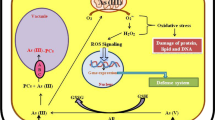
Abstract
Arsenic (As) is a biological non-essential metalloid toxic to both plants and animals. Sources of As toxicity include both geogenic and anthropogenic. Arsenic accumulation in soil leads to deterioration of physiological properties of soil resulting in reduction of soil fertility and crop yield. Arsenic enters into the food chain either by consumption of As-contaminated water or by intake of plants cultivated in As-contaminated soil as plants accumulate As in different edible parts. Arsenate [As (V)] and arsenite [As (III)] are two inorganic forms of arsenic that are available to plants. They are well known for toxicity symptoms in plants with the former being the most toxic form of arsenic. Arsenic toxicity in plants leads to many morphological and physiological changes like reduction in growth, decrease in number of leaves, decrease in germination rate, plasmolysis of the root cells, demodulation, necrosis of leaf tips, leaf wilting, disruption of cellular membrane structure leading to electrolyte leakage, photosynthesis inhibition, and disruption of cellular energy flow. In response to arsenic toxicity, the plants use various detoxification mechanisms, which include non-enzymatic and enzymatic antioxidant defense mechanisms, hyperaccumulation, and phytochelation synthesis for protection of cells and subcellular systems. Hence, it is necessary to understand the bioavailability of As, its assimilation, metabolism, and toxicity in plants for mitigation of As from the contaminated soil and water. Many plant species including halophytes and glycophytes are potential candidates for mitigating toxic effects of As, thus paving the way for detoxification of the As-contaminated soils through phytoextraction, phytostabilization, and phytoexcretion of As. The chapter presents an overview of significant sources of As contamination, As toxicity and bioavailability, potentiality of various plant species to cope up with arsenic toxicity, and their mechanisms of adaptations to heavy metal stress proving their potential role in phytoextraction, phytostabilization, and phytoexcretion of heavy metal-contaminated saline as well as non-saline soils.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- As:
-
Arsenic
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- BCF:
-
Bioconcentration factor
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- DMA:
-
Dimethylarsinic acid
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- H2O2:
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MMA:
-
Monomethylarsonic acid
- O2•−:
-
Superoxide
- OH•:
-
Hydroxyl radicals
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- Tf:
-
Translocation factor
- TMAO:
-
Trimethylarsine oxide
References
Abbas G, Murtaza B, Bibi I, Shahid M, Niazi N, Khan M, Amjad M, Hussain M (2018) Arsenic uptake, toxicity, detoxification, and speciation in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular aspects. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:59–104
Abercrombie JM, Halfhill MD, Ranjan P, Rao MR, Saxton AM, Yuan JS, Stewart CN Jr (2008) Transcriptional responses of Arabidopsis thaliana plants to As (V) stress. BMC Plant Biol 8:87
Ahsan N, Lee DG, Alam I, Kim PJ, Lee JJ, Ahn YO, Kwak SS, Lee IJ, Bahk JD, Kang KY, Renaut J, Komatsu S, Lee BH (2008) Comparative proteomic study of arsenic-induced differentially expressed proteins in rice roots reveals glutathione plays a central role during As stress. Proteomics 8:3561–3576
Ahsan N, Lee DG, Kim KH, Alam I, Lee SH, Lee KW, Lee H, Lee BH (2010) Analysis of arsenic stress-induced differentially expressed proteins in rice leaves by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis coupled with mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 78:224–231
Ampiah-Bonney RJ, Tyson JF, Lanza GR (2007) Phytoextraction of arsenic from soil by Leersia oryzoides. Int J Phytoremediation 9:31–40
Araújo WL, Tohge T, Ishizaki K, Leaver CJ, Fernie AR (2011) Protein degradation—an alternative respiratory substrate for stressed plants. Trends Plant Sci 16:489–498
Aslam R, Bostan N, Nabgha-e-Amen MM, Safdar W (2011) A critical review on halophytes: salt tolerant plants. J Med Plant Res 5:7108–7118
Bienert GP, Thorsen M, Schüssler MD (2008) A subgroup of plant aquaporins facilitate the bi-directional diffusion of As(OH)3 and Sb(OH)3 across membranes. BMC Bioinf 6(1):26
Bona E, Cattaneo C, Cesaro P, Marsano F, Lingua G, Cavaletto M, Berta G (2010) Proteomic analysis of Pteris vittata fronds: two arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi differentially modulate protein expression under arsenic contamination. Proteomics 10:3811–3834
Bucher M (2007) Functional biology of plant phosphate uptake at root and mycorrhiza interfaces. New Phytol 173:11–26
Carrasco JA, Armario P, Pajuelo E, Burgos A, Caviedes MA, López R, Chamber MA, Palomares AJ (2005) Isolation and characterisation of symbiotically effective rhizobium resistant to arsenic and heavy metals after the toxic spill at the Aznalcóllar pyrite mine. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1131–1147
Castrillo G, Sánchez-Bermejo E, de Lorenzo L (2013) WRKY6 transcription factor restricts arsenate uptake and transposon activation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:2944–2957
Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Misra P, Tiwari M, Shri M, Shukla D, Kumar S, Rai A, Pandey A, Nigam D, Tripathi RD, Tuli R (2009) Comparative transcriptome analysis of arsenate and arsenite stresses in rice seedlings. Chemosphere 74:688–702
