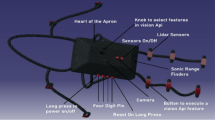
Abstract
Acquiring information of objects or obstacles ahead and accordingly deciding navigation direction is one of the major problems that visually impaired persons face in their day to day life. However there had been a lot of efforts taken for research towards helping the blinds, yet there is no any concrete, globally accepted and used solution available till date. Vision assistive devices are transferable electronic equipment that can also be hold in hands or easily wear by the users to help them sense the obstacles ahead. This paper tries to identify the currently available assistive technologies for visually impaired persons which use advanced image processing techniques. There is an increasing interest in using those techniques for the use of development of cost effective, easily wearable, hassle free, comfortable to operate and user approachable assistive technique for visually damaged population all over the world. These techniques if combined with some other technical components such as sensors, ultrasonic pulse-echo, infrared light transceivers, GPS systems, acoustic feedback techniques, vibration pads etc. can bring forth a very feature enriched assistive system that can overcome many of the lacunas of previously proposed solutions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kay, L.: An ultrasonic sensing probe as a mobility aid for the blind. Ultrasonics, 2(2) (1964). https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-624X(64)90382-8. https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/ultrasonics/vol/2/issue/2.
Koren, J., Borenstein, Y.: The vector field histogram-fast obstacle avoidance for mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 7(3) (1991).https://doi.org/10.1109/70.88137. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/88137/citations#citations.
Borenstein, J., Ulrich, I.: The guidecane-a computerized travel aid for the active guidance of blind pedestrians. Paper presented at the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 25 April 1997 (1997)
Loomis, J.M., Golledge, R.G., Klatzky, R.L.: Navigation system for the blind: auditory display modes and guidance. Presence 7(2), 193–203 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1162/105474698565677. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6788010
Kay, L.: Auditory perception of objects by blind persons using bioacoustic high resolution air sonar. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 107, 3266–3275 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1121/1.429399
Kim, Y.J., Kim, C.-H., Kim, B.K.: Design of an auditory guidance system for the blind with signal transformation from stereo ultrasonic to binaural audio. Artif. Life Robot. 4(4) (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481178
Ross, D.A., Blasch, B.B.: Wearable interfaces for orientation and wayfinding. Paper presented at the Fourth International ACM Conference on Assistive Technologies, Arlington, Virginia, USA, 13–15 November 2000
Loomis, J.M., Golledge, R.G., Klatzky, R.: Gps-Based Navigation Systems for the Visually Impaired. Fundam. Wearab. Comput. Augment. Reality 429, 46 (2001)
Kulyukin, V., Gharpure, C., Nicholson, J., Pavithran, S.: RFID in robot-assisted indoor navigation for the visually impaired. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004
Fernández, J.L., Sanz, R., Benayas, J.A., Diéguez, A.R.: Improving collision avoidance for mobile robots in partially known environments: the beam curvature method. Robot. Auton. Syst. 46, 205–219 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2004.02.004. www.elsevier.com/locate/robot
Calder, D.J.: Assistive technology interfaces for the blind. In: 3rd IEEE International Conference on Digital Ecosystems and Technologies, Istanbul, France. IEEE, 1–3 June 2009 (2009)
Dionisi, A., Sardini, E., Serpelloni, M.: Wearable object detection system for the blind. Paper presented at the IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (2012)
Rodríguez, A., Yebes, J.J., Alcantarilla, P.F., Bergasa, L.M., Almazán, J., Cela, A.: Assisting the Visually Impaired: Obstacle Detection and Warning System by Acoustic Feedback. Sens.—Open Access J. 12(2), 17476–17496 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3390/s121217476. www.mdpi.com/journal/sensors
Al-Fahoum, A., Al-Hmoud, H., Al-Fraihat, A.: A smart infrared microcontroller-based blind guidance system. Active Passive Electron. Compon. 2013, 1–7 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/726480
Sharma, P., Shimi, S.L., Chatterji, S.: Design of microcontroller based virtual eye for the blind. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Technol. (IJSRET), 3(8), 1137–1142 (2014). https://doi.org/10.17148/IJIREEICE.2015.3306. www.ijsret.org
Dakopoulos, D., Bourbakis, N.G.: Wearable obstacle avoidance electronic travel aids for blind: a survey. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 40(1), 25–35 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCC.2009.2021255.
