Abstract
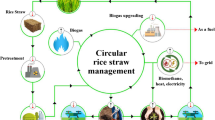
The crop residues and stubbles from agriculture are inevitable products received after harvesting/processing. As the staple food, rice cultivation contributes to ca. 800 million tons of straw at global level. The nutrient-rich biomass demands competent degradation strategies and fruitful use. The cost-effective utilization of paddy straw is found in the production of biochar/hydrochar, producer gas, biogas, power generation, etc. On the contrary, burning rice straw is practiced in many parts of the globe leading to numerous ill effects, viz., release of soot and smoke, greenhouse gas emission, and loss of nutrients. Toward sustainable approach, the paddy straw should be used in all possible ways with the technologies ensuring zero waste and zero harm to the environment. In situ incorporation, composting with help of functional microbes, can be practiced at field level. Further the biomass can be converted to functional carbonized material through either hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) or hydrothermal carbonization (HTC). The low-tech system yields bio-oil and hydrocarbon, respectively. The optimized application of products again to the crop would significantly enhance C status of the soil, reduce GHG emission, and so on. Being abundant in lignin, they can be used as potential feedstock for renewable energy generation like biomethane and bioethanol. To abate the environmental pollution and intensify the soil fertility status, reuse and recycle are the forefront management strategies. Also, paddy straw sets step as valuable tool in the perspective of energy, environment, and economy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Amnuaycheewa, R. Hengaroonprasan, K. Rattanaporn, S. Kirdponpattara, K. Cheenkachorn, M. Sriariyanun, Enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis and biogas production from rice straw by pretreatment with organic acids. Ind. Crop. Prod. 87, 247–254 (2016)
M. Arora, A. Kaur, Azolla pinnata, Aspergillus terreus and Eisenia fetida for enhancing agronomic value of paddy straw. Sci. Rep. 9, 1341 (2019)
A. Arora, S. Priya, P. Sharma, S. Sharma, L. Nain, Evaluating biological pretreatment as a feasible methodology for ethanol production from paddy straw. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 8, 66–72 (2016)
J.S. Bak, J.K. Ko, Y.H. Han, B.C. Lee, I.-G. Choi, K.H. Kim, Improved enzymatic hydrolysis yield of rice straw using electron beam irradiation pretreatment. BioresourTechnol 100, 1285–1290 (2009)
C. Balingbing, N. Van Hung, A.P. Roxas, D. Aquino, M.G. Barbacias, M. Gummert, An assessment on the technical and economic feasibility of mechanized rice straw collection in the Philippines. Sustainability 12(17), 7150 (2020)
A. Barakat, C. Mayer-Laigle, A. Solhy, R.A. Arancon, H. De Vries, R. Luque, Mechanical pretreatments of lignocellulosic biomass: Towards facile and environmentally sound technologies for biofuels production. RSC Adv. 4, 48109–48127 (2014)
R. Chandra, H. Takeuchi, T. Hasegawa, Hydrothermal pretreatment of rice straw biomass: A potential and promising method for enhanced methane production. Appl. Energy 94, 129–140 (2012)
K.-L. Chang et al., Enhanced enzymatic conversion with freeze pretreatment of rice straw. Biomass Bioenergy 35, 90–95 (2011)
X. Chen, Y. Zhang, Y. Gu, Z. Liu, Z. Shen, H. Chu, X. Zhou, Enhancing methane production from rice straw by extrusion pretreatment. Appl. Energy 122, 34–41 (2014)
X. Chen et al., Improving biomethane yield by controlling fermentation type of acidogenic phase in two-phase anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and rice straw. Chem. Eng. J. 273, 254–260 (2015)
R.A. Dar, M. Arora, U.G. Phutela, Optimization of cultural factors of newly isolated microalga Spirulina subsalsa and its co-digestion with paddy straw for enhanced biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 5, 185–198 (2019)
A. Darmawan, A.C. Fitrianto, M. Aziz, K. Tokimatsu, Enhanced electricity production from rice straw. Energy Procedia 142, 271–277 (2017)
L.P. Devendra, A. Pandey, Hydrotropic pretreatment on rice straw for bioethanol production. Renew. Energy 98, 2–8 (2016)
R. Divyabharathi, P. Subramanian, Hydrothermal liquefaction of paddy straw for biocrude production. Mater Today: Proc. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.390
