Abstract
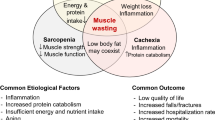
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is very common in the elderly. CKD-related metabolic derangements increase the risk of skeletal muscle wasting, so the prevalence of sarcopenia and frailty are substantially higher in CKD patients compared to the general population. Sarcopenia is defined according to the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia (AWGS), while frailty according to the Japanese version of the Cardiovascular Health Study (J-CHS) in Japan. Sarcopenia and frailty are closely associated with protein-energy wasting. Frailty is also more prevalent in female than in male in CKD patients.
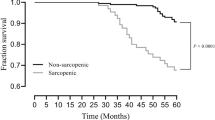
Sarcopenia and frailty are both related to survival prognosis and accelerated progression to end-stage kidney disease in patients with non-dialysis-dependent CKD. In dialysis patients, low muscle strength rather than muscle mass volume is more strongly associated with physical inactivity, inflammation, and total mortality. Frailty is also an independent predictor of cognitive impairment, hospitalization, and mortality in the dialysis population.
Given the convincing relationship between sarcopenia, frailty, and adverse clinical outcomes, we should be more aware of the concept of sarcopenia and frailty and prevent their progressions especially in older patients with advanced CKD.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas B, Wulf S, Bikbov B, Perico N, Cortinovis M, Courville de Vaccaro K, Flaxman A, Peterson H, Delossantos A, Haring D, Mehrotra R, Himmelfarb J, Remuzzi G, Murray C, Naghavi M. Maintenance dialysis throughout the world in years 1990 and 2010. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26:2621–33.
Liyanage T, Ninomiya T, Jha V, Neal B, Patrice HM, Okpechi I, Zhao MH, Lv J, Garg AX, Knight J, Rodgers A, Gallagher M, Kotwal S, Cass A, Perkovic V. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet. 2015;385:1975–82.
United States Renal Data System. USRDS annual data report. Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health; 2015. p. 2015.
Masakane I, Nakai S, Ogata S, Kimata N, Hanafusa N, Hamano T, Wakai K, Wada A, Nitta K. An overview of regular dialysis treatment in Japan (as of 31 December 2013). Ther Apher Dial. 2015;19:540–74.
Mills KT, Xu Y, Zhang W, Bundy JD, Chen CS, Kelly TN, Chen J, He J. A systematic analysis of worldwide population-based data on the global burden of chronic kidney disease in 2010. Kidney Int. 2015;88:950–7.
Hill NR, Fatoba ST, Oke JL, Hirst JA, O’Callaghan CA, Lasserson DS, Hobbs FD. Global prevalence of chronic kidney disease - a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0158765.
Xie Y, Bowe B, Mokdad AH, Xian H, Yan Y, Li T, Maddukuri G, Tsai CY, Floyd T, Al-Aly Z. Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study highlights the global, regional, and national trends of chronic kidney disease epidemiology from 1990 to 2016. Kidney Int. 2018;94:567–81.
Murphy D, McCulloch CE, Lin F, Banerjee T, Bragg-Gresham JL, Eberhardt MS, Morgenstern H, Pavkov ME, Saran R, Powe NR, Hsu CY, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Chronic Kidney Disease Surveillance Team. Trends in prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 2016;165:473–81.
Imai E, Horio M, Watanabe T, Iseki K, Yamagata K, Hara S, Ura N, Kiyohara Y, Moriyama T, Ando Y, Fujimoto S, Konta T, Yokoyama H, Makino H, Hishida A, Matsuo S. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the Japanese general population. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2009;13:621–30.
O’Hare AM, Choi AI, Bertenthal D, Bacchetti P, Garg AX, Kaufman JS, Walter LC, Mehta KM, Steinman MA, Allon M, McClellan WM, Landefeld CS. Age affects outcomes in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:2758–65.
