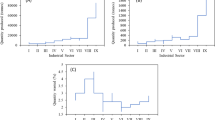
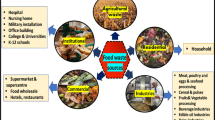
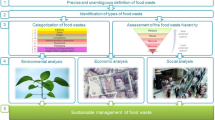
Abstract
Food wastes are increasingly becoming renowned as potential antagonists of a clean and green atmosphere. The unrestrained disposal of immense quotients of food wastes (FW) has substantively effectuated severe environmental pollution in many countries, thereby contributing to the sudden intensity of global warming. Contrariwise, food wastes, if properly harnessed, might serve as an inexhaustible feedstock for production of sustainable energy, value-added biochemicals and agriculture, thereby tackling the dual impasse of resource exhaustion and waste aggregation. This study would, therefore, serve to give a historian appraisal of food wastes and their environmental fates, and also suggest sustainable waste management possibilities that would accelerate our strides towards a circular economy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldaya MM, Allan JA, Hoekstra AY (2010) Strategic importance of green water in international crop trade. Ecol Econ 69(4):887–894. catering%20waste%20leaflet.pdf
DEFRA (Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs) (2014) Feeding catering waste to farmed animals is illegal. http://www.chippingnortonvets.co.uk/modules/downloadspl2/files/DEFRA%20
DEFRA, Environment Agency, WRAP (2011) Applying the waste hierarchy: evidence summary. London
EcoWatch (2017) World’s soils have lost 133bn tonnes of carbon since the dawn of agriculture. https://www.ecowatch.com/soil-carbon-loss-2478725457.html
European Parliament and the Council of the European Union (2008) Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the council of 19 November 2008 on waste and repealing certain directives. Official Journal of the European Union. 312: 3–30.
European Parliament Council (1989) A community strategy for waste management, SEC/89/934 (final). Brussels
European Union (2017) Commission regulation (EU) 2017/893 of 24 May 2017 amending annexes I and IV to regulation (EC) no 999/2001 of the European Parliament and of the council and annexes X, XIV and XV to commission regulation (EU) no 142/2011 as regards the provisions on processed animal protein (text with EEA relevance). OJ L. Vol. 138
Eurostat (2017) Municipal waste treatment in EU-27 by type of treatment, (kg per capita), 1995–2017
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) (2011) Global food losses and food waste: extent, causes and prevention. Rome
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) (2013a) Food waste footprint: Impacts on natural resources. http://www.fao.org/docrep/018/i3347e/i3347e.pdf
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) (2013b) Food loss and waste: definition and scope
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) (2013c) Food wastage footprint. Impacts on natural resources. In: Presentation of the FAO FWF study. Food Wastage Footprint project
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) (2015) Healthy soils are the basis for healthy food production. http://www.fao.org/soils-2015/News/news-detail/en/c/277682/
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) (2009) How to feed the world in 2050. Food and Agriculture Organization
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) (2015) The state of food insecurity in the world meeting the 2015 international hunger targets: taking stock of uneven progress. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Food and Agriculture Organization, International Fund for Agricultural Development, UNICEF, World Food Programme and World Health Organization (2017) The state of food security and nutrition in the world 2017: building resilience for peace and food security
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, FAO. 2014. Food wastage footprint. Full-cost accounting. Final report. Rome, Italy
Garcia-garcia G, Woolley E, Rahimifard S (2015) A framework for a more efficient approach to food waste management. Int J Food Eng 1(1):65–72
Garcia-garcia G, Woolley E, Rahimifard S, Colwill J, White R, Needham L (2017) A methodology for sustainable management of food waste. Waste Biomass Valor 8:2209–2227
Garnett T (2011) Where are the best opportunities for reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the food system (including the food chain)? Food Policy 36:S23–S32
Gebhardt S, Thomas R (2002) Nutritive value of foods. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Home and Garden Bulletin 72
Goodier C (2010) Carbon footprint. In: Cohen N, Robbins P (eds) Green cities: an A-to-Z guide. SAGE Publications, London, pp 49–53
Gunders D (2012) Wasted: how America is losing up to 40 percent of its food from farm to fork to landfill. In: Natural resources defense council issue paper, IP: 12-06-B
Hoekstra AY, Mekonnen MM (2012) The water footprint of humanity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(9):3232–3237
Hoekstra AY, Chapagain AK, Aldaya MM, Mekonnen MM (2011) The water footprint assessment manual. Setting the global standard. Water Footprint Network, London
Kings A (2018) Food waste: a growing global concern with dire consequences. Biotech. https://born2invest.com/articles/food-waste-growing-global-concern/
Kosseva MR (2009) Processing of food wastes. In: Taylor SL (ed.) Advances in food and nutrition research, vol 58. pp 57–136
Lipinski B, Hanson C, Lomax J, Kitinoja L, Waite R, Searchinger T (2013) Reducing food loss and waste. In: Working paper, installment 2 of creating a sustainable food future. World Resources Institute, Washington. http://www.worldresourcesreport.org
