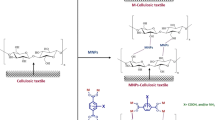
Abstract
Cellulosic textiles mostly facilitate the growth of microorganism due to their larger surface area and capability to hold moisture, which is responsible for several devastating effects not only to consumer but also to the textile itself. Health related consciousness and hygienic perception of products stimulated the intensive research to mitigate the pathogenic effects and development of microbe free materials. Textile researchers have also been paying rigorous attention for developing different antibacterial agents to fulfill the increased demands of ecofriendly antibacterial textiles. The main emphasis of this chapter was to give an overview of advancements in development of different organic and inorganic antibacterial agents, their inclusion during fiber formation or at textile finishing stage, mode of action of different antibacterial agents, durability and the environmental impact of leaching and bound antibacterial textiles.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Textiles Intelligence LTD (2013) Antimicrobial fibres, fabrics and apparel: innovative weapons against infection. Peform Appa Mark 47:25–57
Zhou C-E, Kan C, Matinlinna J, Tsoi J (2017) Regenerable antibacterial cotton fabric by plasma treatment with dimethylhydantoin: antibacterial activity against S. aureus. Coatings 7(1):11
Windler L, Height M, Nowack B (2013) Comparative evaluation of antimicrobials for textile applications. Environ Int 53:62–73
Kyung Wha O, Young Joo N (2014) Antimicrobial activity of cotton fabric treated with extracts from the lotus plant. Text Res J 84(15):1650–1660
Morais DS, Guedes RM, Lopes MA (2016) Antimicrobial approaches for textiles: from research to market. Materials 9(6):498
Ibrahim NA (2015) Nanomaterials for antibacterial textiles. In: Nanotechnology in diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of infectious diseases. Academic Press, pp 191–216
Jothi D (2009) Experimental study on antimicrobial activity of cotton fabric treated with Aloe gel extract from Aloe vera plant for controlling the Staphylococcus aureus (bacterium). Afr J Microbiol Res 3(5):228–232
Saraswathi R, Krishnan P, Dilip C (2010) Antimicrobial activity of cotton and silk fabric with herbal extract by micro encapsulation. Asian Pac J Trop Med 3(2):128–132
Saif MJ, Zia KM, Rehman F, Ahmad MN, Kiran S, Gulzar T (2015) An eco-friendly, permanent, and non-leaching antimicrobial coating on cotton fabrics. J Text Inst 106:907–911
Javid A, Raza ZA, Hussain T, Rehman A (2014) Chitosan microencapsulation of various essential oils to enhance the functional properties of cotton fabric. J Microencapsul 2048:1–8
Tang J, Chen Q, Xu L, Zhang S, Feng L, Cheng L, Xu H, Liu Z (2013) Graphene oxide–silver nanocomposite as a highly effective antibacterial agent with species-specific mechanisms. ACS Appl Mater interfaces 5(9):3867–3874
Javid A, Kumar M, Yoon S, Lee JH, Han JG (2017) Size-controlled growth and antibacterial mechanism for Cu: C nanocomposite thin films. Phys Chem Chem Phys 19(1):237–244
Ashraf M, Campagne C, Perwuelz A, Champagne P, Leriche A, Courtois C (2013) Development of superhydrophilic and superhydrophobic polyester fabric by growing Zinc Oxide nanorods. J Colloid Interface Sci 394(1):545–553
Yetisen AK, Qu H, Manbachi A, Butt H, Dokmeci MR, Hinestroza JP, Skorobogatiy M, Khademhosseini A, Yun SH (2016) Nanotechnology in Textiles. ACS Nano 10(3):3042–3068
Gebbharadt LD, Bachtold JG (1955) Proceedings of the society for experimental biology and medicine, vol 88. Blackwell Science
Qian L, Sun G (2003) Durable and regenerable antimicrobial textiles: synthesis and applications of 3-methylol-2,2,5,5-tetramethylimidazolidin-4-one (MTMIO). J Appl Polym Sci 89(9):2418–2425