Demoulin N, Beguin C, Labriola L, Jadoul M. Preparing renal replacement therapy in stage 4 CKD patients referred to nephrologists: a difficult balance between futility and insufficiency. A cohort study of 386 patients followed in Brussels. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26:220–6.
Sud M, Tangri N, Levin A, Pintilie M, Levey AS, Naimark DM. CKD stage at nephrology referral and factors influencing the risks of ESRD and death. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;63:928–36.
Obi Y, Kimura T, Nagasawa Y, Yamamoto R, Yasuda K, Sasaki K, Kitamura H, Imai E, Rakugi H, Isaka Y, Hayashi T. Impact of age and overt proteinuria on outcomes of stage 3 to 5 chronic kidney disease in a referred cohort. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5:1558–65.
Iimori S, Naito S, Noda Y, Sato H, Nomura N, Sohara E, Okado T, Sasaki S, Uchida S, Rai T. Prognosis of chronic kidney disease with normal-range proteinuria: The CKD-ROUTE study. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0190493.
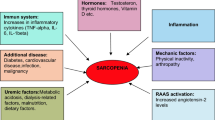
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie Y, Bruyère O, Cederholm T, Cooper C, Landi F, Rolland Y, Sayer AA, Schneider SM, Sieber CC, Topinkova E, Vandewoude M, Visser M, Zamboni M, Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2), and the Extended Group for EWGSOP2. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48:16–31.
Chen LK, Liu LK, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung TW, Bahyah KS, Chou MY, Chen LY, Hsu PS, Krairit O, Lee JS, Lee WJ, Lee Y, Liang CK, Limpawattana P, Lin CS, Peng LN, Satake S, Suzuki T, Won CW, Wu CH, Wu SN, Zhang T, Zeng P, Akishita M, Arai H. Sarcopenia in Asia: consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15:95–101.
Pereira RA, Cordeiro AC, Avesani CM, Carrero JJ, Lindholm B, Amparo FC, Amodeo C, Cuppari L, Kamimura MA. Sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease on conservative therapy: prevalence and association with mortality. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30:1718–25.
Souza VA, Oliveira D, Barbosa SR, Corrêa JODA, Colugnati FAB, Mansur HN, Fernandes NMDS, Bastos MG. Sarcopenia in patients with chronic kidney disease not yet on dialysis: analysis of the prevalence and associated factors. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0176230.
Zhou Y, Hellberg M, Svensson P, Höglund P, Clyne N. Sarcopenia and relationships between muscle mass, measured glomerular filtration rate and physical function in patients with chronic kidney disease stages 3-5. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018;33:342–8.
Ishikawa S, Naito S, Iimori S, Takahashi D, Zeniya M, Sato H, Nomura N, Sohara E, Okado T, Uchida S, Rai T. Loop diuretics are associated with greater risk of sarcopenia in patients with non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0192990.
D’Alessandro C, Piccoli GB, Barsotti M, Tassi S, Giannese D, Morganti R, Cupisti A. Prevalence and correlates of sarcopenia among elderly CKD outpatients on tertiary care. Nutrients. 2018;10:E1951.
Harada K, Suzuki S, Ishii H, Aoki T, Hirayama K, Shibata Y, Negishi Y, Sumi T, Kawashima K, Kunimura A, Shimbo Y, Tatami Y, Kawamiya T, Yamamoto D, Morimoto R, Yasuda Y, Murohara T. Impact of skeletal muscle mass on long-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease. Am J Cardiol. 2017;119:1275–80.
McIntyre CW, Selby NM, Sigrist M, Pearce LE, Mercer TH, Naish PF. Patients receiving maintenance dialysis have more severe functionally significant skeletal muscle wasting than patients with dialysis-independent chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:2210–6.
Isoyama N, Quershi AR, Avesani CM, et al. Comparative associations of muscle mass and muscle strength with morality in dialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;9:1720–8.
