Abstract
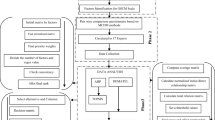
Improving profits while not practicing detrimental environmental activities has always been a conflict of interest faced by many companies. Economic, social and environmental factors can be improved simultaneously by using the concept of sustainability. Factors which affect the sustainable supply chain management were studied keeping in mind the customer requirements, which ultimately translated into improved performance of the companies. The proposed approach was applied to a case study involving Indian automobile industries situated near around Delhi region, India. The factors in the automobile supply chain were found and examined using ISM methodology. Contextual relationships among the driving factors were formulated, and a hierarchy of these factors was developed. The factors’ driving and dependence power were visually presented by making use of MICMAC analysis. ‘Government rules and regulations’ was identified as the key factor for improving the sustainability of the supply chain, while ‘low energy building’ and ‘postponement and customization’ were highly dependent in nature.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saththasivam, G., Fernando, Y.: Integrated sustainable supply chain management: current practices and future direction. In: Green Supply Chain Management for Sustainable Business Practice, pp. 218–233. IGI Global, Hershey, PA (2017). https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-0635-5.ch008
Luthra, S., Garg, D., Haleem, A.: The impacts of critical success factors for implementing green supply chain management towards sustainability: an empirical investigation of Indian automobile industry. J. Clean. Prod. 121, 142–158 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.095
Esfahbodi, A., Zhang, Y., Watson, G.: Sustainable supply chain management in emerging economies: trade-offs between environmental and cost performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 181, 350–366 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2016.02.013
Mousazadeh, M., Torabi, S.A., Pishvaee, M.S.: Green and reverse logistics management under fuzziness. In: Supply Chain Management Under Fuzziness, vol 313, pp. 607–637. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-53939-8_26
Afande, F.O., Ratemo, B.M., Nyaribo, F.N.: Adoption of supply chain management practices: review of determining factors. Innov. Syst. Des. Eng. 6(5), 72–77 (2015)
Khare, A., Misra, R.K., Dubey, A., et al.: Exploiting mobile technology for achieving supply chain integration in Indian retail. J. Asia-Pac. Bus. 13(2), 177–202 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/10599231.2012.637845
Elgazzar, S.H., Tipi, N.S., Hubbard, N.J., et al.: Linking supply chain processes’ performance to a company’s financial strategic objectives. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 223(1), 276–289 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2012.05.043
Bhinge, R., Moser, R., Moser, E., et al.: Sustainability optimization for global supply chain decision-making. Procedia CIRP 26, 323–328 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.07.105
Ketzenberg, M.E., Van Der Laan, E., Teunter, R.H.: Value of information in closed loop supply chains. Prod. Oper. Manag. 15(3), 393–406 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1937-5956.2006.tb00253.x
Hudnurkar, M., Jakhar, S., Rathod, U.: Factors affecting collaboration in supply chain: a literature review. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 133, 189–202 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.04.18
Gupta, S., Palsule-Desai, O.D.: Sustainable supply chain management: review and research opportunities. IIMB Manag. Rev. 23(4), 234–245 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iimb.2011.09.002
Lai, W.T., Chen, C.F.: Behavioral intentions of public transit passengers—the roles of service quality, perceived value, satisfaction and involvement. Transp. Policy 18(2), 318–325 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2010.09.003
Tsironis, L.K., Matthopoulos, P.P.: Towards the identification of important strategic priorities of the supply chain network: an empirical investigation. Bus. Process Manag. J. 21(66), 1279–1298 (2015)
Hadiguna, R.A.: Decision support system of performance assessment for sustainable supply chain management. Int. J. Green Comput. (IJGC) 4(2), 24–37 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4018/jgc.2013070103
Qureshi, F., Li, W., Kara, S., et al.: Unit process energy consumption models for material addition processes: a case of the injection molding process. In: Leveraging Technology for a Sustainable World, pp. 269–274. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29069-5_46
Srinivasan, S., Grasman, S.E.: Supply network planning models using enterprise resource planning systems. In: Business Information Systems: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools and Applications (2010), pp. 605–620. IGI Global, Hershey, PA. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-61520-969-9.ch039
Germani, M., Mandolini, M., Marconi, M., et al.: A system to increase the sustainability and traceability of supply chains. Procedia CIRP 29, 227–232 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2015.02.199