Curteza A (2011) Sustainable textiles. Radar 2(1):19–21
Dring I (2003) Antimicrobial, rot proofing and hygiene finishes. In: Textile finishing. Society of Dyers and Colourists, Bradford, pp 351–371
Siedenbiedel F, Tiller JC (2012) Antimicrobial polymers in solution and on surfaces: overview and functional principles. Polymers (Basel) 4(4):46–71
Shahidi S, Wiener J (2012) Antibacterial agents in textile industry. In: Antimicrobial agents, pp. 387–406
Sawan SP, Shalon T, Subramanyam S, Yurkovetskiy A (1996) Contact-killing non-leaching antimicrobial materials. US5849311A
Karthik S, Suriyaprabha R, Vinoth M, Srither SR, Manivasakan P, Rajendran V, Valiyaveettil S (2017) Larvicidal, super hydrophobic and antibacterial properties of herbal nanoparticles from: Acalypha indica for biomedical applications. RSC Adv 7(66):41763–41770
Mamillapalli V (2016) Nanoparticles for herbal extracts. Asian J Pharm 10(2 Supplement):S54–S60
Vigneshwaran N, Ashtaputre NM, Varadarajan PV, Nachane RP, Paralikar KM, Balasubramanya RH (2007) Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Aspergillus flavus. Mater Lett 61(6):1413–1418
Ahmed H, Rajendran R, Balakumar C (2012) Nanoherbal coating of cotton fabric to enhance antimicrobial durability. Appl Chem 45(2012):7840–7843
Chandrasekar S, Vijayakumar S, Rajendran R (2014) Application of chitosan and herbal nanocomposites to develop antibacterial medical textile. Biomed Aging Pathol 4(1):59–64
Singh MN, Hemant KSY, Ram M, Shivakumar HG (2010) Microencapsulation: a promising technique for controlled drug delivery. Res Pharm Sci 5(2):65–77
Gupta A, Dey B (2013) Microencapsulation for controlled drug delivery: a comprehensive review. Sunsari Tech Coll J 1(1):48–54
Nagavarma BVN, Yadav HKS, Ayaz A, Vasudha LS, Shivakumar HG (2012) Different techniques for preparation of polymeric nanoparticles—a review. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 5:16–23
Fievez V, Garinot M, Schneider Y, Préat V (2006) Nanoparticles as potential oral delivery systems of proteins and vaccines: a mechanistic approach. J Controlled Rel 116(1):1–27
Oliveira FR, Fernandes M, Carneiro N, Pedro Souto A (2013) Functionalization of wool fabric with phase-change materials microcapsules after plasma surface modification. J Appl Polym Sci 128(5):2638–2647
Rehman A, Javed A, Raza ZA, Hussain T (2014) Chitosan micro capsulation of various essential oils to enhance the functional properties of cotton fabric. J Microencapsul 31:461–468
Hayashi MA, Bizerra FC, Da Silva PI (2013) Antimicrobial compounds from natural sources. Front Microbiol 4:195
Sivakumar V, Vijaeeswarri J, Anna JL (2011) Effective natural dye extraction from different plant materials using ultrasound. Ind Crops Prod 33(1):116–122
Syamili E, Elayarajah B, Rajendran R, Venkatraja B, Kumar PA (2012) Antibacterial cotton finish using green tea leaf extracts interacted with copper. Asian J Text 2(1):6–16
Straccia MC, Romano I, Oliva A, Santagata G, Laurienzo P (2014) Crosslinker effects on functional properties of alginate/N-succinylChitosan based hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym 108(1):321–330
Rode C, Zieger M, Wyrwa R, Thein S, Wiegand C, Weiser M, Ludwig A, Wehner D, Hipler U (2015) Antibacterial zinc oxide nanoparticle coating of polyester fabrics. J Text Sci Technol 1(August):65–74
Ali SW, Purwar R, Joshi M, Rajendran S (2014) Antibacterial properties of aloe vera gel-finished cotton fabric. Cellulose 21(3):2063–2072
Joshi M, Ali SW, Rajendran S (2007) Antibacterial finishing of polyester/cotton blend fabrics using Neem (Azadirachta indica): a natural bioactive agent. J Appl Polym Sci 106(2):793–800
