Abstract
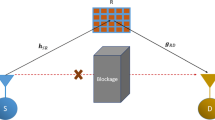
As one of the key technologies for deployment of future wireless networks, the state-of-the-art reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have rapidly gained a massive interest among researchers. In a specific case study, we study the outage performance of RIS-aided wireless systems in the presence of non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) scheme. In particular, different power factors are allocated to users which belong to a dedicated group. We the derive the exact outage probability of two users in a group. Specifically, it is assumed that the RIS is placed between the source and the users and the far user has better performance under the assistance of RIS. We also provide a comparative analysis to investigate the effect of the main parameters on the outage performance of our proposed system, such as the number of tunable elements of the RIS, power allocation factors, target rates, and the average signal-to-noise ratio at the base station. By using Monte Carlo simulation, we verify our analytical results via simulations. Our main results reported in this paper show the positive effect once we deploy RISs for guaranteeing fairness among NOMA users in wireless systems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basar E, Di Renzo M, De Rosny J, Debbah M, Alouini M, Zhang R (2019) Wireless communications through reconfigurable intelligent surfaces. IEEE Access 7:116 753–116 773
Renzo MD et al (2019) Smart radio environments empoweblack by AI reconfigurable meta-surfaces: an idea whose time has come. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 129
Wu Q, Zhang R (2020) Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network. IEEE Commun Mag 58(1):106–112
Basar E, Renzo MD, de Rosny J, Debbah M, Alouini M-S, Zhang R (2019) Wireless communications through reconfigurable intelligent surfaces. IEEE Access 7:116 753–116 773
Huang et al C (2019) Holographic MIMO surfaces for 6G wireless networks: opportunities, challenges, and trends. arXiv:1911.12296
Liu F et al (2018) Programmable metasurfaces: state of the art and prospects. In: proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS)
Yang H, Cao X, Yang F, Gao J, Xu S, Li M, Chen X, Zhao Y, Zheng Y, Sijia L (2016) A programmable metasurface with dynamic polarization, scattering and focusing control. Sci Rep 6(35692)
Liaskos C et al (2015) Design and development of software defined metamaterials for nanonetworks. IEEE Circuits Syst Mag 15(4):12–25. Fourthquarter
Liu X, Liu Y, Chen Y, Poor HV RIS enhanced massive non-orthogonal multiple access networks: deployment and passive beamforming design. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2020.3018823
Nemati M, Park J, Choi J (2020) RIS-assisted coverage enhancement in millimeter-wave cellular networks. IEEE Access 8:188171–188185
Alexandropoulos GC, Vlachos E (2020) A hardware architecture for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces with minimal active elements for explicit channel estimation. In: ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP). Barcelona, Spain, pp 9175–9179
C. H. et al (2019) Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 18(8):4157–4170
Boulogeorgos AAA, Alexiou A (2020) “Ergodic capacity analysis of reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted wireless systems. IEEE 3rd 5G World Forum (5GWF). Bangalore, India, 395–400
Wu Q, Zhang R (2019) Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 18(11):5394–5409
Guo H, Liang Y, Chen J, Larsson EG (2020) Weighted sum-rate maximization for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided wireless networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 19(5):3064–3076
Chen J, Liang Y-C, Pei Y, Guo H (2019) Intelligent reflecting surface: a programmable wireless environment for physical layer security. IEEE Access 7:82 599–82 612
Guan X, Wu Q, Zhang R (2020) Intelligent reflecting surface assisted secrecy communication: is artificial noise helpful or not? IEEE Wirel Commun Lett 9(6):778–782
Do D-T et al (2019) Wireless power transfer enabled NOMA relay systems: two SIC modes and performance evaluation. Telkomnika 17(6):2697–2703
Do D-T, Le C-B, Le A-T (2019) Cooperative underlay cognitive radio assisted NOMA: secondary network improvement and outage performance. Telkomnika 17(5):2147–2154
Li X, Li J, Liu Y, Ding Z, Nallanathan A (2020) Residual transceiver hardware impairments on cooperative NOMA networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 19(1):680–695
Li X, Li J, Li L (2020) Performance analysis of impaiblack SWIPT NOMA relaying networks over imperfect weibull channels. IEEE Syst J 14(1):669–672
Li X, Liu M, Deng C, Mathiopoulos PT, Ding Z, Liu Y (2020) Full-duplex cooperative NOMA relaying systems with I/Q imbalance and imperfect SIC. IEEE Wirel Commun Lett 9(1):17–20
Li Xingwang, Wang Qunshu, Peng Hongxing, Zhang Hui, Do Dinh-Thuan, Rabie Khaled M, Kharel Rupak, Cavalcante Charles C (2020) A unified framework for HS-UAV NOMA network: performance analysis and location optimization. IEEE Access 8:13329–13340
Do D-T, Thi Nguyen T-T (2018) Exact outage performance analysis of amplify-and forward-aware cooperative NOMA. Telkomnika 16(5):1966-1973
Do D-T, Le C-B (2018) Exploiting outage performance of wireless powered NOMA. Telkomnika 16 (5):1907–1917
Zeng J et al (2018) Investigation on evolving single-carrier NOMA into multi-carrier NOMA in 5G. IEEE Access 6:48268–48288
Liu G, Wang Z, Hu J, Ding Z, Fan P (2019) Cooperative NOMA broadcasting/multicasting for low-latency and high-reliability 5G cellular V2X communications. IEEE Internet Things J 6(5):7828–7838
Yang L, Yuan Y (2020) Secrecy outage probability analysis for RIS-assisted NOMA systems. Electron Lett 56(23):1254–1256
Elhattab M, Arfaoui MA, Assi C, Ghrayeb A Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted coordinated multipoint in downlink NOMA networks. IEEE Commun Lett. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3029717
Li Y, Jiang M, Zhang Q, Qin J Joint beamforming design in multi-cluster MISO NOMA reconfigurable intelligent surface-aided downlink communication networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3032695
Hou T, Liu Y, Song Z, Sun X, Chen Y, Hanzo L (2020) Reconfigurable intelligent surface aided NOMA networks. IEEE J Selected Areas Commun 38(11):2575–2588
Do D-T (2020) Anh-Tu Le and Byung Moo Lee, “NOMA in cooperative underlay cognitive radio networks under imperfect SIC. IEEE Access 8:86180–86195
Yue X, Liu Y (2020) Performance analysis of intelligent reflecting surface assisted NOMA networks. arXiv
Boulogeorgos A-AA, Alexiou A (2020) Performance analysis of reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted wireless systems and comparison with relaying. IEEE Access 8:94463–94483
Gradshteyn IS, Ryzhik IM (2000) Table of integrals, series and products, 6th edn. Academic Press, New York, NY, USA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
7 Appendix A
7 Appendix A
The outage probability \(P_{NU} \) can be further computed by
Let \(t = \rho x + 1 \rightarrow \frac{{t - 1}}{\rho } = x \rightarrow \frac{1}{\rho }dt = dx\), \({P_{NU}}\) can be reformulated by
Using [35, Eq. (3.381.3)], (13) can be reformulated by (14)
This completes the proof.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Le, CB., Do, DT., Sur, S.N. (2022). Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)-Assisted Wireless Systems: Potentials for 6G and a Case Study. In: Dhar, S., Mukhopadhyay, S.C., Sur, S.N., Liu, CM. (eds) Advances in Communication, Devices and Networking. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 776. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2911-2_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2911-2_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-2910-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-2911-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)