Abstract
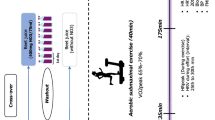
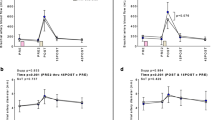
It is still not known whether dietary nitrate can improve blood pressure (BP) and muscular strength in prehypertensives women. The current study investigated the effects of chronic (14-day) nitrate-rich beetroot extract supplementation on the blood pressure responses, maximal isometric handgrip strength and breath nitric oxide level in pre-hypertensive women. In a double-blind, randomized, crossover design, 9 prehypertensives females completed all assessments at pre-supplementation (as control; PRE) and 2-h after orally consumed beetroot extract (BRE; 250 mg·kg−1·day−1) and placebo (PLA; red coloring powder with negligible NO3− and NO2− content), with a washout period of 10 days separating each trial. BRE reduced systolic blood pressure (BRE: 126 ± 2.2 vs. PLA: 132 ± 4.0 vs. PRE: 131 ± 3.2 mmHg; P < 0.05). Similarly, diastolic blood pressure (BRE: 80 ± 4.6 vs. PLA: 84 ± 4.5 vs. PRE: 82 ± 4.4 mmHg; P < 0.05) and mean arterial pressure (BRE: 95 ± 3.5 vs. PLA: 100 ± 3.7 vs. PRE: 98 ± 3.4 mmHg; P < 0.05) were all lowered following BRE supplementation. However, no statistically significant changes were observed in maximal isometric handgrip strength across the trial condition. Additionally, resting fractional exhaled nitric oxide was elevated by ~124% and ~138% compared to the PRE and PLA condition, respectively (both P < 0.05). These findings suggest chronic (14-day) beetroot extract supplementation can significantly improve BP indices in the high-normal BP (prehypertension) population, but not handgrip strength.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghee, L.K., Kooi, C.W.: A review of metabolic syndrome research in Malaysia. Med. J. Malays. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046365
Hardman, A., Stensel, D.: Physical Activity and Health: The Evidence Explained, 1st edn. Psychology Press, London (2003)
Dewhurst-Trigg, R., Yeates, T., Blackwell, J.R., Thompson, C., Linoby, A., Morgan, P.T., Bailey, S.J.: Lowering of blood pressure after nitrate-rich vegetable consumption is abolished with the co-ingestion of thiocyanate-rich vegetables in healthy normotensive males. Nitric Oxide – Biol. Chem. 74, 39–46 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2018.01.009
Hobbs, D.A., George, T.W., Lovegrove, J.A.: The effects of dietary nitrate on blood pressure and endothelial function: a review of human intervention studies. Nutr. Res. Rev. 26(2), 210–222 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954422413000188
Sanders, T.: A dose response study of the effects of increased fruit and vegetable intake on vascular function. Food Stand. Agency 1–57 (2007)
Habermeyer, M., Roth, A., Guth, S., Diel, P., Engel, K.H., Epe, B., Eisenbrand, G.: Nitrate and nitrite in the diet: how to assess their benefit and risk for human health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201400286
Shannon, O.M., Duckworth, L., Barlow, M.J., Woods, D., Lara, J., Siervo, M., O’Hara, J.P.: Dietary nitrate supplementation enhances high-intensity running performance in moderate normobaric hypoxia, independent of aerobic fitness. Nitric Oxide – Biol. Chem. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2016.08.001
Christie, A.D., Tonson, A., Larsen, R.G., DeBlois, J.P., Kent, J.A.: Human skeletal muscle metabolic economy in vivo: effects of contraction intensity, age, and mobility impairment. AJP: Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00083.2014
WHO, Primary Registries: WHO. World Health Organization (2019). https://www.who.int/ictrp/network/primary/en/. Accessed 30 May 2019
Wylie, L.: Dietary Nitrate Supplementation: Dose-Response Relationships and Effects on Intermittent Exercise Performance. University of Exeter. https://ore.exeter.ac.uk/repository/handle/10871/24290. Accessed 14 Apr 2016
Vanhatalo, A., Bailey, S.J., Blackwell, J.R., DiMenna, F.J., Pavey, T.G., Wilkerson, D.P., Jones, A.M.: Acute and chronic effects of dietary nitrate supplementation on blood pressure and the physiological responses to moderate-intensity and incremental exercise. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 299(4), R1121–R1131 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00206.2010
