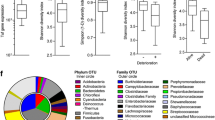
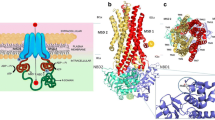
Abstract
It is believed that Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) is an age-related chronic, progressive, and histopathologically associated fibrosing interstitial lung disorder which primarily affects the elderly. Despite tremendous progress in our knowledge of pathophysiology of diseases, we still do not know the possible causes of IPF. According to current research evidences, it is proposed that IPF may develop genotype as a result of repeated alveolar damage causing an abnormal wound-healing response. Genomic variations in epithelial integrity and host defence genes put people at risk for IPF, whereas immunosuppression and overt respiratory infection are supposed to have a high death rate. The role of infection in disease etiopathogenesis has long been suspected and its progression, or as a cause of acute aggravation, although preliminary investigations using classic culture procedures have formed inconsistent findings. Current approach of culture-independent microbiological analysis procedures to IPF patients has previously revealed various unacknowledged variations in lung microbiome and also a high microbial burden in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) in patients with IPF. However, connection does not always imply causation. Furthermore, lung microbiome is still incompletely defined, and more studies need to be done to explore species other than viruses and bacteria, such as fungus. The knowledge of microbiome’s role in aetiology and IPF progression might leads to its modification, allowing targeted therapeutic treatment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand S, Mande SS (2018) Diet, microbiota and gut-lung connection. Front Microbiol 9:2147
Bacci G, Taccetti G, Dolce D, Armanini F, Segata N, Di Cesare F et al (2020) Untargeted metagenomic investigation of the airway microbiome of cystic fibrosis patients with moderate-severe lung disease. Microorganisms 8(7):1003
Beck JM, Young VB, Huffnagle GB (2012) The microbiome of the lung. Transl Res 160(4):258–266
Bhagirath AY, Li Y, Somayajula D, Dadashi M, Badr S, Duan K (2016) Cystic fibrosis lung environment and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. BMC Pulm Med 16(1):174
Blanchard AC, Waters VJ (2019) Microbiology of cystic fibrosis airway disease. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 40(6):727–736
Budden KF, Shukla SD, Rehman SF, Bowerman KL, Keely S, Hugenholtz P et al (2019) Functional effects of the microbiota in chronic respiratory disease. Lancet Respir Med 7(10):907–920
Carney SM, Clemente JC, Cox MJ, Dickson RP, Huang YJ, Kitsios GD et al (2020) Methods in lung microbiome research. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 62(3):283–299
Caverly LJ, Zhao J, LiPuma JJ (2015) Cystic fibrosis lung microbiome: opportunities to reconsider management of airway infection. Pediatr Pulmonol 50(Suppl 40):S31–S38
Chmiel JF, Aksamit TR, Chotirmall SH, Dasenbrook EC, Elborn JS, LiPuma JJ et al (2014) Antibiotic management of lung infections in cystic fibrosis. I. the microbiome, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative bacteria, and multiple infections. Ann Am Thorac Soc 11(7):1120–1129
Chunxi L, Haiyue L, Yanxia L, Jianbing P, Jin S (2020) The gut microbiota and respiratory diseases: new evidence. J Immunol Res 2020:2340670
Cribbs SK, Beck JM (2017) Microbiome in the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis and lung transplant-related disease. Transl Res 179:84–96
Cuthbertson L, Walker AW, Oliver AE, Rogers GB, Rivett DW, Hampton TH et al (2020) Lung function and microbiota diversity in cystic fibrosis. Microbiome. 8(1):45
de Almeida OGG, Capizzani C, Tonani L, Grizante Barião PH, da Cunha AF, De Martinis ECP et al (2020) The lung microbiome of three Young Brazilian patients with cystic fibrosis colonized by fungi. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:598938