Nadiger VG, Shukla SR (2017) Antibacterial properties of silk fabric treated with aloe vera and silver nanoparticles. J Text Inst 108(3):385–396
Pinho E, Magalhães L, Henriques M, Oliveira R (2011) Antimicrobial activity assessment of textiles: standard methods comparison. Ann Microbiol 61(3):493–498
Schindler WD, Hauser PJ (2004) Chemical finishing of textiles. CRC, The Textile Institute, Manchester
Hui F, Debiemme-Chouvy C (2013) Antimicrobial N-halamine polymers and coatings: a review of their synthesis, characterization, and applications. Biomacromol 14(3):585–601
Li R, Hu P, Ren X, Worley SD, Huang TS (2013) Antimicrobial N-halamine modified Chitosan films. Carbohydr Polym 92(1):534–539
Liang J, Wu R, Wang JW, Barnes K, Worley SD, Cho U, Lee J, Broughton RM, Huang TS (2007) N-halamine biocidal coatings. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34(2):157–163
Ren T, Dormitorio TV, Qiao M, Huang T-S, Weese J (2018) N-halamine incorporated antimicrobial nonwoven fabrics for use against avian influenza virus. Vet Microbiol 218:78–83
Liu Y, Ren X, Liang J (2015) Antibacterial modification of cellulosic materials. BioResources 10(1):1964–1985
Liang J, Chen Y, Ren X, Wu R, Barnes K, Worley SD, Broughton RM, Cho U, Kocer H, Huang TS (2007) Fabric treated with antimicrobial N-halamine epoxides. Ind Eng Chem Res 46(20):6425–6429
Demir B, Cerkez I, Worley SD, Broughton RM, Huang TS (2015) N-halamine-modified antimicrobial polypropylene nonwoven fabrics for use against airborne bacteria. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(3):1752–1757
Cheng X, Li R, Du J, Sheng J, Ma K, Ren X, Huang TS (2015) Antimicrobial activity of hydrophobic cotton coated with N-halamine. Polym Adv Technol 26(1):99–103
Xue Y, Xiao H, Zhang Y (2015) Antimicrobial polymeric materials with quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts. Int J Mol Sci 16(2):3626–3655
Zhu P, Sun G (2004) Antimicrobial finishing of wool fabrics using quaternary ammonium salts. J Appl Polym Sci 93(3):1037–1041
Riaz S, Ashraf M, Hussain T, Hussain MT (2019) Modification of silica nanoparticles to develop highly durable superhydrophobic and antibacterial cotton fabrics. Cellulose 26(8):5159–5175
Aslanidou D, Karapanagiotis I (2018) Superhydrophobic, superoleophobic and antimicrobial coatings for the protection of silk textiles. Coatings 8(3):101
Berendjchi A, Khajavi R, Yazdanshenas ME (2011) Fabrication of superhydrophobic and antibacterial surface on cotton fabric by doped silica-based sols with nanoparticles of copper. Nanoscale Res Lett 6(1):594
Aiba S (1992) Studies on chitosan: 4. Lysozymic hydrolysis of partially N-acetylated Chitosans. Int J Macromol 14:225–228
Ravi Kumar MNV (2000) A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React Funct Polym 46:1–27
Tolimate A, Desrieres J, Rhazia M (2003) Contribution to the preparation of chitins and chitosans with controlled physico-chemical properties. Polymer (Guildf) 44:7939–7952
Goy RC, de Britto D, Assis OBG (2009) A review of the antimicrobial activity of Chitosan. Polímeros 19(3):241–247
Huang KS, Wu WJ, Chen JB, Lian HS (2008) Application of low-molecular-weight chitosan in durable press finishing. Carbohydr Polym 73(2):254–260
Abdel-Halim ES, Abdel-Mohdy FA, Al-Deyab SS, El-Newehy MH (2010) Chitosan and monochlorotriazinyl-β-cyclodextrin finishes improve antistatic properties of cotton/polyester blend and polyester fabrics. Carbohydr Polym 82(1):202–208
Moses JJ, Venkataraman VK (2016) Study of chemical treated cotton fabric for functional finishes using chitosan. J Text Apparel Technol Manag 10(1):1–17
Zhang Z, Chen L, Ji J, Huang Y, Chen D (2003) Antibacterial properties of cotton fabrics treated with chitosan. Text Res J 73(12):1103–1106