D. Dong, Q. Feng, K. McGrouther, M. Yang, H. Wang, W. Wu, Effects of biochar amendment on rice growth and nitrogen retention in a waterlogged paddy field. J. Soils Sediments 15, 153–162 (2015)
Y. Gu, Y. Zhang, X. Zhou, Effect of Ca(OH)2 pretreatment on extruded rice straw anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 196, 116–122 (2015)
J. Guggolz, G. Kohler, T. Klopfenstein, Composition and improvement of grass straw for ruminant nutrition. J. Anim. Sci. 33, 151–156 (1971)
M. Hans, S. Kumar, A.K. Chandel, I. Polikarpov, A review on bioprocessing of paddy straw to ethanol using simultaneous saccharification and fermentation process. Biochemist 85, 125–134 (2019)
S.H.A. Hassan et al., Electricity generation from rice straw using a microbial fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 39, 9490–9496 (2014)
S. Imman, J. Arnthong, V. Burapatana, V. Champreda, N. Laosiripojana, Influence of alkaline catalyst addition on compressed liquid hot water pretreatment of rice straw. Chem. Eng. J. 278, 85–91 (2015)
J.-y. Park et al., A novel lime pretreatment for subsequent bioethanol production from rice straw – Calcium capturing by carbonation (CaCCO) process. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 6805–6811 (2010)
J. Kainthola, A.S. Kalamdhad, V.V. Goud, Enhanced methane production from anaerobic co-digestion of rice straw and Hydrilla verticillata and its kinetic analysis. Biomass Bioenergy 125, 8–16 (2019)
A. Kamara, H.S. Kamara, M.S. Kamara, Effect of rice straw biochar on soil quality and the early growth and biomass yield of two rice varieties. Agric. Sci. 6, 798–806 (2015)
H.S. Kambo, A. Dutta, A comparative review of biochar and hydrochar in terms of production, physico-chemical properties and applications. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 45, 359–378 (2015)
K. Kaur, U.G. Phutela, Enhancement of paddy straw digestibility and biogas production by sodium hydroxide-microwave pretreatment. Renew. Energy 92, 178–184 (2016)
H. Kausar, M. Sariah, H. Mohd Saud, M. Zahangir Alam, M. Razi Ismail, Development of compatible lignocellulolytic fungal consortium for rapid composting of rice straw. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 64, 594–600 (2010)
M. Kim et al., Hydrogen and methane production from untreated rice straw and raw sewage sludge under thermophilic anaerobic conditions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 38, 8648–8656 (2013)
P. Li et al., Rice straw decomposition affects diversity and dynamics of soil fungal community, but not bacteria. J. Soils Sediments 18, 248–258 (2018)
Q. Li, F. Yang, G. Zheng, Z. Guan, Effects of urea ammonia pretreatment on the batch anaerobic fermentation efficiency of corn stovers. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Engg. 12(4), 169–173 (2019)
Y. Liu, H. Lu, S. Yang, Y. Wang, Impacts of biochar addition on rice yield and soil properties in a cold waterlogged paddy for two crop seasons. Field Crop Res. 191, 161–167 (2016)
E. Mahmoud, M. Ibrahim, P. Robin, N. Akkal-Corfini, M. El-Saka, Rice straw composting and its effect on soil properties. Compost. Sci. Util. 17, 146–150 (2009)
S. Marimuthu, Studies on stubble management in paddy. PhD dissertation, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, 1994
S. Mirmohamadsadeghi, K. Karimi, A. Zamani, H. Amiri, I.S. Horváth, Enhanced solid-state biogas production from lignocellulosic biomass by organosolv pretreatment. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 350414 (2014)
S. Munda et al., Dynamics of soil organic carbon mineralization and C fractions in paddy soil on application of rice husk biochar. Biomass Bioenergy 115, 1–9 (2018)
Y. Nakamura, T. Sawada, E. Inoue, Enhanced ethanol production from enzymatically treated steam-exploded rice straw using extractive fermentation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 76, 879–884 (2001)
S. Negi, H. Dhar, A. Hussain, S. Kumar, Biomethanation potential for co-digestion of municipal solid waste and rice straw: A batch study. Bioresour. Technol. 254, 139–144 (2018)
