Abstract
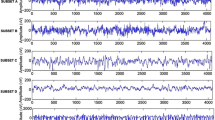
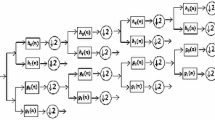
Epilepsy is a disorder of the neurology characterized by epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizure can be analyzed via the normal and abnormal brain activity. This anomalous activity can only be observed by using an efficient algorithm. An effective algorithm method also uses signal processing, in which an epileptic signal can be considered as an input signal. This paper introduces an epileptic signal detection technique and compares the characteristics of the brain signals at different stages. Our algorithm is based on the signal processing techniques used in the EEG signal to detect epilepsy. We present a computer-aided automatic detection and classification method for the focal and non-focal EEG signal in this article. Dual Tree Complex Wavelet Transform (DT-CWT) decomposes the EEG signal, and the characteristics are determined from the decomposed coefficients. These functions are trained and classified using classifier ANN and CANFIS. The proposed system achieves 99% accuracy for EEG signal classification. The experimental results are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed classification method for classifying the EEG focal and non-focal signals.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.S. Fisher, C. Acevedo, A. Arzimanoglou, A. Bogacz, J.H. Cross, C.E. Elger, L. Forsgren, J.A. French, M. Glynn, D.C. Hesdorffer, B.I. Lee, G.W. Mathern, S.L. Moshe, E. Perucca, I.E. Scheffer, T. Tomson, M. Watanabe, S. Wiebe, A practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia 55(4):475–482 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.12550
L.D. Iasemidis, Epileptic seizure prediction and control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 50(5), 549–558 (2003)
D.J. Cross, J.E. Cavazos, The Role of Sprouting and Plasticity in Epileptogenesis and Behavior; Behavioral Aspects of Epilepsy (Demos Medical Publishing, New York, NY, USA, 2007)
S. Pati, A.V. Alexopoulos, Pharmacoresistant epilepsy: from pathogenesis to current and emerging therapies. Clevel Clin. J. Med. 77, 457–467 (2010)
R. Sharma, R.B. Pachori, U.R. Acharya, An integrated index for the identification of focal electroencephalogram signals using discrete wavelet transform and entropy measures. Entropy 17(8), 5218–5240 (2015)
Y. Li, X. Li, M. Ratcliffe, L. Liu, Y. Qi, Q. Liu, A real-time EEG-based BCI system for attention recognition in ubiquitous environment, in Proceedings of 2011 internationalworkshop on ubiquitous affective awareness and intelligent interaction, 2011 (pp. 33–40); N.-H. Liu, C.-Y. Chiang, H.-C. Chu, Recognizing the degree of human attention using EEG signals from mobile sensors. Sensors 13(8), 10273–10286 (2013)
L. Xu, J. Liu, G. Xiao, W. Jin, Characterization and classification of EEG attention based on fuzzy entropy, in Third international conference on digital manufacturing and automation(ICDMA), pp. 277–280. IEEE
B. Hu, X. Li, S. Sun, M. Ratcliffe, Attention recognition in EEG-based affective learning research using CFS + KNN algorithm. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 15(1), 38–45 (2016)
B. Hamadicharef, H. Zhang, C. Guan, C. Wang, K.S. Phua, K.P. Tee, et al., Learning EEG-based spectral-spatial patterns for attention level measurement, in IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems, pp. 1465–1468. IEEE
C.-F. Lin, J.-D. Zhu, Hilbert-Huang transformationbased time-frequency analysis methods in biomedical signal applications, in Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part H—Journal of Engineering in Medicine, vol. 226, no. (H3), pp. 208–216 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mariam Bee, M.K., Vidhya, K. (2021). Epileptic Seizure Severity Analysis Using Artificial Neural Network and CANFIS Classification Approach. In: Tavares, J.M.R.S., Chakrabarti, S., Bhattacharya, A., Ghatak, S. (eds) Emerging Technologies in Data Mining and Information Security. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 164. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9774-9_53
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9774-9_53
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-9773-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-9774-9
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)