Şahan G, Demir A (2016) A green application of nano sized Chitosan in textile finishing. TEKSTİL ve KONFEKSİYON 26(4):414–420
Scacchetti FAP, Pinto E, Soares GMB (2017) Preparation and characterization of cotton fabrics with antimicrobial properties through the application of chitosan/silver-zeolite film. Procedia Eng 200:276–282
Perelshtein I, Ruderman E, Perkas N, Tzanov T, Beddow J, Joyce E, Mason TJ, Blanes M, Mollá K, Patlolla A, Frenkel AI, Gedanken A (2013) Chitosan and chitosan-ZnO-based complex nanoparticles: formation, characterization, and antibacterial activity. J Mater Chem B 1(14):1968–1976
Regös J, Hitz HR (1974) Investigations on the mode of action of triclosan, a broad spectrum antimicrobial agent. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A 226(3):390–401
Orhan M, Kut D, Gunesoglu C (2009) Improving the antibacterial activity of cotton fabrics finished with triclosan by the use of 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic acid and citric acid. J Appl Polym Sci 111(3):1344–1352
Orhan M, Kut D, Gunesoglu C (2007) Use of triclosan as antibacterial agent in textiles. Indian J Fibre Text Res 32(1):114–118
Ranganath AS, Sarkar AK (2014) Evaluation of durability to laundering of triclosan and chitosan on a textile substrate. J Text 2014:1–5
Kari C, Nagy Z, Kovacs P, Hernadi F (2009) Mechanism of the growth inhibitory effect of cysteine on Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol 68(3):349–356
Caldeira E, Piskin E, Granadeiro L, Silva F, Gouveia IC (2013) Biofunctionalization of cellulosic fibres with l-cysteine: assessment of antibacterial properties and mechanism of action against Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Biotechnol 168(4):426–435
Xu Q, Duan P, Zhang Y, Fu F, Liu X (2018) Double protect copper nanoparticles loaded on L-cysteine modified cotton fabric with durable antibacterial properties. Fibers Polym 19(11):2324–2334
Perni S, Hakala V, Prokopovich P (2013) Biogenic synthesis of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles capped with L-cysteine. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 460:219–224
Xu QB, Gu JY, Zhao Y, Ke XT, Liu XD (2017) Antibacterial cotton fabric with enhanced durability prepared using L-cysteine and silver nanoparticles. Fibers Polym 18(11):2204–2211
Gouveia IC, Sá D, Henriques M (2012) Functionalization of wool with L-cysteine: process characterization and assessment of antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity. J Appl Polym Sci 124(2):1352–1358
Kelleher SM, Habimana O, Lawler J, Reilly BO’, Daniels S, Casey E, Cowley A (2015) Cicada wing surface topography: an investigation into the bactericidal properties of nanostructural features. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, acsami.5b08309
Bazaka K, Jacob MV, Chrzanowski W, Ostrikov K (2015) Anti-bacterial surfaces: natural agents, mechanisms of action, and plasma surface modification. RSC Adv 5(60):48739–48759
Kim SS, Park JE, Lee J (2011) Properties and antimicrobial efficacy of cellulose fiber coated with silver nanoparticles and 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane (3-MPTMS). J Appl Polym Sci 119(4):2261–2267
Liston EM, Martinu L, Wertheimer MR (1993) Plasma surface modification of polymers for improved adhesion: a critical review. J Adhes Sci Technol 7(10):1091–1127
Xu W, Liu X (2003) Surface modification of polyester fabric by corona discharge irradiation. Eur Polym J 39(1):199–202
Vertommen MAME, Nierstrasz VA, van der Veer M, Warmoeskerken MMCG (2005) Enzymatic surface modification of poly(ethylene terephthalate). J Biotechnol 120(4):376–386
