Abstract
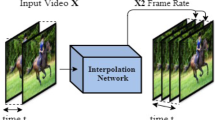
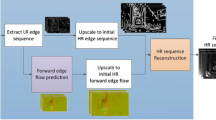
Flow-based video frame interpolation (VFI) is the process of synthesizing new frames in between the original frames in a video by estimating the motion of pixels. In this paper, usage of flow-based VFI methods has been proposed on 3D MRI images in order to convert low-resolution (LR) images into their high-resolution (HR) counterparts. This paper demonstrates the process of increasing the spatial resolution of the 3D image successively along all three axes to obtain a super-resolution (SR) 3D image using VFI. Quantitative analysis of the results proposes that this method of 3D spatial enhancement outperforms the previously proposed methods in the majority of the circumstances.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weishaupt B, Köchli D, Victor D, Marincek (2006) How does MRI work? An introduction to the physics and function of magnetic resonance imaging
Huppertz HJ, Wellmer J, Staack AM, Altenmüller DM, Urbach H, Kröll J (2008) Voxel-based 3D MRI analysis helps to detect subtle forms of subcortical band heterotopia. Epilepsia 49(5):772–785. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01436.x
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
Wu CY, Singhal N, Krähenbühl P (2018) Video compression through image interpolation. Lecture notes computer science (including Subseries lecture notes artificial intelligence lecture notes bioinformatics), vol 11212. LNCS, pp 425–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01237-3_26
Turaga P, Chellappa R, Veeraraghavan A (2010) Advances in video-based human activity analysis: challenges and approaches, 1st ed, vol 80, no. C. Elsevier Inc.
Bao W, Lai WS, Ma C, Zhang X, Gao Z, Yang MH (2019) Depth-aware video frame interpolation. In: Proceedings of IEEE computer social conference computer vision pattern recognition, vol 2019, pp 3698–3707. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00382
Huang Z, Zhang T, Heng W, Shi B, Zhou S (2020) RIFE: real-time intermediate flow estimation for video frame interpolation 2020 (Online). Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2011.06294
Oktay O et al (2016) Multi-input cardiac image super-resolution using convolutional neural networks. Lecture notes computer science (including subseries lecture notes artificial intelligence lecture notes bioinformatics), vol 9902. LNCS, pp 246–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46726-9_29
Pham CH, Ducournau A, Fablet R, Rousseau F (2017) Brain MRI super-resolution using deep 3D convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of international symposium biomedical imaging, pp 197–200. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2017.7950500
Sánchez I, Vilaplana V (2018) Brain MRI super-resolution using 3D generative adversarial networks, arXiv, no. Midl, pp 1–8
Chen Y, Xie Y, Zhou Z, Shi F, Christodoulou AG, Li D (2018) Brain MRI super resolution using 3D deep densely connected neural networks. In: 2018 IEEE 15th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI 2018), pp 739–742. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2018.8363679
Chen Y, Christodoulou AG, Zhou Z, Shi F, Xie Y, Li D (2020) MRI super-resolution with GAN and 3D multi-level densenet: smaller, faster, and better, arXiv, no. Debiao Li
Wang Y, Teng Q, He X, Feng J, Zhang T (2019) CT-image of rock samples super resolution using 3D convolutional neural network. Comput Geosci 133(24):104314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2019.104314
Chaudhari AS et al (2018) Super-resolution musculoskeletal MRI using deep learning. Magn Reson Med 80(5):2139–2154. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.27178
Jurek J, Kociński M, Materka A, Elgalal M, Majos A (2020) CNN-based superresolution reconstruction of 3D MR images using thick-slice scans. Biocybern Biomed Eng 40(1):111–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2019.10.003
Du J et al (2020) Super-resolution reconstruction of single anisotropic 3D MR images using residual convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing 392:209–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.10.102
Shi J et al (2019) MR image super-resolution via wide residual networks with fixed skip connection. IEEE J. Biomed Heal Inform 23(3):1129–1140. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2018.2843819
McDonagh S et al (2017) Context-sensitive super-resolution for fast fetal magnetic resonance imaging. Lecture notes computer science (including Subseries lecture notes artificial intelligence lecture notes bioinformatics), vol 10555 LNCS, pp 116–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67564-0_12
Thurnhofer-Hemsi K, López-Rubio E, Domínguez E, Luque-Baena RM, Roé-Vellvé N (2020) Deep learning-based super-resolution of 3D magnetic resonance images by regularly spaced shifting. Neurocomputing 398:314–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.05.107
Zhao C, Carass A, Dewey BE, Prince JL (2018) Self super-resolution for magnetic resonance images using deep networks. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering , The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore , MD 21218 USA Department of Computer Science , The Johns Hopkins University , Baltimore , MD 2121,” Electrical Engineering System Science, no. Isbi, pp 365–368
Du J, Wang L, Gholipour A, He Z, Jia Y (2019) Accelerated super-resolution MR image reconstruction via a 3D densely connected deep convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings 2018 IEEE international conference bioinformatics biomedical BIBM, pp 349–355. https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM.2018.8621073
Zeng K, Zheng H, Cai C, Yang Y, Zhang K, Chen Z (2018) Simultaneous single- and multi-contrast super-resolution for brain MRI images based on a convolutional neural network. Comput Biol Med 99(January):133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.06.010
Jiang H, Sun D, Jampani V, Yang MH, Learned-Miller E, Kautz J (2018) Super SloMo: high quality estimation of multiple intermediate frames for video interpolation. In: Proceedings IEEE computer social conference computing vision pattern recognition, pp 9000–9008. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00938
Xu X, Siyao L, Sun W, Yin Q, Yang MH (2019) Quadratic video interpolation. arXiv, no. NeurIPS
Menze BH et al (2015) The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(10):1993–2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2377694
Bakas S et al (2017) Advancing the cancer genome atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci Data 4 170117. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2017.117
Bakas S et al (2018) Identifying the best machine learning algorithms for brain tumor segmentation, progression assessment, and overall survival prediction in the BRATS Challenge, (Online). Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1811.02
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gulzar, S., Arora, S. (2022). Optical Flow Video Frame Interpolation Based MRI Super-Resolution. In: Agrawal, S., Gupta, K.K., Chan, J.H., Agrawal, J., Gupta, M. (eds) Machine Intelligence and Smart Systems. Algorithms for Intelligent Systems. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9650-3_35
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9650-3_35
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-9649-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-9650-3
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)