Abstract
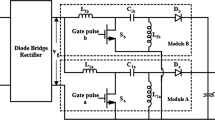
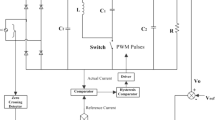
In recent years, photovoltaic is widely used in diverse applications. This photovoltaic is a device that converts solar power into DC electrical power. The direct current from PV is given as an input to Single Ended Primary Inductance Converter (SEPIC). In the most recent decade of power generation systems, this converter is used in many applications such as industrial, agriculture, electric vehicles, etc. This paper shows the Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) for Photovoltaic system and high efficiency is achieved by using Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) which was one of the simplest and fast converging techniques. The above mentioned topology is analyzed by using MATLAB/SIMULINK platform and the result is acquired for Standard Test Conditions (STC).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sera D, Mathe L, Kerekes T, Spataru SV, Teodorescu R (2013) On the perturb and observe and ıncremental conductance MPPT methods for PV systems. IEEE J Photovolt 3(3)
Danila Shirly AR, Srinath G, Prasad S, Vignesh S, Viswnathan M (2020) Design and hardware implementation of modified SEPIC converter based ANFIS controller. TEST Eng Manage 83: 26768–26776. ISSN: 0193–4120
Bansal M, Maiya RR (2020) Phototransistor: the story so far. J Electron 2(04):202–210
Nirmal D (2019) High performance flexible nanoparticles based organic electronics. J Electron 1(02):99–106
Sangeetha M, Kiruthika S, Priyadharshini R, Divya K (2019) Power factor correction using DC-DC SEPIC converter optimized with fuzzy logic controller. Int J Innov Res in Sci Eng Technol 8(3)
Raghavendra KV, Zeb K, Muthusamy A, Krishna TN, Kumar SV, Kim DH, Kim MS, Cho HG, Kim HJ (2020) A comprehensive review of DC–DC converter topologies and modulation strategies with recent advances in solar photovoltaic systems. Adv Power Electr Technol Renew Energy Syst J Electron
Suganyadevi MV, Lakshmi D, Ajay L, Ananth T, Balaji N, Mathavan K (2020) Design and development of SEPIC converter fed BLDC motor drive for photovoltaic application. Int J Adv Sci Technol 29(10(S)): 3153–3163
Mohanraj K, Yokesh Kiran B (2019) PV Integrated SEPIC converter using maximum power point tracking for Ac loads. Int J Recent Technol Eng (IJRTE) 8(1S4). ISSN: 2277- 3878
Danila Shirly AR (2016) Analysis of perturb and observe and incremental conductance MPPT techniques for solar powered SEPIC converter. Int J Eng Sci Comput (IJESC) 6(3); 2906–2913
Dhivya P, Ranjith Kumar K (2017) MPPT based control of SEPIC converter using firefly algorithm for solar PV system under partial shaded conditions. In: 2017 ınternational conference on ınnovations in green energy and healthcare technologies (IGEHT)
Suganya V, Danila Shirly AR (2016) Solar powered battery charger using sliding mode controller. Int J Eng Sci Comput (IJESC) 6(3): 3012–3018
Gu W, Zhang D (2008) Designing a SEPIC converter, Excellent design guidelines, national semiconductor in application note, April, 1–6. Ltd
Lian KL, Jhang JH, Tian IS (2014) A maximum power point tracking method based on perturb-and- observe combined with particle swarm optimization 4(2): 626–633
Ishaque K, Salman Z, Amjad M, Mekhilef S (2012) An improved particle swarm optimization (PSO)-based MPPT for PV with reduced steady-state oscillation. IEEE Trans Power Electron. 27(8):3627–3638 (2012)
ME Ali, MS Al-Saud, AG Abokhalil, HMH Farh, Photovoltaic maximum power point tracking under dynamic partial shading changes by novel adaptive particle swarm optimization strategy, Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Danila Shirly, A.R., Roshini, R., Priyanka, E., Sindhuja, M., Steffy Jones, A. (2022). Design and Implementation of Photovoltaic Powered SEPIC DC-DC Converter Using Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) Technique. In: Ranganathan, G., Bestak, R., Palanisamy, R., Rocha, Á. (eds) Pervasive Computing and Social Networking. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 317. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5640-8_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5640-8_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-5639-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-5640-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)