Son WK, Youk JH, Lee TS, Park WH (2004) Preparation of antimicrobial ultrafine cellulose acetate fibers with silver nanoparticles. Macromol Rapid Commun 25(18):1632–1637
Ifuku S, Tsuji M, Morimoto M, Saimoto H, Yano H (2009) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles templated by TEMPO-mediated oxidized bacterial cellulose nanofibers. Biomacromol 10(9):2714–2717
Gray JE, Norton PR, Alnouno R, Marolda CL, Valvano MA, Griffiths K (2003) Biological efficacy of electroless-deposited silver on plasma activated polyurethane. Biomaterials 24(16):2759–2765
Zhang G, Liu Y, Gao X, Chen Y (2014) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles and antibacterial property of silk fabrics treated by silver nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett 9(1):216
Maria LCS, Santos ALC, Oliveira PC, Valle ASS, Barud HS, Messaddeq Y, Ribeiro SJL (2010) Preparation and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles impregnated in bacterial cellulose. Polímeros 20(1):72–77
Tam KH, Djurišić AB, Chan CMN, Xi YY, Tse CW, Leung YH, Chan WK, Leung FCC, Au DWT (2008) Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanorods prepared by a hydrothermal method. Thin Solid Films 516(18):6167–6174
Yazdanshenas ME, Shateri-Khalilabad M (2012) In situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles on alkali-treated cotton fabrics. J Ind Text 42(4):459–474
Duan Y, Jia J, Wang S, Yan W, Jin L, Wang Z (2007) Preparation of antimicrobial poly(ε-caprolactone) electrospun nanofibers containing silver-loaded zirconium phosphate nanoparticles. J Appl Polym Sci 106(2):1208–1214
Rangari VK, Mohammad GM, Jeelani S, Hundley A, Vig K, Singh SR, Pillai S (2010) Synthesis of Ag/CNT hybrid nanoparticles and fabrication of their nylon-6 polymer nanocomposite fibers for antimicrobial applications. Nanotechnology 21(9):095102
Ji JH, Jung JH, Kim SS, Yoon J-U, Park JD, Choi BS, Chung YH, Kwon IH, Jeong J, Han BS, Shin JH, Sung JH, Song KS, Yu IJ (2007) Twenty-eight-day inhalation toxicity study of silver nanoparticles in Sprague-Dawley rats. Inhal Toxicol 19(10):857–871
Rai MK, Deshmukh SD, Ingle AP, Gade AK (2012) Silver nanoparticles: the powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 112(5):841–852
Shateri Khalil-Abad M, Yazdanshenas ME, Nateghi MR (2009) Effect of cationization on adsorption of silver nanoparticles on cotton surfaces and its antibacterial activity. Cellulose 16(6):1147–1157
Yeo SY, Jeong SH (2003) Preparation and characterization of polypropylene/silver nanocomposite fibers. Polym Int 52(7):1053–1057
Dubas ST, Kumlangdudsana P, Potiyaraj P (2006) Layer-by-layer deposition of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles on textile fibers. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 289(1–3):105–109
Kelly FM, Johnston JH (2011) Colored and functional silver nanoparticle-wool fiber composites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(4):1083–1092
Ali SW, Rajendran S, Joshi M (2011) Synthesis and characterization of chitosan and silver loaded chitosan nanoparticles for bioactive polyester. Carbohydr Polym 83(2):438–446
Perelshtein I, Applerot G, Perkas N, Grinblat J, Gedanken A (2012) A one-step process for the antimicrobial finishing of textiles with crystalline TiO2 nanoparticles. Chem Eur J 18(15):4575–4582
Montazer M, Seifollahzadeh S (2011) Enhanced self-cleaning, antibacterial and UV protection properties of nano TiO2 treated textile through enzymatic pretreatment. Photochem Photobiol 87(4):877–883
Sivakumar PM, Balaji S, Prabhawathi V, Neelakandan R, Manoharan PT, Doble M (2010) Effective antibacterial adhesive coating on cotton fabric using ZnO nanorods and chalcone. Carbohydr Polym 79(3):717–723