Dickson RP (2016) The microbiome and critical illness. Lancet Respir Med 4(1):59–72
Dmitrijeva M, Kahlert CR, Feigelman R, Kleiner RL, Nolte O, Albrich WC et al (2021) Strain-resolved dynamics of the lung microbiome in patients with cystic fibrosis. MBio 12(2):e02863–e02820
Drakopanagiotakis F, Wujak L, Wygrecka M, Markart P (2018) Biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Matrix Biol 68-69:404–421
Fastrès A, Felice F, Roels E, Moermans C, Corhay JL, Bureau F et al (2017) The lung microbiome in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a promising approach for targeted therapies. Int J Mol Sci 18(12):2735
Flume PA, Chalmers JD, Olivier KN (2018) Advances in bronchiectasis: endotyping, genetics, microbiome, and disease heterogeneity. Lancet 392(10150):880–890
Françoise A, Héry-Arnaud G (2020) The microbiome in cystic fibrosis pulmonary disease. Genes 11(5):536
Han MK, Huang YJ, Lipuma JJ, Boushey HA, Boucher RC, Cookson WO et al (2012) Significance of the microbiome in obstructive lung disease. Thorax 67(5):456–463
Han MK, Zhou Y, Murray S, Tayob N, Noth I, Lama VN et al (2014) Lung microbiome and disease progression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an analysis of the COMET study. Lancet Respir Med 2(7):548–556
Heirali AA, Acosta N, Storey DG, Workentine ML, Somayaji R, Laforest-Lapointe I et al (2019) The effects of cycled inhaled aztreonam on the cystic fibrosis (CF) lung microbiome. J Cyst Fibros 18(6):829–837
Héry-Arnaud G, Boutin S, Cuthbertson L, Elborn SJ, Tunney MM (2019) The lung and gut microbiome: what has to be taken into consideration for cystic fibrosis? J Cyst Fibros 18(1):13–21
Huang YJ, LiPuma JJ (2016) The microbiome in cystic fibrosis. Clin Chest Med 37(1):59–67
Invernizzi R, Wu BG, Barnett J, Ghai P, Kingston S, Hewitt RJ et al (2021) The respiratory microbiome in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis is distinct from that of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 203(3):339–347
Kanda T, Goto T, Hirotsu Y, Masuzaki R, Moriyama M, Omata M (2020) Molecular mechanisms: connections between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 21(4):1525
Kitsios GD, Rojas M, Kass DJ, Fitch A, Sembrat JC, Qin S et al (2018) Microbiome in lung explants of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a case-control study in patients with end-stage fibrosis. Thorax 73(5):481–484
Lipinski JH, Moore BB, O’Dwyer DN (2020) The evolving role of the lung microbiome in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 319(4):L675–Ll82
Lira-Lucio JA, Falfán-Valencia R, Ramírez-Venegas A, Buendía-Roldán I, Rojas-Serrano J, Mejía M et al (2020) Lung microbiome participation in local immune response regulation in respiratory diseases. Microorganisms. 8(7):1059
Lynch SV (2016) The lung microbiome and airway disease. Ann Am Thorac Soc 13 Suppl 2(Suppl 5):S462–S4s5
Mammen MJ, Scannapieco FA, Sethi S (2020) Oral-lung microbiome interactions in lung diseases. Periodontology 2000 83(1):234–241
Mendez R, Banerjee S, Bhattacharya SK, Banerjee S (2019) Lung inflammation and disease: a perspective on microbial homeostasis and metabolism. IUBMB Life 71(2):152–165
Metwally AA, Ascoli C, Turturice B, Rani A, Ranjan R, Chen Y et al (2020) Pediatric lung transplantation: dynamics of the microbiome and bronchiolitis obliterans in cystic fibrosis. J Heart Lung Transplant 39(8):824–834
Moffatt MF, Cookson WO (2017) The lung microbiome in health and disease. Clin Med (Lond) 17(6):525–529
Monsó E (2020) Look at the wood and not at the tree: the microbiome in chronic obstructive lung disease and cystic fibrosis. Arch Bronconeumol 56(1):5–6
Morris A, Gibson K, Collman RG (2014) The lung microbiome in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis What does it mean and what should we do about it? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 190(8):850–852
Morton JT, Aksenov AA, Nothias LF, Foulds JR, Quinn RA, Badri MH et al (2019) Learning representations of microbe-metabolite interactions. Nat Methods 16(12):1306–1314