Memon MA (2010) Integrated solid waste management based on the 3R approach. J Mater Cycles Waste 12(1):30–40
Monier V, Mudgal S, Escalon V, O’Connor C, Gibon T (2010) Preparatory study on food waste across EU 27. European Commission (DG ENV), Directorate C – Industry
Moorcroft S (2012) A coming food waste revolution? https://innovationmanagement.se/2012/05/16/a-coming-food-waste-revolution/
Newman D, Cepeda-Márquez R, Zeller K (2018) Global food waste management: an implementation guide for cities. World Biogas Assoc:20
Odeniyi OA, Unuofin JO, Adebayo-Tayo BC, Wakil SM, Onilude AA (2017) Production characteristics, activity patterns and biodecolourisation applications of thermostable laccases from Corynebacterium efficiens and Enterobacter ludwigii. J Sci Ind Res 76:562–569
Osorio LLDR, Flórez-López E, Grande-Tovar CD (2021) The potential of selected Agri-food loss and waste to contribute to a circular economy: applications in the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Molecules 26(2):515
Östergren K, Gustavsson J, Bos-Brouwers H, Timmermans T, Hansen O (2014) FUSIONS definitional framework for food waste. Full report, Food Use for Social Innovation by Optimising Waste Prevention Strategies (FUSIONS)
Pfaltzgraff LA, De Bruyn M, Cooper EC, Budarin V, Clark JH (2013) Food waste biomass: a resource for high-value chemicals. Green Chem 15:307–314
Quested T, Parry A (2011) New estimates for household food and drink waste in the UK. Waste and Resources Action Program (WRAP)
Ren Y, Yu M, Wu C, Wang Q, Gao M, Huang Q, Liu Y (2017) A comprehensive review on food waste anaerobic digestion: research updates and tendencies. Bioresour Technol 247:1069–1076
Riemer J, Kristoffersen M (1999) Information on waste management practices. A proposed electronic framework. European Environmental Agency, Copenhagen
Roka K (2019) Environmental and social impacts of food waste. In: Leal Filho W, Azul A, Brandli L, Özuyar P, Wall T (eds) Responsible consumption and production. Encyclopedia of the UN sustainable development goals. Springer, Cham
Roychand R, Patel S, Halder P, Kundu S, Hampton J, Bergmann D, Surapaneni A, Shah K, Pramanik BK (2021) Recycling biosolids as cement composites in raw, pyrolysed and ashed forms: a waste utilisation approach to support circular economy. J Build Eng:102199
Searchinger T, Hanson C, Ranganathan J, Lipinski B, Waite R, Winterbottom R, Dinshaw A, Heimlich R (2013) The great balancing act. In: Working paper, installment 1 of creating a sustainable FoodFuture. World Resources Institute, Washington. http://www.worldresourcesreport.org
The European Union (2009) The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union: regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 October 2009. Off J Eur Union 300: 1–33
UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) (2014) Prevention and reduction of food and drink waste in businesses and households – Guidance for governments, local authorities, businesses and other organisations, Version 1.0
Unuofin JO (2020a) Treasure from dross: application of agroindustrial wastes-derived thermo-halotolerant laccases in the simultaneous bioscouring of denim fabric and decolorization of dye bath effluents. Ind Crop Prod 147:112251
Unuofin JO (2020b) Sustainability potentials of novel laccase tinctures from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia BIJ16 and Bordetella bronchiseptica HSO16: from dye decolourization to denim bioscouring. Biotechnol Rep 25:e00409
Unuofin JO, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2019a) Aptitude of oxidative enzymes for treatment of wastewater pollutants: a laccase perspective. Molecules 24(11):2064
Unuofin JO, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2019b) Utilization of agroindustrial wastes for the production of laccase by Achromobacter xylosoxidans HWN16 and Bordetella bronchiseptica HSO16. J Environ Manag 231:222–231
Unuofin JO, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2019c) Maize Stover as a feedstock for enhanced laccase production by two gammaproteobacteria: a solution to agroindustrial waste stockpiling. Ind Crop Prod 129:611–623
Unuofin JO, Moubasher HA, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2019d) Production of polyextremotolerant laccase by Achromobacter xylosoxidans HWN16 and Citrobacter freundii LLJ16. Biotechnol Rep 22:e00337
Vandermeersch T, Alvarenga RAF, Ragaert P, Dewulf J (2014) Environmental sustainability assessment of food waste valorization options. Resour Conserv Recycl 87:57–64
World Bank (2019) Solid waste management. http://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/urbandevelopment/brief/solid-waste-management
WRAP (2009) Household food and drink waste in the UK. http://www.wrap.org.uk/sites/files/wrap/Household_food_and_ drink_waste_in_the_UK_-_report.pdf
WRAP (Waste and Resources Action Programme) (2011) Applying the waste hierarchy. A guide to business. Banbury
WWF (World Wildlife Fund for Nature) (2017) Food loss and waste: facts and futures taking steps towards a more sustainable food future. http://awsassets.wwf.org.za/downloads/WWF_Food_ Loss_and_Waste_WEB.pdf
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Unuofin, J.O., Aladekoyi, O.J., Odeniyi, O.A. (2021). Food Wastes: Perceptions, Impacts and Management. In: Haq, I., Kalamdhad, A.S. (eds) Emerging Treatment Technologies for Waste Management. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2015-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2015-7_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-2014-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-2015-7
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)