Appierot G, Lipovsky A, Dror R, Perkas N, Nitzan Y, Lubart R, Gedanken A (2009) Enhanced antibacterial activity of nanocrystalline ZnO due to increased ROS-mediated cell injury. Adv Funct Mater 19(6):842–852
Braydich-Stolle L (2005) In vitro cytotoxicity of nanoparticles in mammalian germline stem cells. Toxicol Sci 88(2):412–419
El-Nahhal IM, Zourab SM, Kodeh FS, Semane M, Genois I, Babonneau F (2012) Nano-structured copper oxide-cotton fibers: synthesis, characterization and applications. Int Nano Lett 2(1):14
Castro C, Sanjines R, Pulgarin C, Osorio P, Giraldo SA, Kiwi J (2010) Structure–reactivity relations for DC-magnetron sputtered Cu-layers during E. coli inactivation in the dark and under light. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 216(2–3):295–302
Mary G, Bajpai SK, Chand N (2009) Copper (II) ions and copper nanoparticles-loaded chemically modified cotton cellulose fibers with fair antibacterial properties. J Appl Polym Sci 113(2):757–766
Sambale F, Wagner S, Stahl F, Khaydarov RR, Scheper T, Bahnemann D (2015) Investigations of the toxic effect of silver nanoparticles on mammalian cell lines. J Nanomater 2015:1–9
Shalumon KT, Anulekha KH, Nair SV, Nair SV, Chennazhi KP, Jayakumar R (2011) Sodium alginate/poly(vinyl alcohol)/nano ZnO composite nanofibers for antibacterial wound dressings. Int J Biol Macromol 49(3):247–254
Dastjerdi R, Mojtahedi MRM, Shoshtari AM, Khosroshahi A (2010) Investigating the production and properties of Ag/TiO2/PP antibacterial nanocomposite filament yarns. J Text Inst 101(3):204–213
Daoud WA, Xin JH, Zhang Y-H (2005) Surface functionalization of cellulose fibers with titanium dioxide nanoparticles and their combined bactericidal activities. Surf Sci 599(1–3):69–75
Kiwi J, Rtimi S, Pulgarin C (2013) Cu, Cu/TiO2 thin films sputtered by up to date methods on non-thermal thin resistant substrates leading to bacterial inactivation. Microb Pathog Strateg Combat Them Sci Technol Educ 74–82
Hebeish AA, Abdelhady MM, Youssef AM (2013) TiO2 nanowire and TiO2 nanowire doped Ag-PVP nanocomposite for antimicrobial and self-cleaning cotton textile. Carbohydr Polym 91(2):549–559
Shi L, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Su H, Tan T (2008) Antibacterial and anti-mildew behavior of chitosan/nano-TiO2 composite emulsion. Korean J Chem Eng 25(6):1434–1438
Reddy KM, Feris K, Bell J, Wingett DG, Hanley C, Punnoose A (2007) Selective toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Appl Phys Lett 90(21):2139021–2139023
Raghupathi KR, Koodali RT, Manna AC (2011) Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 27(7):4020–4028
Zhang L, Jiang Y, Ding Y, Daskalakis N, Jeuken L, Povey M, O’Neill AJ, York DW (2010) Mechanistic investigation into antibacterial behaviour of suspensions of ZnO nanoparticles against E. coli. J Nanoparticle Res 12(5):1625–1636
Ashraf M, Dumont F, Campagne C, Champagne P, Perwuelz A, Leriche A, Chihib N-E (2014) Development of antibacterial polyester fabric by growth of ZnO nanorods. J Eng Fiber Fabr 9(1):15–22
Hatamie A, Khan A, Golabi M, Turner APF, Beni V, Mak WC, Sadollahkhani A, Alnoor H, Zargar B, Bano S, Nur O, Willander M (2015) Zinc oxide nanostructure-modified textile and its application to biosensing, photocatalysis, and as antibacterial material. Langmuir 31(39):10913–10921
Agrawal DP (2002) Medicinal properties of neem: new findings, pp 1–5
Mao LMJW (2008) Durable freshness through antimicrobial finishes. Ext Mag 30(4):13–16
AbdElhady MM (2012) Preparation and characterization of chitosan/zinc oxide nanoparticles for imparting antimicrobial and UV protection to cotton fabric. Int J Carbohydr Chem 2012:1–6
Shafei AE, Abou-Okeil A (2011) ZnO/carboxymethyl chitosan bionano-composite to impart antibacterial and UV protection for cotton fabric. Carbohydr Polym 83(2):920–925
