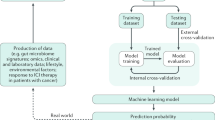
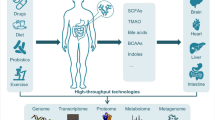
Abstract
Gastrointestinal cancers remain a major threat to the global community. In recent years, the multifaceted effect of the microbiome in cancer development modulation and its potential therapeutic role are gaining well-deserved recognition. Artificial intelligence has been put to test in assisting clinicians with excellent performance. With the influx of data generated from sequencings in microbiome studies, there is an uprising application of artificial intelligence in microbiome data analysis. In this article, we discuss the pivotal role of the microbiome in gastrointestinal cancers, current approaches for microbiome research, and the potential applications of artificial intelligence in microbiome data analysis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold M, Abnet CC, Neale RE, Vignat J, Giovannucci EL, McGlynn KA, et al. Global burden of 5 major types of gastrointestinal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):335–349.e15.
Behary J, Amorim N, Jiang XT, Raposo A, Gong L, McGovern E, et al. Gut microbiota impact on the peripheral immune response in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease related hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):187.
Belkaid Y, Hand TW. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell. 2014;157(1):121–41.
Bokulich NA, Chung J, Battaglia T, Henderson N, Jay M, Li H, et al. Antibiotics, birth mode, and diet shape microbiome maturation during early life. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(343):343ra82.
Chen S, Zhang L, Li M, Zhang Y, Sun M, Wang L, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum reduces METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification and contributes to colorectal cancer metastasis. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):1248.
Clish CB. Metabolomics: an emerging but powerful tool for precision medicine. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2015;1(1):a000588.
Dai D, Yang Y, Yu J, Dang T, Qin W, Teng L, et al. Interactions between gastric microbiota and metabolites in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(12):1104.
Eraslan G, Avsec Z, Gagneur J, Theis FJ. Deep learning: new computational modelling techniques for genomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20(7):389–403.
Gao Y, Bi D, Xie R, Li M, Guo J, Liu H, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum enhances the efficacy of PD-L1 blockade in colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):398.
Goldenberg SL, Nir G, Salcudean SE. A new era: artificial intelligence and machine learning in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2019;16(7):391–403.
Gorkiewicz G, Moschen A. Gut microbiome: a new player in gastrointestinal disease. Virchows Arch. 2018;472(1):159–72.
Guinane CM, Cotter PD. Role of the gut microbiota in health and chronic gastrointestinal disease: understanding a hidden metabolic organ. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. 2013;6(4):295–308.
Hassan C, Balsamo G, Lorenzetti R, Zullo A, Antonelli G. Artificial intelligence allows leaving-in-situ colorectal polyps. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(11):2505–2513.e4.
Hsiao WW, Metz C, Singh DP, Roth J. The microbes of the intestine: an introduction to their metabolic and signaling capabilities. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 2008;37(4):857–71.
Knights D, Kuczynski J, Koren O, Ley RE, Field D, Knight R, et al. Supervised classification of microbiota mitigates mislabeling errors. ISME J. 2011;5(4):570–3.
Kong C, Liang L, Liu G, Du L, Yang Y, Liu J, et al. Integrated metagenomic and metabolomic analysis reveals distinct gut-microbiome-derived phenotypes in early-onset colorectal cancer. Gut. 2022.
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521(7553):436–44.
Li F, Hitch TCA, Chen Y, Creevey CJ, Guan LL. Comparative metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analyses reveal the breed effect on the rumen microbiome and its associations with feed efficiency in beef cattle. Microbiome. 2019;7(1):6.
Liu YX, Qin Y, Chen T, Lu M, Qian X, Guo X, et al. A practical guide to amplicon and metagenomic analysis of microbiome data. Protein Cell. 2021;12(5):315–30.
Luchini C, Pea A, Scarpa A. Artificial intelligence in oncology: current applications and future perspectives. Br J Cancer. 2022;126(1):4–9.
McCulloch JA, Davar D, Rodrigues RR, Badger JH, Fang JR, Cole AM, et al. Intestinal microbiota signatures of clinical response and immune-related adverse events in melanoma patients treated with anti-PD-1. Nat Med. 2022;28(3):545–56.
Obermeyer Z, Emanuel EJ. Predicting the future—big data, machine learning, and clinical medicine. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(13):1216–9.
Peroni DG, Nuzzi G, Trambusti I, Di Cicco ME, Comberiati P. Microbiome composition and its impact on the development of allergic diseases. Front Immunol. 2020;11:700.
Ren Z, Li A, Jiang J, Zhou L, Yu Z, Lu H, et al. Gut microbiome analysis as a tool towards targeted non-invasive biomarkers for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2019;68(6):1014–23.
Sender R, Fuchs S, Milo R. Are we really vastly outnumbered? Revisiting the ratio of bacterial to host cells in humans. Cell. 2016;164(3):337–40.
Sharpton TJ. An introduction to the analysis of shotgun metagenomic data. Front Plant Sci. 2014;5:209.
Silver D, Huang A, Maddison CJ, Guez A, Sifre L, van den Driessche G, et al. Mastering the game of go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature. 2016;529(7587):484–9.
Sugimura N, Li Q, Chu ESH, Lau HCH, Fong W, Liu W, et al. Lactobacillus gallinarum modulates the gut microbiota and produces anti-cancer metabolites to protect against colorectal tumourigenesis. Gut. 2021;71(10):2011–21.
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49.
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Hamady M, Fraser-Liggett CM, Knight R, Gordon JI. The human microbiome project. Nature. 2007;449(7164):804–10.
Verberkmoes NC, Russell AL, Shah M, Godzik A, Rosenquist M, Halfvarson J, et al. Shotgun metaproteomics of the human distal gut microbiota. ISME J. 2009;3(2):179–89.
Vuik F, Dicksved J, Lam SY, Fuhler GM, van der Laan L, van de Winkel A, et al. Composition of the mucosa-associated microbiota along the entire gastrointestinal tract of human individuals. United European Gastroenterol J. 2019;7(7):897–907.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Cheung, H., Lin, Y. (2023). Machine Learning on Microbiome Research in Gastrointestinal Cancer. In: Yu, J. (eds) Microbiome in Gastrointestinal Cancer. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4492-5_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4492-5_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-4491-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-4492-5
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)