Uysal, F., Tosun, Ö.: Fuzzy TOPSIS-based computerized maintenance management system selection. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 23(2), 212–228 (2012)
Luthra, S., Garg, D., Haleem, A.: Green supply chain management: Implementation and performance—a literature review and some issues. J. Adv. Manag. Res. 11(1), 20–46 (2014)
Luthra, S., Mangla, S.K., Diabat, A.: Using AHP to evaluate barriers in adopting sustainable consumption and production initiatives in a supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 181, 342–349 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2016.04.001
Sindhwani, R., Malhotra, V.: Modelling and analysis of agile manufacturing system by ISM and MICMAC analysis. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 8(2), 253–263 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-016-0426-2
Li, S., Rao, S.S., Ragu-Nathan, T.S., et al.: Development and validation of a measurement instrument for studying supply chain management practices. J. Oper. Manag. 23(6), 618–641 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2005.01.002
Webster, S., Mitra, S.: Competitive strategy in remanufacturing and the impact of take-back laws. J. Oper. Manag. 25(6), 1123–1140 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2007.01.014
Atasu, A., Van Wassenhove, L.N., Sarvary, M.: Efficient take-back legislation. Prod. Oper. Manag. 18(3), 243–258 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1937-5956.2009.01004.x
Leong, G.K., Snyder, D.L., Ward, P.T.: Research in the process and content of manufacturing strategy. Omega 18(2), 109–122 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0483(90)90058-H
Zairi, M.: Benchmarking for best practice: continuous learning through sustainable innovation. Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford, UK (1998)
Aichlmayr, M.: Never touching the floor. Transp. Distrib. 42(9), 47–52 (2001)
Tan, L.T., Hwang, A.R.: Imported technology and R&D in the Taiwanese electronic industry. Rev. Dev. Econ. 6(1), 77–90 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9361.00142
Ferrer, Carbonell A., Frijters, P.: How important is methodology for the estimates of the determinants of happiness? Econ. J. 114(497), 641–659 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0297.2004.00235.x
Luthra, S., Haleem, A.: Hurdles in implementing sustainable supply chain management: An analysis of Indian automobile sector. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 189, 175–183 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.03.212
Soltis, D.E., Soltis, P.S., Pires, J.C.: Recent and recurrent polyploidy in Tragopogon (Asteraceae): cytogenetic, genomic and genetic comparisons. Biol. J. Lin. Soc. 82(4), 485–501 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2004.00335.x
Robb, D.J., Xie, B., Arthanari, T.: Supply chain and operations practice and performance in Chinese furniture manufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 112(2), 683–699 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2007.04.011
Patterson, S.L., Abel, T., Deuel, T.A., et al.: DNF rescues deficits in basal synaptic transmission and hippocampal LTP in BDNF knockout mice. Neuron 16(6), 1137–1145 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80140-3
Simatupang, T.M., Sridharan, R.: Design for supply chain collaboration. Bus. Process Manag. J. 14(3), 401–418 (2008)
Cai, J.F., Candès, E.J., Shen, Z.A.: singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion. SIAM J. Optim. 20(4), 1956–1982 (2010)
Zacharia, Z.G., Nix, N.W., Lusch, R.F.: An analysis of supply chain collaborations and their effect on performance outcomes. J. Bus. Logist. 30(2), 101–123 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2158-1592.2009.tb00114.x
Van Hoek, R.I.: Measuring the unmeasurable-measuring and improving performance in the supply chain. Supply Chain Manag.: Int. J. 3(4), 187–192 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1108/13598549810244232
Tyagi, M., Kumar, P., Kumar, D.: Analysis of interactions among the drivers of green supply chain management. Int. J. Bus. Perform. Supply Chain Model. 7(1), 92–108 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBPSCM.2015.068137
Shuaib, M., Khan, U., Haleem, A.: Modeling knowledge sharing factors and understanding its linkage to competitiveness. Int. J. Global Bus. Compet. 11(1), 23–36 (2016)
Kumar, D., Jain, S., Tyagi, M., Kumar, P.: Quantitative assessment of mutual relationship of issues experienced in greening supply chain using ISM-fuzzy MICMAC approach. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 30(2), 162–178 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kumar, D., Shuaib, M., Tyagi, M., Walia, R.S., Singh, P. (2021). Mapping of Critical Success Factors for Sustainable Supply Chain Performance System. In: Tyagi, M., Sachdeva, A., Sharma, V. (eds) Optimization Methods in Engineering. Lecture Notes on Multidisciplinary Industrial Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4550-4_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4550-4_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-4549-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-4550-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)