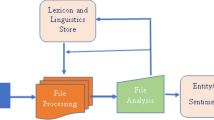
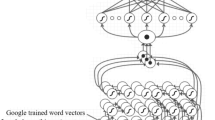
Abstract
With the rapid growth of Internet technology in recent years, an innovative legal research tool for Indian case laws has been established to save time for legal professionals. Sentiment analysis employs head notes from comparable previous instances to determine the main structure of a current case. Word embedding techniques such as GloVe and Word2Vec have shown to be especially effective at converting words into dense vectors. We use the Indian Supreme Court dataset and compare the performance of various deep learning models such as basic neural network, convolutional neural network, and recurrent neural network with GloVe embedding. GloVe + convolution neural network + attention mechanism, a new sentiment analysis model based on sentiment word embedding and integrating convolution neural network and attention mechanism, is introduced in this study analysis. The embedding vector is used to improve the sentiment features in the sentences. Then, we employ convolutional neural networks to extract the important sentiment and context-level features in the sentences, and we weight the features using the attention method. In this study, we look at 5000 positive and 5000 negative sentiments. Based on the experimental results, we conclude that our approach delivers high-quality legal reference information from full judgment texts, allowing lawyers to forecast positive and negative verdicts in a cost-effective and time-saving manner.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J, Wu Y, Feng W, Wang J (2019) Spatially attentive visual tracking using multi-model adaptive response fusion. IEEE Access 7:83873–83887
Chen Y, Wang J, Xia R, Zhang Q, Cao Z, Yang K (2019) The visual object tracking algorithm research based on adaptive combination kernel. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 10(12):4855–4867
Vaissnave V, Deepalakshmi P (2020) Data transcription for India’s Supreme Court documents using deep learning algorithms. Int J Electron Gov Res (IJEGR) 16(4):21–41
Vaissnave V, Deepalakshmi P (2022) A keyword-based multi-label text categorization in the Indian legal domain using bi-LSTM. In: Soft computing: theories and applications. Springer, Singapore, pp 213–227
Zhang J, Wang W, Lu C, Wang J, Sangaiah AK. Lightweight deep network for traffic sign classification. Ann Telecommun. To be published. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12243-019-00731-9
Tu Y, Lin Y, Wang J, Kim J-U (2018) Semi-supervised learning with generative adversarial networks on digital signal modulation classification. Comput Mater Contin 55(2):243–254
Wang J, Gao Y, Liu W, Sangaiah AK, Kim H-J (2019) An intelligent data gathering schema with data fusion supported for mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. Int J Distrib Sens Netw 15(3). Art. no. 155014771983958
Tang Z, Ding X, Zhong Y, Yang L, Li K (2018) A self-adaptive Bell–LaPadula model based on model training with historical access logs. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 13(8):2047–2061
Zeng D, Dai Y, Li F, Sherratt R, Wang J (2018) Adversarial learning for distant supervised relation extraction. Comput Mater Contin 55(1):121–136
Abid F, Alam M, Yasir M, Li C (2019) Sentiment analysis through recurrent variants latterly on convolutional neural network of Twitter. Future Gener Comput Syst 95:292–308
Jianqiang Z, Xiaolin G, Xuejun Z (2018) Deep convolution neural networks for Twitter sentiment analysis. IEEE Access 6:23253–23260
Hyun D, Park C, Yang M-C, Song I, Lee J-T, Yu H (2019) Target-aware convolutional neural network for target-level sentiment analysis. Inf Sci 491:166–178
Ma Y, Peng H, Khan T, Cambria E, Hussain A (2018) Sentic LSTM: a hybrid network for targeted aspect-based sentiment analysis. Cogn Comput 10(4):639–650
Mudalige CR, Karunarathna D, Rajapaksha I, de Silva N, Ratnayaka G, Perera AS, Pathirana R (2020) SigmaLaw-ABSA: dataset for aspect-based sentiment analysis in legal opinion texts. In: 2020 IEEE 15th international conference on industrial and information systems (ICIIS), Nov 2020. IEEE, pp 488–493
Giatsoglou M, Vozalis MG, Diamantaras K, Vakali A, Sarigiannidis G, Chatzisavvas KC (2017) Sentiment analysis leveraging emotions and word embeddings. Expert Syst Appl 69:214–224
Li Y, Pan Q, Yang T, Wang S, Tang J, Cambria E (2017) Learning word representations for sentiment analysis. Cogn Comput 9(6):843–851
Sun C, Huang L, Qiu X (2019) Utilizing BERT for aspect-based sentiment analysis via constructing auxiliary sentences. arXiv:1903.09588. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.09588
Jung Y, Hu J (2015) A K-fold averaging cross-validation procedure. J Nonparametr Stat 27(2):167–179
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vaissnave, V., Deepalakshmi, P. (2022). Comparative Analysis: Sentiment Analysis for Legal Judgment Text in India’s Supreme Court Based on GloVe Pretrained Word Embedding and Deep Learning Models. In: Kumar, R., Ahn, C.W., Sharma, T.K., Verma, O.P., Agarwal, A. (eds) Soft Computing: Theories and Applications. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 425. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-0707-4_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-0707-4_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-0706-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-0707-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)