Kim JK, Choi SR, Choi MJ, et al. Prevalence of and factors associated with sarcopenia in elderly patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin Nutr. 2014;33:64–8.
Lamarca F, Carrero JJ, Rodrigues JC, Bigogno FG, Fetter RL, Avesani CM. Prevalence of sarcopenia in elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients: the impact of different diagnostic criteria. J Nutr Health Aging. 2014;18:710–7.
Bataille S, Serveaux M, Carreno E, Pedinielli N, Darmon P, Robert A. The diagnosis of sarcopenia is mainly driven by muscle mass in hemodialysis patients. Clin Nutr. 2017;36:1654–60.
Kittiskulnam P, Chertow GM, Carrero JJ, Delgado C, Kaysen GA, Johansen KL. Sarcopenia and its individual criteria are associated, in part, with mortality among patients on hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2017;92:238–47.
Giglio J, Kamimura MA, Lamarca F, Rodrigues J, Santin F, Avesani CM. Association of sarcopenia with nutritional parameters, quality of life, hospitalization, and mortality rates of elderly patients on hemodialysis. J Ren Nutr. 2018;28:197–207.
Kamijo Y, Kanda E, Ishibashi Y, Yoshida M. Sarcopenia and frailty in PD: impact on mortality, malnutrition, and inflammation. Perit Dial Int. 2018;38:447–54.
Kato A, Ishida J, Endo Y, Takita T, Furuhashi M, Maruyama Y, Odamaki M. Association of abdominal visceral adiposity and thigh sarcopenia with changes of arteriosclerosis in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26:1967–76.
Fried LP, Ferrucci L, Darer J, Williamson JD, Anderson G. Untangling the concepts of disability, frailty and comorbidity: implications for improving targeting and care. J Gerontrol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2004;59:225–63.
Mitnitski AB, Mogilner AJ, Rockwood K. Accumulation of deficits as a proxy measure of aging. Sci World J. 2001;1:323–36.
Searle SD, Mitnitski A, Gahbauer EA, Gill TM, Rockwood K. A standard procedure for creating a frailty index. BMC Geriatr. 2008;8:24.
Satake S, Senda K, Hong YJ, Miura H, Endo H, Sakurai T, Kondo I, Toba K. Validity of the Kihon checklist for assessing frailty status. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2016;16:709–15.
Satake S, Shimada H, Yamada M, Kim H, Yoshida H, Gondo Y, Matsubayashi K, Matsushita E, Kuzuya M, Kozaki K, Sugimoto K, Senda K, Sakuma M, Endo N, Arai H. Prevalence of frailty among community-dwellers and outpatients in Japan as defined by the Japanese version of the Cardiovascular Health Study criteria. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2017;17:2629–34.
Carrero JJ, Johansen KL, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P, Cuppari L, Avesani CM. Screening for muscle wasting and dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2016;90:53–60.
Roshanravan B, Khatri M, Robinson-Cohen C, Levin G, Patel KV, de Boer IH, Seliger S, Ruzinski J, Himmelfarb J, Kestenbaun B. A prospective study of frailty in nephrology-referred patients with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60:912–21.
Hiraki K, Yasuda T, Hotta C, Izawa KP, Morio Y, Watanabe S, Sakurada T, Shibagaki Y, Kimura K. Decreased physical function in pre-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2013;17:2252–31.
Lee S, Lee S, Harada K, Bae S, Makizako H, Doi T, Tsutsumimoto K, Hotta R, Nakakubo S, Park H, Suzuki T, Shimada H. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2017;17:1527–33.
Lee S, Lee S, Bae S, Harada K, Jung S, Imaoka M, Makizako H, Doi T, Shimada H. Relationship between chronic kidney disease without diabetes mellitus and components of frailty in community-dwelling Japanese older adults. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2018;18:286–92.