Muhlebach MS, Zorn BT, Esther CR, Hatch JE, Murray CP, Turkovic L et al (2018) Initial acquisition and succession of the cystic fibrosis lung microbiome is associated with disease progression in infants and preschool children. PLoS Pathog 14(1):e1006798
Mur LA, Huws SA, Cameron SJ, Lewis PD, Lewis KE (2018) Lung cancer: a new frontier for microbiome research and clinical translation. Ecancermedicalscience 12:866
O’Dwyer DN, Ashley SL, Gurczynski SJ, Xia M, Wilke C, Falkowski NR et al (2019) Lung microbiota contribute to pulmonary inflammation and disease progression in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 199(9):1127–1138
O’Dwyer DN, Garantziotis S (2021) The lung microbiome in health, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a heavy bacterial burden to bear. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 203(3):281–283
Paudel KR, Dharwal V, Patel VK, Galvao I, Wadhwa R, Malyla V et al (2020) Role of lung microbiome in innate immune response associated with chronic lung diseases. Front Med 7:554
Permall DL, Pasha AB, Chen XQ, Lu HY (2019) The lung microbiome in neonates. Turk J Pediatr 61(6):821–830
Quinn RA, Adem S, Mills RH, Comstock W, DeRight GL, Humphrey G et al (2019) Neutrophilic proteolysis in the cystic fibrosis lung correlates with a pathogenic microbiome. Microbiome 7(1):23
Ramsey KA, Schultz A, Stick SM (2015) Biomarkers in paediatric cystic fibrosis lung disease. Paediatr Respir Rev 16(4):213–218
Rogers GB, Bruce KD, Hoffman LR (2017) How can the cystic fibrosis respiratory microbiome influence our clinical decision-making? Curr Opin Pulm Med 23(6):536–543
Saint-Criq V, Lugo-Villarino G, Thomas M (2021) Dysbiosis, malnutrition and enhanced gut-lung axis contribute to age-related respiratory diseases. Ageing Res Rev 66:101235
Salisbury ML, Han MK, Dickson RP, Molyneaux PL (2017) Microbiome in interstitial lung disease: from pathogenesis to treatment target. Curr Opin Pulm Med 23(5):404–410
Scialo F, Amato F, Cernera G, Gelzo M, Zarrilli F, Comegna M et al (2021) Lung microbiome in cystic fibrosis. Life. 11(2):94
Shukla SD, Budden KF, Neal R, Hansbro PM (2017) Microbiome effects on immunity, health and disease in the lung. Clin Transl Immunol 6(3):e133
Spagnolo P, Molyneaux PL, Bernardinello N, Cocconcelli E, Biondini D, Fracasso F et al (2019) The role of the Lung’s microbiome in the pathogenesis and progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci 20(22):5618
Takahashi Y, Saito A, Chiba H, Kuronuma K, Ikeda K, Kobayashi T et al (2018) Impaired diversity of the lung microbiome predicts progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res 19(1):34
Tan JY, Tang YC, Huang J (2020) Gut microbiota and lung injury. Adv Exp Med Biol 1238:55–72
Tojo R, Suárez A, Clemente MG, de los Reyes-Gavilán CG, Margolles A, Gueimonde M et al (2014) Intestinal microbiota in health and disease: role of bifidobacteria in gut homeostasis. World J Gastroenterol 20(41):15163–15176
Tong X, Su F, Xu X, Xu H, Yang T, Xu Q et al (2019) Alterations to the lung microbiome in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 9:149
Torrisi SE, Kahn N, Vancheri C, Kreuter M (2020) Evolution and treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Presse Med. 49(2):104025
Tracy M, Cogen J, Hoffman LR (2015) The pediatric microbiome and the lung. Curr Opin Pediatr 27(3):348–355
Trivedi R, Barve K (2020) Gut microbiome a promising target for management of respiratory diseases. Biochem J 477(14):2679–2696
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Pathak, S. et al. (2022). Microbiome in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. In: Gupta, G., Oliver, B.G., Dua, K., Singh, A., MacLoughlin, R. (eds) Microbiome in Inflammatory Lung Diseases. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8957-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8957-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-8956-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-8957-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)