Abstract
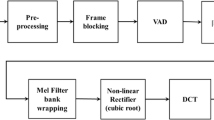
The goal is to build an efficient speaker identification framework for broad sets of data in noisy conditions. The key phases of traditional recognition procedures are feature extraction, network training, and checking features. In this experimental work, Silence removal methodologies are proposed to improve accurate recognition. Pitch & Pitch strength factors are extracted from the original speech digital signals as unique characteristics. Multilinear Principle Factor Analysis (MPCA) is used to minimize the dimension of the feature matrix. During the extraction process, silence elimination using Zero Cross Rate and End State Detection methods are incorporated to source utterance. These properties are considered in later testing phase, where SVM based classification is employed. Forward Loking Schostic (FOLOS) is perhaps the most appropriate algorithm used to classify speakers effectively. The experimental findings demonstrated that the suggested approaches rationally increase performance for massive data in noisy conditions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, S., Wu, Z., Qian, Y.: Data augmentation using deep generative models for embedding based speaker recognition. In: IEEE/ACM Transaction on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, vol. 2, pp. 2598–2609 (2020)
Lee, J.Y., Choi, B.J., Kim, N.S.: Robust alignment using gating mechanism for end-to-end speech synthesis. IEEE Sign. Process. Lett. 27, 2004–2008 (2020)
Boulianne, G.: A study of ınductive biases for unsupervised speech representation learning. In: IEEE/ACM Transaction on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, vol. 28, pp. 2781–2795 (2020)
He, X., Chen, M., Yang, J.: 3-D Convolutional recurrent neural networks with attention model for speech emotion recognition. IEEE Sig. Proc. Letters 25(10), 1440–1444 (2018)
Hanifa, R.M., Isa, K., Mohamad, S.: Comparative analysis on different cepstral features for speaker ıdentification recognition. In: 2020 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development, IEEE Publisher (2020)
Ridha, D., Suyanto, S.: Removing unvoiced segment to ımprove text ındependent speaker recognition. In: 2019 International Seminar on Research of Information Technology and Intelligent Systems. IEEE Publisher (2019)
Furui, S.: 40 Years of Progress in Automatic Speaker Recognition. Lecture Notes in Computer Science book series. In: Advances in Biometrics, pp. 1050–105 (2011)
Imam, S.A., Bansal, P., Singh, V.: Revıew: speaker recognıtıon usıng automated systems. AGU Int. J. Eng. Tech. 5, 31–38 (2015)
Khamparia, A., Singh, A., Luhach, A.K.: Performance comparison of Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark. In: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Advanced Information for Computing Research, pp. 1–5 (2019)
Rao, P.R.K.: Random forest algorithm with a half-voting and weighted decision trees for ınterior pedestrian tracking. Int. J. Recent Tech. Eng. 8(3), 6971–6976 (2019)
Rao, P.R.K., Rao, Y.S.: Dimensionality reduction techniques and SVM algorithms for large population speaker ıdentification. Int. J. Sig. Proc. Syst. 4(2), 86–95 (2016)
Deshpande, M.S., Holambe, R.S.: Robust speaker identification in the presence of car noise. Int. J. Bio. 3(3), 234–245 (2017)
Zhao, X., Wang, Y., Wang, D.: Robust speaker identification in noisy and reverberant conditions In: IEEE/ACM Transaction on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, vol. 22(4) (2014)
Ming, J., Hazen, T.J., Glass, J.R.: Robust speaker recognition in noisy conditions. In: IEEE Transaction on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, vol. 15(5) (2005)
Li, X., Tan, T., Chen, X.: Pattern Recognition Book. Springer (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-4154-3
Delcroix, M., Watanabe, S., Metze, F.: New Era for Robust Speech Recognition. Springer book (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-64680-0
Chakroun, R., Frikha, M.: Robust features for text-independent speaker recognition with short utterances. Neural Comput. Appl. 32(17), 13863–13883 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04793-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rao, S.V.A., Rao, P.R.K. (2021). Silence Elimination for Robust Speaker Detection in Large Database. In: Luhach, A.K., Jat, D.S., Bin Ghazali, K.H., Gao, XZ., Lingras, P. (eds) Advanced Informatics for Computing Research. ICAICR 2020. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1393. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3660-8_47
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3660-8_47
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-3659-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-3660-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)