multicriteria assessment in GIS environments for siting biomass plants. Land Use Policy 31, 326–335 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.07.014
Saaty, T.L.: The Analytic Hierarchy Process. McGraw-Hill, New York (1996)
Segalàs, J., Ferrer-Balas, D., Svanstrom, M., Lundqvist, U., Mulder, K.F.: What has to be learnt for sustainability? A comparison of bachelor engineering education competences at three European universities. Sustain. Sci. 4(1), 17–27 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-009-0068-2
Selçuk, L.: An avalanche hazard model for Bitlis Province, Turkey, using GIS based multi-criteria decision analysis. Turk. J. Earth Sci. 22, 523–535 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3906/yer-1201-10
Shee, D.Y., Wang, Y.S.: Multi-criteria evaluation of the web-based e-learning system: a methodology based on learner satisfaction and its applications. Comput. Educ. 50(3), 894–905 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2006.09.005
Su, C.H., Tzeng, G.H., Hu, S.K.: Cloud e-learning service strategies for improving elearning innovation performance in a fuzzy environment by using a new hybrid fuzzy multiple attribute decision-making model. Interact. Learn. Environ. 24(8), 1812–1835 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2015.1057742
Thames, M.H., Ball, D.L.: What mathematical knowledge does teaching require? Knowing mathematics in and for teaching. Teach. Child. Math. 17(4), 220–229 (2010). https://doi.org/10.5951/TCM.17.4.0220
Thomas, I.: Critical thinking, transformative learning, sustainable education, and problem-based learning in universities. J. Transform. Educ. 7, 245–264 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1177/2F1541344610385753
UNESCO: UN Decade of Education for Sustainable Development, 2005–2014: The DESD at a Glance. UNESDOC, New York (2005)
Wan, S., Zhong, L., Dong, J.: A new method for group decision making with hesitant fuzzy preference relations based on multiplicative consistency. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28(7), 1449–1463 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2914008
Wei, X., Cheng, I., Chen, N.S., Yang, X., Liu, Y., Dong, Y., Zhai, X.: Effect of the flipped classroom on the mathematics performance of middle school students. Educ. Tech. Res. Dev. 68(3), 1461–1484 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-020-09752-x
Wu, W.W.: Segmenting critical factors for successful knowledge management implementation using the fuzzy DEMATEL method. Appl. Soft Comput. 12(1), 527–535 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2011.08.008
Wu, W.W., Lee, Y.T.: Developing global managers’ competencies using the fuzzy DEMATEL method. Exp. Syst. Appl. 32(2), 499–507 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2005.12.005
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control. 8, 338–353 (1965)
Zeleny, M.: Multiple Criteria Decision Making. McGraw-Hill, New York (1982)
Zare, M., Pahl, C., Rahnama, H., Nilashi, M., Mardani, A., Ibrahim, O., Ahmadi, H.: Multi-criteria decision making approach in e-learning: a systematic review and classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 45, 108–128 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.04.020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Jeong, J.S., González-Gómez, D., Yllana-Prieto, F. (2023). Multi-criteria Decision Analysis and Fuzzy-Decision-Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (MCDA and F-DEMATEL) Method for Flipped and Sustainable Mathematics Teaching as a Real-Life Application. In: Sahoo, L., Senapati, T., Yager, R.R. (eds) Real Life Applications of Multiple Criteria Decision Making Techniques in Fuzzy Domain. Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing, vol 420. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4929-6_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4929-6_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-4928-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-4929-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)