R.A.C. Passetti, L.C.G. Passetti, R.J. Gruninger, G.O. Ribeiro, M.R. Marami Milani, I.N. Prado, T.A. McAllister, Effect of ammonia fibre expansion (AFEX) treatment of rice straw on in situ digestibility, microbial colonization, acetamide levels and growth performance of lambs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 261, 114411 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2020.114411
D.C. Pedraza-Zapata, A.M. Sánchez-Garibello, B. Quevedo-Hidalgo, N. Moreno-Sarmiento, I. Gutiérrez-Rojas, Promising cellulolytic fungi isolates for rice straw degradation. J. Microbiol. 55, 711–719 (2017)
U.G. Phutela, N. Sahni, S.S. Sooch, Fungal degradation of paddy straw for enhancing biogas production. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 4, 660–665 (2011)
E.P.A. Pratiwi, Y. Shinogi, Rice husk biochar application to paddy soil and its effects on soil physical properties, plant growth, and methane emission. Paddy Water Environ. 14, 521–532 (2016)
X. Qin et al., Long-term effect of biochar application on yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions in a rice paddy cropping system: A four-year case study in south China. Sci. Total Environ. 569–570, 1390–1401 (2016)
S. Sagia, A. Sharma, S. Singh, S. Chaturvedi, P.K.S. Nain, L. Nain, Single cell oil production by a novel yeast Trichosporon mycotoxinivorans for complete and ecofriendly valorization of paddy straw. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 44, 60–68 (2020)
S. Sarangi, T. Lama, Straw composting using earthworm (Eudrilus eugeniae) and fungal inoculant (Trichoderma viridae) and its utilization in rice (Oryza sativa)-groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) cropping system. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 83, 420–425 (2013)
M. Saritha, A. Arora, L. Nain, Pretreatment of paddy straw with Trametes hirsuta for improved enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour. Technol. 104, 459–465 (2012)
C. Sarnklong, J. Cone, W. Pellikaan, W. Hendriks, Utilization of rice straw and different treatments to improve its feed value for ruminants: A review. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 23, 680–692 (2010)
A. Sato, S. Soeprijanto, A. Widjaja, Influence of alkaline hydrothermal pretreatment of rice straw on biomass composition. Int. Energy J. 19, 2 (2019)
T.A. Shah, C.C. Lee, W.J. Orts, R. Tabassum, Biological pretreatment of rice straw by ligninolytic Bacillus sp. strains for enhancing biogas production. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 38, e13036 (2019)
R.K. Sharma, D.S. Arora, Solid state degradation of paddy straw by Phlebia floridensis in the presence of different supplements for improving its nutritive status. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 65, 990–996 (2011)
A. Sharma, R. Sharma, A. Arora, R. Shah, A. Singh, K. Pranaw, L. Nain, Insights into rapid composting of paddy straw augmented with efficient microorganism consortium. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 3, 54 (2014)
G. Sheikh et al., Effect of feeding urea molasses treated rice straw along with fibrolytic enzymes on the performance of Corriedale Sheep. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 5, 2626–2630 (2017)
S. Shrivastava, S. Verma, A. Patra, V. Arya, M. Manna, Efficacy of ligno-cellulolytic microbial consortia on biodegradation of paddy residues and its effect on biological properties of soil. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 8, 1612–1616 (2019)
G. Singh, A. Tiwari, H. Rathore, S. Prasad, P. Hariprasad, S. Sharma, Valorization of paddy straw using de-oiled cakes for P. ostreatus cultivation and utilization of spent mushroom substrate for biopesticide development. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 1–14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-00957-y
I. Syaichurrozi, Biogas production from co-digestion Salvinia molesta and rice straw and kinetics. Renew. Energy 115, 76–86 (2018)
M. Taha, E. Shahsavari, K. Al-Hothaly, A. Mouradov, A.T. Smith, A.S. Ball, E.M. Adetutu, Enhanced biological straw saccharification through coculturing of lignocellulose-degrading microorganisms. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 175, 3709–3728 (2015)
N.X. Trach, M. Mo, C.X. Dan, Effects of treatment of rice straw with lime and/or urea on responses of growing cattle. Livest. Res. Rural. Dev. 13, 47 (2001)
