Abstract
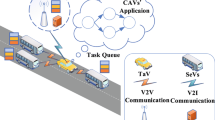
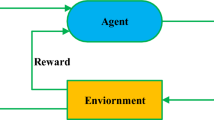
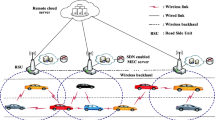
Intelligent and Connected Vehicles (ICV) can effectively improve driving safety and traffic efficiency. With the national approach of energy conservation and emission reduction continuously promoting, Electric vehicles (EV) have become the main body of the next generation ICV. For the limited computing capacity and endurance of EV, it cannot meet the high computational requirements of in-vehicle intelligent applications. Therefore, it is a great challenge to design a appropriate offloading approach to reduce failure rate of vehicular applications and energy consumption of offloading, while considering inter-dependencies of applications, position change of vehicles and computing power of collaborative vehicles. In this paper, ICV computation offloading model is formulated as Markov Decision Process (MDP). A computing offloading approach based on Reinforcement Learning (RL) is proposed, which adopts Q-Learning based on Simulated Annealing (SA-QL) to optimize failure rate of vehicular applications and energy consumption of offloading. The simulated results show that the proposed approach can reduces the failure rate of vehicular applications and energy consumption of offloading.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adiththan, A., Ramesh, S., Samii, S.: Cloud-assisted control of ground vehicles using adaptive computation offloading techniques. In: 2018 Design, Automation Test in Europe Conference Exhibition (DATE). pp. 589–592 (2018). https://doi.org/10.23919/DATE.2018.8342076
Azimifar, M., Todd, T.D., Khezrian, A., Karakostas, G.: Vehicle-to-vehicle forwarding in green roadside infrastructure. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 65(2), 780–795 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2015.2402177
Bondok, A.H., Lee, W., Kim, T.: Efficient scheduling for VANET considering renewable energy. In: 2020 22nd International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), pp. 217–221 (2020). https://doi.org/10.23919/ICACT48636.2020.9061360
Dai, P., et al.: Multi-armed bandit learning for computation-intensive services in MEC-empowered vehicular networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(7), 7821–7834 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2020.2991641
Dai, Y., Xu, D., Maharjan, S., Zhang, Y.: Joint load balancing and offloading in vehicular edge computing and networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(3), 4377–4387 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2018.2876298
Dong, P., Wang, X., Rodrigues, J.: Deep reinforcement learning for vehicular edge computing: an intelligent offloading system. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3317572
Feng, J., Liu, Z., Wu, C., Ji, Y.: AVE: autonomous vehicular edge computing framework with ACO-based scheduling. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 66(12), 10660–10675 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2017.2714704
Guo, M., Wang, Y., Sun, H., Liu, Y.: Research on q-learning algorithm based on metropolis criterion. J. Comput. Res. Dev. 39(6), 684–688 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-002-0038-4
Hou, X., et al.: Reliable computation offloading for edge-computing-enabled software-defined IoV. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(8), 7097–7111 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.2982292
Hu, B., Li, J.: An edge computing framework for powertrain control system optimization of intelligent and connected vehicles based on curiosity-driven deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(8), 7652–7661 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.3007100
Ke, H., Wang, J., Deng, L., Ge, Y., Wang, H.: Deep reinforcement learning-based adaptive computation offloading for MEC in heterogeneous vehicular networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(7), 7916–7929 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2020.2993849
Li, J., Xiao, Z., Li, P.: Discrete-time multi-player games based on off-policy q-learning. IEEE Access 7, 134647–134659 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2939384
Li, X., Dang, Y., Aazam, M., Peng, X., Chen, T., Chen, C.: Energy-efficient computation offloading in vehicular edge cloud computing. IEEE Access 8, 37632–37644 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2975310
Liu, L., Chen, C., Pei, Q., Maharjan, S., Zhang, Y.: Vehicular edge computing and networking: a survey. Mob. Netw. Appl. 26(3), 1145–1168 (2021)
Luo, Q., Li, C., Luan, T.H., Shi, W.: Collaborative data scheduling for vehicular edge computing via deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(10), 9637–9650 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.2983660
Lèbre, M.A., Le Mouël, F., Ménard, E.: Microscopic vehicular mobility trace of Europarc roundabout, Creteil, France (2015)
Mao, Y., Zhang, J., Song, S.H., Letaief, K.B.: Power-delay tradeoff in multi-user mobile-edge computing systems. In: 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), pp. 1–6 (2016). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/GLOCOM.2016.7842160
Meng, B., Yang, F., Liu, J., Wang, Y.: A survey of brake-by-wire system for intelligent connected electric vehicles. IEEE Access 8, 225424–225436 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3040184
Qin, Y., Huang, D., Zhang, X.: Vehicloud: Cloud computing facilitating routing in vehicular networks. In: 2012 IEEE 11th International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications, pp. 1438–1445 (2012). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TrustCom.2012.16
Raza Naqvi, S.S., Wang, S., Ahmed, M., Anwar, M.: A survey on vehicular edge computing: architecture, applications, technical issues, and future directions. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2019, 1–19 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3159762
Speck, C., Bucci, D.J.: Distributed UAV swarm formation control via object-focused, multi-objective sarsa. In: 2018 Annual American Control Conference (ACC), pp. 6596–6601. IEEE (2018)
Sun, Y., Song, J., Zhou, S., Guo, X., Niu, Z.: Task replication for vehicular edge computing: a combinatorial multi-armed bandit based approach. In: 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), pp. 1–7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8647564
Sutton, R.S.: Learning to predict by the methods of temporal differences. Mach. Learn. 3(1), 9–44 (1988)
Wang, J., Feng, D., Zhang, S., Tang, J., Quek, T.Q.S.: Computation offloading for mobile edge computing enabled vehicular networks. IEEE Access 7, 62624–62632 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2915959
Xiaoping, D., Dongxin, L., Shen, L., Qiqige, W., Wenbo, C.: Coordinated control algorithm at non-recurrent freeway bottlenecks for intelligent and connected vehicles. IEEE Access 8, 51621–51633 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2980626
Xu, X., Zhang, X., Liu, X., Jiang, J., Qi, L., Bhuiyan, M.Z.A.: Adaptive computation offloading with edge for 5g-envisioned internet of connected vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(8), 5213–5222 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.2982186
Zeng, F., Chen, Q., Meng, L., Wu, J.: Volunteer assisted collaborative offloading and resource allocation in vehicular edge computing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(6), 3247–3257 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.2980422
Zhan, W., et al.: Deep-reinforcement-learning-based offloading scheduling for vehicular edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(6), 5449–5465 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.2978830
Zhao, J., Li, Q., Gong, Y., Zhang, K.: Computation offloading and resource allocation for cloud assisted mobile edge computing in vehicular networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 68(8), 7944–7956 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2019.2917890
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lin, K., Lin, B., Shao, X. (2022). Reinforcement Learning-Based Computation Offloading Approach in VEC. In: Sun, Y., et al. Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing. ChineseCSCW 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1491. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4546-5_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4546-5_44
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-4545-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-4546-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)