Petkova P, Francesko A, Fernandes MM, Mendoza E, Perelshtein I, Gedanken A, Tzanov T (2014) Sonochemical coating of textiles with hybrid ZnO/Chitosan antimicrobial nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(2):1164–1172
Buşilă M, Muşat V, Textor T, Mahltig B (2015) Synthesis and characterization of antimicrobial textile finishing based on Ag:ZnO nanoparticles/Chitosan biocomposites. RSC Adv 5(28):21562–21571
Alviano D, Alviano C (2009) Plant extracts: search for new alternatives to treat microbial diseases. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 10(1):106–121
Cai Y, Luo Q, Sun M, Corke H (2004) Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of 112 traditional Chinese medicinal plants associated with anticancer. Life Sci 74(17):2157–2184
Handique PJ (2013) Antibacterial properties of leaf extracts of Strobilanthes cusia (Nees) Kuntze, a rare ethno-medicinal plant of Manipur, India. Int J PharmTech Res 5(3):1281–1285
Shelton RM (1991) Aloe vera: its chemical and therapeutic properties. Int J Dermatol 30(10):679–683
Day MJ (2008) Immunomodulatory therapy. In: Small animal clinical pharmacology. W.B. Saunders, pp 270–286
Ibrahim W, Sarwar Z, Abid S, Munir U, Azeem A (2017) Aloe vera leaf gel extract for antibacterial and softness properties of cotton. J Text Sci Eng 07(03):1–6
Ammayappan L, Jeyakodi Moses J (2009) Study of antimicrobial activity of aloe vera, Chitosan, and curcumin on cotton, wool, and rabbit hair. Fibers Polym 10(2):161–166
Vastrad JV, Byadgi SA (2018) Eco-friendly antimicrobial finishing of cotton fabric using plant extracts. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 7(2):284–292
Ayyoob M, Khurshid MF, Asad M, Shah SNH (2015) Assessment of eco-friendly natural antimicrobial textile finish extracted from aloe vera and Neem plants. Fibres Text East Eur 23(6):120–123
Hein NT, Hnin SS, Htay DH (2008) A study on the effect of antimicrobial agent from aloe vera gel on bleached cotton fabric. Certif J 4(2):7–11
Mitchell MJ, Smith SL, Johnson S, Morgan ED (2002) Effects of the Neem tree compounds azadirachtin, salannin, nimbin, and 6-desacetylnimbin on ecdysone 20-monooxygenase activity. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 35(12):199–209
Joshi M, Ali SW, Purwar R, Rajendran S (2009) Ecofriendly antimicrobial finishing of textiles using bioactive agents based on natural products. Indian J Fibre Text Res 34(3):295–304
Ganesan P, Vardhini KJ (2015) Herbal treated microbial resistant fabrics for healthcare textiles. Indian J Nat Prod Resour 6(3):227–230
Purwar R, Mishra P, Joshi M (2008) Antibacterial finishing of cotton textiles using Neem extract. AATCC Rev 8(2):36–43
Rajendran R, Radhai R, Balakumar C, Ahamed HAM, Vigneswaran C, Vaideki K (2018) Synthesis and characterization of neem chitosan nanocomposites for development of antimicrobial cotton textiles. J Eng Fiber Fabr 7(1):155892501200700
Sayed U (2017) Application of essential oils for finishing of textile substrates. J Text Eng Fash Technol 1(2):42–47
Khurshid MF, Ayyoob M, Asad M (2015) Assessment of eco-friendly natural antimicrobial textile finish extracted from aloe vera and neem plants. Fibres Text East Europe 6(114):120–123
Patel BH (2009) Dyeing and antimicrobial finishing of polyurethane fibre with neem leaves extract. Man-Made Text India 52(4):112–116
Inprasit T, Motina K, Pisitsak P, Chitichotpanya P (2018) Dyeability and antibacterial finishing of hemp fabric using natural bioactive neem extract. Fibers Polym 19(10):2121–2126
Patel MH, Pratibha D (2014) Grafting of medical textile using neem leaf extract for production of antimicrobial textile. Res J Recent Sci 3(IVC-2014):24–29