J. Wang, M. Zhang, Z. Xiong, P. Liu, G. Pan, Effects of biochar addition on N2O and CO2 emissions from two paddy soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 47, 887–896 (2011)
X. Wang, X. Lu, F. Li, G. Yang, Effects of temperature and carbon-nitrogen (C/N) ratio on the performance of anaerobic co-digestion of dairy manure, chicken manure and rice straw: Focusing on ammonia inhibition. PLoS One 9, e97265 (2014)
N. Wang, Z.-Z. Chang, X.-M. Xue, J.-G. Yu, X.-X. Shi, L.Q. Ma, H.-B. Li, Biochar decreases nitrogen oxide and enhances methane emissions via altering microbial community composition of anaerobic paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 581, 689–696 (2017)
S. Wang, Y. Ruan, W. Zhou, Z. Li, J. Wu, D. Liu, Net energy analysis of small-scale biogas self-supply anaerobic digestion system operated at psychrophilic to thermophilic conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 174, 226–236 (2018)
S.G. Wi, I.S. Choi, K.H. Kim, H.M. Kim, H.-J. Bae, Bioethanol production from rice straw by popping pretreatment. Biotechnol. Biofuels 6, 166 (2013)
X. Xu et al., Rice straw biochar mitigated more N2O emissions from fertilized paddy soil with higher water content than that derived from ex situ biowaste. Environ. Pollut. 263, 114477 (2020)
B.-Y. Yeon, H.-K. Kwak, Y.-S. Song, H.-J. Jun, H.-J. Cho, C.-H. Kim, Changes in rice yield and soil organic matter content under continued application of rice straw compost for 50 years in paddy soil. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 40, 454–459 (2007)
D. Yin, X. Wang, B. Peng, C. Tan, L.Q. Ma, Effect of biochar and Fe-biochar on Cd and As mobility and transfer in soil-rice system. Chemosphere 186, 928–937 (2017)
M. Yu, G. Zeng, Y. Chen, H. Yu, D. Huang, L. Tang, Influence of Phanerochaete chrysosporium on microbial communities and lignocellulose degradation during solid-state fermentation of rice straw. Process Biochem. 44, 17–22 (2009)
T. Zhang , L. Liu, Z. Song, G. Ren, Y. Feng, H.X. Yang, Biogas production by Co-digestion of goat manure with three crop residues. PLoS One 8, e66845. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0066845. (2013)
H. Zhang, P. Zhang, J. Ye, Y. Wu, W. Fang, X. Gou, G. Zeng, Improvement of methane production from rice straw with rumen fluid pretreatment: A feasibility study. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 113, 9–16 (2016)
G. Zhao, F. Ma, L. Wei, H. Chua, Using rice straw fermentation liquor to produce bioflocculants during an anaerobic dry fermentation process. Bioresour. Technol. 113, 83–88 (2012)
J. Zhao, Z. Dong, J. Li, L. Chen, Y. Bai, Y. Jia, T. Shao, Ensiling as pretreatment of rice straw: The effect of hemicellulase and Lactobacillus plantarum on hemicellulose degradation and cellulose conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 266, 158–165 (2018)
G. Zhou, S. Gao, Y. Lu, Y. Liao, J. Nie, W. Cao, Co-incorporation of green manure and rice straw improves rice production, soil chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties in a typical paddy field in southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 197, 104499 (2020)
S. Zhu, Y. Wu, Z. Yu, J. Liao, Y. Zhang, Pretreatment by microwave/alkali of rice straw and its enzymic hydrolysis. Process Biochem. 40, 3082–3086 (2005a)
S. Zhu et al., Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of microwave/alkali pre-treated rice straw to ethanol. Biosyst. Eng. 92, 229–235 (2005b)
S. Zhu, W. Huang, W. Huang, K. Wang, Q. Chen, Y. Wu, Pretreatment of rice straw for ethanol production by a two-step process using dilute sulfuric acid and sulfomethylation reagent. Appl. Energy 154, 190–196 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry
Geetha Thanuja, K., Marimuthu, S., Ramesh, D., Karthikeyan, S. (2021). Paddy Straw-Based Circular Economy for Sustainable Waste Management. In: Baskar, C., Ramakrishna, S., Baskar, S., Sharma, R., Chinnappan, A., Sehrawat, R. (eds) Handbook of Solid Waste Management. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7525-9_35-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7525-9_35-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-7525-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-7525-9
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Earth and Environm. ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Earth and Environmental Sciences