Roshanravan B, Khatri M, Robinson-Cohen C, Levin G, Patel KV, de Boer IH, Seliger S, Ruzinski J, Himmelfarb J, Kestenbaum B. A prospective study of frailty in nephrology-referred patients with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60:912–21.
Lee SJ, Son H, Shin SK. Influence of frailty on health-related quality of life in pre-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease in Korea: a cross-sectional study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015;13:70.
Shlipak MG, Stehman-Breen C, Fried LF, Song X, Siscovick D, Fried LP, Psaty BM, Newman AB. The presence of frailty in elderly persons with chronic renal insufficiency. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43:861–7.
Takeuchi H, Uchida HA, Kakio Y, Okuyama Y, Okuyama M, Umebayashi R, Wada K, Sugiyama H, Sugimoto K, Rakugi H, Wada J. The prevalence of frailty and its associated factors in Japanese hemodialysis patients. Aging Dis. 2018;9:192–207.
Lee SY, Yang DH, Hwang E, Kang SH, Park SH, Kim TW, Lee DH, Park K, Kim JC. The prevalence, association, and clinical outcomes of frailty in maintenance dialysis patients. J Ren Nutr. 2017;27:106–12.
Johansen KL, Delgado C, Kaysen GA, Chertow GM, Chiang J, Dalrymple LS, Segal MR, Grimes BA. Frailty among patients receiving hemodialysis: evolution of components and associations with mortality. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2019;74:380–6.
McAdams-DeMarco MA, Tan J, Salter ML, Gross A, Meoni LA, Jaar BG, Kao WH, Parekh RS, Segev DL, Sozio SM. Frailty and cognitive function in incident hemodialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10:2181–9.
Delgado C, Shieh S, Grimes B, Chertow GM, Dalrymple LS, Kaysen GA, Kornak J, Johansen KL. Association of self-reported frailty with falls and fractures among patients mew to dialysis. Am J Nephrol. 2015;42:134–40.
Fouque D, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple J, Cano N, Chauveau P, Cuppari L, Franch H, Guarnieri G, Ikizler TA, Kaysen G, Lindholm B, Massy Z, Mitch W, Pineda E, Stenvinkel P, Treviño-Becerra A, Wanner C. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008;73:391–8.
Carrero JJ, Thomas F, Nagy K, Arogundade F, Avesani CM, Chan M, Chmielewski M, Cordeiro AC, Espinosa-Cuevas A, Fiaccadori E, Guebre-Egziabher F, Hand RK, Hung AM, Ikizler TA, Johansson LR, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Karupaiah T, Lindholm B, Marckmann P, Mafra D, Parekh RS, Park J, Russo S, Saxena A, Sezer S, Teta D, Ter Wee PM, Verseput C, Wang AYM, Xu H, Lu Y, Molnar MZ, Kovesdy CP. Global prevalence of protein-energy wasting in kidney disease: a meta-analysis of contemporary observational studies from the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. J Ren Nutr. 2018;28:380–92.
Yasui S, Shirai Y, Tanimura M, Matsuura S, Saito Y, Miyata K, Ishikawa E, Miki C, Hamada Y. Prevalence of protein-energy wasting (PEW) and evaluation of diagnostic criteria in Japanese maintenance hemodialysis patients. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2016;25:292–9.
Takahashi H, Inoue K, Shimizu K, Hiraga K, Takahashi E, Otaki K, Yoshikawa T, Furuta K, Tokunaga C, Sakakibara T, Ito Y, Tokai Renal Nutrition Study Group. Comparison of nutritional risk scores for predicting mortality in Japanese chronic hemodialysis patients. J Ren Nutr. 2017;27:201–6.
Disclosures
I declare that I have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kato, A. (2020). Epidemiology of Sarcopenia and Frailty in CKD. In: Kato, A., Kanda, E., Kanno, Y. (eds) Recent Advances of Sarcopenia and Frailty in CKD. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-2365-6_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-2365-6_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-2364-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-2365-6
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)