Abstract
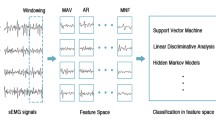
Surface electromyography (sEMG) has recently been commonly used in sign language recognition owing to its numerous advantages (i.e., portability, lightweight, and ease of use) over cameras and inertial sensors. We proposed a real-time Chinese sign language recognition model based on sEMG signals in this research. sEMG data was collected using MYO armband on nine healthy volunteers who performed a series of 15 gestures. The signal was preprocessed using a sliding window method followed by a muscle detection operation. Five time-domain features were extracted from the preprocessed signal for feature extraction. We used a feed-forward Artificial Neural Network (ANN) to classify the signals with an activation time threshold to recognize the gestures. This model is 94.9% in accuracy and reacts in around 195.19 ms (real-time).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao, W., Fang, G., Zhao, D., Chen, Y.: A Chinese sign language recognition system based on SOFM/SRN/HMM. J. Pattern Recognit. 37, 2389–2402 (2004)
Liu, K., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Real-time robust vision-based hand gesture recognition using stereo images. J. Real-Time Image Proc. 11(1), 201–209 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-013-0333-6
Benalcazar, M.E., et al.: Real-time hand gesture recognition using the Myo armband and muscle activity detection. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting, pp. 1--6. Salinas, Ecuador (2017)
Benalcazar, M.E., Jaramillo, A.G., Zea, A., Paez, A., Andaluz, V.H.: Hand gesture recognition using machine learning and the Myo armband. In: Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference, pp. 1075--1079. Kos, Greece (2017)
Adib, F., Hsu, C., Mao, H., Katabi, D., Durand, F.: Capturing the human figure through a wall. J. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 1–13 (2015)
Rossi, M., Benatti, S., Farella, E., Benini, L.: Hybrid EMG classifier based on HMM and SVM for hand gesture recognition in prosthetics. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), pp. 1700–1705. Seville, Spain (2015)
Motoche, C., Benalcázar, M.E.: Real-time hand gesture recognition based on electromyographic signals and artificial neural networks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, pp.4–7, Rhodes, Greece (2018)
Joshi, A., Monnier, C., Betke, M., Sclaroff, S.: Comparing random forest approaches to segmenting and classifying gestures. Image Vis. J. Comput. 58, 86–95 (2017)
Asif, A.R., et al.: Performance evaluation of convolutional neural network for hand gesture recognition using EMG. J. Sens. 20, 1642 (2020)
Mizuno, H., Tsujiuchi, N., Koizumi, T.: Forearm motion discrimination technique using real-time emg signals. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. EMBC, Annual International Conference of the IEEE, pp. 4435–4438. IEEE (2011)
Zhang, Z., Yang, K., Qian, J., Zhang, L.: Real-time surface EMG pattern recognition for hand gestures based on an artificial neural network. J. Sens. (Basel). 19(14), 3170 (2019)
Zhang, Z., Su, Z., Yang, G.: Real-time Chinese sign language recognition based on artificial neural networks. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), pp. 1413–1417, Dali, China, (2019)
Benalcázar, M.E., Anchundia, C.E., Zea, J.A., Zambrano, P., Jaramillo, A.G., Segura, M.: Real-time hand gesture recognition based on artificial feed-forward neural networks and EMG. In: 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), pp. 1492–1496, Rome, Italy (2018)
Kundu, A.S., Mazumder, O., Lenka, P.K., Bhaumik, S.: Hand gesture recognition based omnidirectional wheelchair control using IMU and EMG sensors. J. raml. Robot. Syst. 3, 1–13 (2017)
Wahid, M.F., Tafreshi, R., Al-Sowaidi, M., Langari, R.: Subject-independent hand gesture recognition using normalization and machine learning algorithms. J. Comput. SCI-NETH 27, 69–76 (2018)
Coteallard, U., et al.: Deep learning for electromyographic hand gesture signal classification using transfer learning. J. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 27(4), 760–771 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Riaz, M.M., Zhang, Z. (2021). Surface EMG Real-Time Chinese Language Recognition Using Artificial Neural Networks. In: Fei, M., Chen, L., Ma, S., Li, X. (eds) Intelligent Life System Modelling, Image Processing and Analysis. LSMS ICSEE 2021 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1467. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7207-1_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7207-1_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-7206-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-7207-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)