Gurubaran, G.K., Ramalingam, M.: A survey of voice aided electronic stick for visually impaired people. Int. J. Innov. Res. Adv. Eng. (IJIRAE) 1(8) (2014). www.ijirae.com
Prakash, J., Harish, P., Deepika, K.: Android based object recognition into voice input to aid visually impaired. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Sci. 3(1) (2015). www.ijates.com
Verschae, R., Ruiz-del-Solar, J.: Object detection: current and future directions. Front. Robot. AI 2, 29 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2015.00029. https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/frobt.2015.00029
Varun Raj, S.P., Das, A.R.: A low cost outdoor assistive navigation system for blind people. Int. J. Innov. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 3(6), 5767–5774 (2015). https://doi.org/10.15680/ijircce.2015.0306149. IJIRCCE. https://www.ijircce.com/upload/2015/june/149_43_A%20LOW.pdf
Ahn, H., Rhee, S.-B.: Research of object recognition and tracking based on feature matching. In: Park, J., Stojmenovic, I., Jeong, H., Yi, G. (eds.) Computer Science and its Applications, vol. 330, pp. 1071–1076. Springer, Heidelberg (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45402-2_152
Csapó, Á., Wersényi, G., Nagy, H., Stockman, T.: A survey of assistive technologies and applications for blind users on mobile platforms: a review and foundation for research. J. Multimod. User Interfaces 9(4), 275–286 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12193-015-0182-7
El-hariri, E., El-Bendary, N., Hassanien, A.E., Snasel, V.: An assistive object recognition system for enhancing seniors quality of life. Paper presented at the International Conference on Communication, Management and Information Technology, ICCMIT 2015 (2015)
Mohane, V., Gode, C.: Object recognition for blind people using portable camera. In: World Conference on Futuristic Trends in Research and Innovation for Social Welfare (WCFTR 2016), Coimbatore, India, 29 Feb–1 March 2016. IEEE (2016)
Udgirkar, S., Sarokar, S., Gore, S., Kakuste, D., Chaskar, S.: Object detection system for blind people. J. Paper Int. J. Innov. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 4(9) (2016). https://doi.org/10.15680/IJIRCCE.2016.0409040
Parkhi, S., Lokhande, S.S., Thombare, N.D.: Vocal vision android application for visually impaired person. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. Res. (IJSETR) 5(6) (2016). www.ijsetr.org
Mohanapriya, R., Nirmala, U., Pearlin Priscilla, C.: Smart vision for the blind people. Int. J. Adv. Res. Electron. Commun. Eng. (IJARECE) 5(7) (2016)
Bhowmick, A., Hazarika, S.M.: An insight into assistive technology for the visually impaired and blind people: state-of-the-art and future trends. J. Multimod. User Interfaces 11(2), 149–172 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12193-016-0235-6
Zraqou, J.S., Alkhadour, W.M., Siam, M.Z.: Real-time objects recognition approach for assisting blind people. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 7(1), (2017). NPRESSCO. https://inpressco.com/category/ijcet
Mocanu, B., Tapu, R., Zaharia, T.: Seeing without sight — an automatic cognition system dedicated to blind and visually impaired people. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), pp. 1452–1459 (2017). https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8265382
Wang, H.-C., Katzschmann, R.K., Teng, S., Araki, B., Giarré, L., Rus, D.: Enabling independent navigation for visually impaired people through a wearable vision-based feedback system. Paper presented at the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017 (2017)
Yashas, M., Maalik, K.S., Ashfaq, M.Z.M., De Silva, K.P.S.H., Ragulan, S.: Blind guider: an it solution for visually impaired people. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 7(11), 700–703 (2017). https://www.ijsrp.org/research-paper-1117.php?rp=P716990
Kaur, B., Bhattacharya, J.: Scene perception system for visually impaired based on object detection and classification using multimodal deep convolutional neural network. J. Electr. Imaging 28(01), 1–16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JEI.28.1.013031
Usha, B.A., Sangeetha, K.N., Vikram, C.M.: Blinds personal assistant application for android. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. (IJRASET) 7(1), 138–144 (2019)
Koharwal, S., Awwad, S.B., Vyakaranam, A.: Navigation system for blind - third eye. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. (TM) 8(5) (2019). IJITEE. https://www.ijitee.org/download/volume-8-issue-5/
Ponnada, S., Yarramalle, S.: Object identification to assist visually challenged. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. (IJEAT) 8(4) (2019): D6619048419/19. Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering Sciences Publication. https://www.ijeat.org/download/volume-8-issue-4/
Kayukawa, S., et al.: Bbeep: a sonic collision avoidance system for blind travellers and nearby pedestrians. Paper presented at the CHI 2019 Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, Scotland, UK, 04–09 May (2019)
Hoang, V.-N., Nguyen, T.-H., Le, T.-L., Tran, T.-H., Vuong, T.-P., Vuillerme, N.: Obstacle detection and warning system for visually impaired people based on electrode matrix and mobile kinect. Vietnam J. Comput. Sci. 4(2), 71–83 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40595-016-0075-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pardeshi, S.R., Pawar, V.J., Kharat, K.D., Chavan, S. (2021). Assistive Technologies for Visually Impaired Persons Using Image Processing Techniques – A Survey. In: Santosh, K.C., Gawali, B. (eds) Recent Trends in Image Processing and Pattern Recognition. RTIP2R 2020. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1380. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0507-9_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0507-9_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-0506-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-0507-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)