Rajput A, Ramachandran M, Gotmare VD, Raichurkar PP (2017) Recent bioactive materials for development of eco-friendly dippers: an overview. J Pharm Sci Res 9(10):1844–1848
Thangamani K, Periasamy R (2017) Study on antimicrobial activity of cotton, bamboo, and soybean fabrics with herbal finishing. Int Res J Pharm 8(5):115–119
Ravindra KB, Murugesh Babu K (2016) Study of antimicrobial properties of fabrics treated with Ocimum sanctum L. (tulsi) extract as a natural active agent. J Nat Fibers 13(5):619–627
El-Shafei A, El-Bisi MK, Zaghloul S, Refai R (2017) Herbal textile finishes—natural antibacterial finishes for cotton fabric. Egypt J Chem 60(2):161–180
Prasad S, Aggarwal BB (2011) Turmeric, the golden spice: from traditional medicine to modern medicine. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis
Nasri H, Sahinfard N, Rafieian M, Rafieian S, Shirzad M, Rafieian-Kopaei M (2014) Turmeric: A spice with multifunctional medicinal properties. J HerbMed Pharmacol J 3(1):5–8
Mirjalili M, Karimi L (2013) Antibacterial dyeing of polyamide using turmeric as a natural dye. Autex Res J 13(2):51–56
Reddy N, Han S, Zhao Y, Yang Y (2013) Antimicrobial activity of cotton fabrics treated with curcumin. J Appl Polym Sci 127(4):2698–2702
Ghoreishian SM, Maleknia L, Mirzapour H, Norouzi M (2013) Antibacterial properties and color fastness of silk fabric dyed with turmeric extract. Fibers Polym 14(2):201–207
Al Sarhan TM, Salem AA (2018) Turmeric dyeing and chitosan/titanium dioxide nanoparticle colloid finishing of cotton fabric. Indian J Fibre Text Res (IJFTR)
Gotmare VD, Kole SS, Athawale RB (2018) Sustainable approach for development of antimicrobial textile material using nanoemulsion for wound care applications. Fash Text 5(1):25
Sharma Y, Dua D, Srivastava N (2016) Antibacterial activity, phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of stem of nicotiana tabacum. Int J Pharm Sci Res 7(3):1156–1167
Ru QM, Wang LJ, Li WM, Wang JL, Ding YT (2012) In vitro antioxidant properties of flavonoids and polysaccharides extract from tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) leaves. Molecules 17(9):11281–11291
Duangsri P, Juntarapun K, Satirapipathkul C (2012) The tobacco leaf extract and antibacterial activity in textile. In: RMUTP international conference: textiles & fashion, pp 3–8
Carson CF, Hammer KA, Riley TV (2006) Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil: a review of antimicrobial and other medicinal properties. Clin Microbiol Rev 19(1):50–62
Kunicka-Styczyńska A, Sikora M, Kalemba D (2009) Antimicrobial activity of lavender, tea tree and lemon oils in cosmetic preservative systems. J Appl Microbiol 107(6):1903–1911
Pohlmann M, Paese K, Frank LA, Guterres SS (2018) Production, characterization and application of nanotechnology-based vegetable multi-component theospheres in nonwovens: a women’s intimate hygiene approach. Text Res J 88(20):2292–2302
Cerempei A, Guguianu E, Muresan EI, Horhogea C, Rîmbu C, Borhan O (2015) Antimicrobial controlled release systems for the knitted cotton fabrics based on natural substances. Fibers Polym 16(8):1688–1695
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Riaz, S., Ashraf, M. (2020). Recent Advances in Development of Antimicrobial Textiles. In: Shahid, M., Adivarekar, R. (eds) Advances in Functional Finishing of Textiles. Textile Science and Clothing Technology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3669-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3669-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-3668-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-3669-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)