Dweik, R.A., Boggs, P.B., Erzurum, S.C., Irvin, C.G., Leigh, M.W., Lundberg, J.O., Taylor, D.R.: An official ATS clinical practice guideline: interpretation of exhaled nitric oxide levels (FeNO) for clinical applications. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 184(5), 602–615 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.9120-11ST
Malaysian Standard: MS ISO 7250-1:2008 basic human body measurements for technological design - part 1: body measurement definitions and landmarks. Dep. Stand, Malaysia (2008)
Barut, C., Demirel, P., Kiran, S.: Evaluation of hand anthropometric measurements and grip strength in basketball, volleyball and handball players. Anatomy (2008). https://doi.org/10.2399/ana.08.055
Cohen, J.: A power primer. Psychol. Bull. (1992). https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.155
Brkić, D., Bošnir, J., Bevardi, M., Bošković, A.G., Miloš, S., Lasić, D., Krivohlavek, A., Racs, A., Trstenjak, N.U.: Nitrate in leafy green vegetables and estimated intake. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 14(3), 31–41 (2017). https://doi.org/10.21010/ajtcam.v14i3.4
Kapil, V., Khambata, R.S., Robertson, A., Caulfield, M.J., Ahluwalia, A.: Dietary nitrate provides sustained blood pressure lowering in hypertensive patients: a randomized, phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Hypertension (2015). https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.114.04675. (Dallas, Tex.: 1979)
Wylie, L.J., Kelly, J., Bailey, S.J., Blackwell, J.R., Skiba, P.F., Winyard, P.G., Jones, A.M.: Beetroot juice and exercise: pharmacodynamic and dose-response relationships. J. Appl. Physiol. 115(3), 325–336 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00372.2013
Barnes, P.J., Dweik, R.A., Gelb, A.F., Gibson, P.G., George, S.C., Grasemann, H., Zamel, N.: Exhaled nitric oxide in pulmonary diseases a comprehensive review. Chest (2010). https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.09-2090
Kroll, J.L., Werchan, C.A., Rosenfield, D., Ritz, T.: Acute ingestion of beetroot juice increases exhaled nitric oxide in healthy individuals. PLoS ONE (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191030
Rodriguez-Mateos, A., Hezel, M., Aydin, H., Kelm, M., Lundberg, J.O., Weitzberg, E., Heiss, C.: Interactions between cocoa flavanols and inorganic nitrate: additive effects on endothelial function at achievable dietary amounts. Free Radic. Biol. Med. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.12.009
Webb, A.J., Patel, N., Loukogeorgakis, S., Okorie, M., Aboud, Z., Misra, S., Ahluwalia, A.: Acute blood pressure lowering, vasoprotective, and antiplatelet properties of dietary nitrate via bioconversion to nitrite. Hypertension (2008). https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.103523
Kapil, V., Milsom, A.B., Okorie, M., Maleki-Toyserkani, S., Akram, F., Rehman, F., Ahluwalia, A.: Inorganic nitrate supplementation lowers blood pressure in humans: role for nitrite-derived NO. Hypertension (2010). https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.153536
Wylie, L.J., Ortiz de Zevallos, J., Isidore, T., Nyman, L., Vanhatalo, A., Bailey, S.J., Jones, A.M.: Dose-dependent effects of dietary nitrate on the oxygen cost of moderate-intensity exercise: acute vs. chronic supplementation. Nitric Oxide 57, 30–39 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2016.04.004
Leopold, J.A., Loscalzo, J.: Organic nitrate tolerance and endothelial dysfunction: role of folate therapy. Minerva Cardioangiol. 51(4), 349–359 (2003)
Acknowledgement
This research was funded by Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS/1/2018/-WAB13/UITM/03/1), Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Linoby, A. et al. (2020). A Randomized Controlled Trial of the Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Blood Pressure, Exhaled Nitric Oxide Level and Maximal Isometric Handgrip Strength in Pre-hypertensive Women. In: Hassan, M., et al. Enhancing Health and Sports Performance by Design. MoHE 2019. Lecture Notes in Bioengineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3270-2_41
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3270-2_41
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-3269-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-3270-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)