Abstract
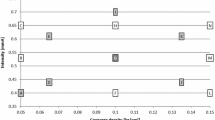
This research work examined the use of non-destructive Barkhausen noise technique in establishing residual stress (RS) depth profile in shot-peened specimens. The main objective was to produce a quantitative study of various Barkhausen noise parameters, including root-mean-square (RMS), full-width at half maximum (FWHM), peak average and pulse counts. A correlation was developed between Barkhausen noise parameters with residual stress values that were measured using X-ray diffraction technique. It was noticed that Barkhausen noise generated was highest at shallower depth of 50 μm and lowest at deeper depth of 400 μm, i.e. Barkhausen noise decreased with increasing depth for all the samples. This was attributed to the shot peening treatment being more effective on the near surface region of the material than in its bulk. After a thorough analysis of the key Barkhausen parameters, RMS was determined to produce the best correlation to RS. The depth profiles of RMS and RS were inversely proportional, and this trend was best reflected in shallower depths of 50 μm to 250 μm where the shot-peening process had greater impact on the specimens.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharpe, W.N., Jr.: Springer Handbook of Experimental Solid Mechanics. Springer, New York (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-30877-7
Liu, H., Tan, C.K.I., Wei, Y., Lim, G., Cheng, W., Maharjan, N.: Robotic hammer peening-induced martensite in austenitic steels: spatial distributions of plastic deformation and phase transformation. Procedia CIRP 87C, 172–177 (2020)
Liu, H., Wei, Y., Tan, C.K.I., Ardi, D.T., Tan, D.C.C., Lee, C.J.J.: XRD and EBSD studies of severe shot peening induced martensite transformation and grain refinements in austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 168, 110574 (2020)
Lee, J.J., Wei, Y., Liu, H., Tan, C.C., Ardi, D.T.: Surface integrity variations of stainless steel 304 upon severe shot peening. In: Materials Science Forum, vol. 1015, pp. 30–35 (2020)
E837-20 Standard Test Method for Determining Residual Stresses by the Hole-Drilling Strain-Gage Method, ASTM E837-20. ASTM International, West Conshohocken (2020)
E2860-20 Standard Test Method for Residual Stress Measurement by X-Ray Diffraction for Bearing Steels. ASTM International (2020)
Fry, A.: Residual stress measurement: XRD depth profiling using successive material removal (2002)
Grum, J., Zerovnik, P., Fefer, D.: Use of Barkhausen effect in measurement of residual stresses in steel after heat treatment and grinding. In: Materials of 15th WCNDT Conference (2000)
Lasaosa, A., Gurruchaga, K., García Navas, V., Martínez-de-Guereñu, A.: Characterisation of in-depth stress state by magnetic Barkhausen noise on machined steel acquiring different frequency bands. In: Advanced Materials Research, vol. 996, pp. 373–379 (2014)
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by an industry alignment fund-prepositioning programme: Advanced Post-processing and Non-Destructive Evaluation for Additive Manufacturing (IAF-PP, Grant no. A20F9a0045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Koh, W.Z.I., Wei, Y. (2022). Correlation Study Between Barkhausen Noise and Depth-Resolved Residual Stress Upon Shot Peening. In: Wei, Y., Chng, S. (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advanced Surface Enhancement (INCASE 2021). INCASE 2021. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5763-4_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5763-4_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-5762-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-5763-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)