Chandrakar V, Naithani SC, Keshavkant S (2016) Arsenic-induced metabolic disturbances and their mitigation mechanisms in crop plants: a review. Biologia 71:367–377
Chen G, Zou X, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Owens G (2014) A short-term study to evaluate the uptake and accumulation of arsenic in Asian willow (Salix sp.) from arsenic-contaminated water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:3275–3284
Danh LT, Truong P, Mammucari R, Foster N, Danh LT, Truong P, Mammucari R, Foster N (2014) A critical review of the arsenic uptake mechanisms and phytoremediation potential of Pteris vittata. Int J Phytoremediation 16:429–453
de Bettencourt AM, Duarte MF, Facchetti S, Florêncio MH, Gomes ML, van’t Klooster HA, Montanarella L, Ritsema R, Vilas-Boas LF (1997) Evidence of the presence of dimethylated, trimethylated and “refractory” arsenic compounds in estuarine salt-marsh halophytes. Appl Organomet Chem 11:439–450
Demir E, Dinier BS, Ozdener Y (2013) Biochemical effects of arsenic stress in the leaves of halophyte Cakile maritima (SCOP) plants under salinity. Fresenius Environ Bull 22:3465–3473
Dong R, Formentin E, Losseso C, Carimi F, Benedetti P, Terzi M, Lo Schiavo F (2005) Molecular cloning and characterization of a phytochelatin synthase gene, PvPCS1, from Pteris vittata L. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 32:527–533
Dwivedi S, Tripathi RD, Tripathi P, Kumar A, Dave R, Mishra S, Singh R, Sharma D, Rai UN, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Adhikari B, Bag MK, Dhankher OP, Tuli R (2010a) Arsenate exposure affects amino acids, mineral nutrient status and antioxidants in rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Environ Sci Technol 15(44):9542–9549
Dwivedi S, Tripathi RD, Srivastava S, Singh R, Kumar A, Tripathi P, Dave R, Rai UN, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Tuli R, Adhikari B, Bag MK (2010b) Arsenic affects mineral nutrients in grains of various Indian rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes grown on arsenic-contaminated soils of West Bengal. Protoplasma 245:113–124
Farooq MA, Islam F, Ali B, Najeeb U, Mao B, Gill RA, Yan G, Siddique KH, Zhou W (2016) Arsenic toxicity in plants: cellular and molecular mechanisms of its transport and metabolism. Environ Exp Bot 132:42–52
Fernández YT, Diaz O, Acuña E, Casanova M, Salazar O, Masaguer A (2016) Phytostabilization of arsenic in soils with plants of the genus Atriplex established in situ in the Atacama Desert. Environ Monit Assess 188:235–246
Fitzgerald EJ, Caffrey JM, Nesaratnam ST, McLoughlin P (2003) Copper and lead concentrations in salt marsh plants on the Suir Estuary, Ireland. Environ Pollut 123:67–74
Flowers TJ, Colmer TD (2008) Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol 179:945–963
Flowers TJ, Galal HK, Bromham L (2010) Evolution of halophytes: multiple origins of salt tolerance in land plants. Funct Plant Biol 37:604–612
Foyer CH, Noctor G, Hodges M (2011) Respiration and nitrogen assimilation: targeting mitochondria-associated metabolism as a means to enhance nitrogen use efficiency. J Exp Bot 62:1467–1482
Francesconi K, Visoottiviseth P, Sridokchan W, Goessler W (2002) Arsenic species in an arsenic hyperaccumulating fern, Pityrogramma calomelanos: a potential phytoremediator of arsenic-contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 284:27–35
García-Salgado S, García-Casillas D, Quijano-Nieto MA, Bonilla-Simón MM (2012) Arsenic and heavy metal uptake and accumulation in native plant species from soils polluted by mining activities. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:559–572
Garg N, Singla P (2011) Arsenic toxicity in crop plants: physiological effects and tolerance mechanisms. Environ Chem Lett 9:303–321
Ghosh S, Shaw AK, Azahar I (2016) Arsenate (AsV) stress response in maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Exp Bot 130:53–67
Gong Z, Lu X, Cullen WR, Le XC (2001) Unstable trivalent arsenic metabolites, monomethylarsonous acid and dimethylarsinous acid. J Anal Atomic Spectrom 16:1409–1413
Gunes A, Inal A, Bagci EG, Kadioglu YK (2010) Combined effect of arsenic and phosphorus on mineral element concentrations of sunflower. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 41:361–372
Gupta M, Sharma P, Sarin NB, Sinha AK (2009) Differential response of arsenic stress in two varieties of Brassica juncea L. Chemosphere 74:1201–1208
Hartley-Whitaker J, Ainsworth G, Meharg A (2001) Copper and arsenic induced oxidative stress in Holcus lanatus L. cloned with differential sensitivity. Plant Cell Environ 24:713–722
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Rahman A, Al Mahmud J, Hossain S, Alam K, Oku H, Fujita M (2017) Actions of biological trace elements in plant abiotic stress tolerance. In: Essential plant nutrients. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 213–274
Isayenkov SV, Maathuis FJ (2008) The Arabidopsis thaliana aquaglyceroporin AtNIP7; 1 is a pathway for arsenite uptake. FEBS Lett 582:1625–1628
Jang YC, Somanna Y, Kim H (2016) Source, distribution, toxicity and remediation of arsenic in the environment—a review. Int J Appl Environ Sci 11:559–581
Jia Y, Huang H, Zhong M, Wang FH, Zhang LM, Zhu YG (2013) Microbial arsenic methylation in soil and rice rhizosphere. Environ Sci Technol 47:3141–3148
Lafuente A, Pajuelo E, Caviedes MA, Rodríguez-Llorente ID (2010) Reduced nodulation in alfalfa induced by arsenic correlates with altered expression of early nodulins. J Plant Physiol 167:286–291
LeBlanc MS, McKinney EC, Meagher RB, Smith AP (2013) Hijacking membrane transporters for arsenic phytoextraction. J Biotech 163:1–9
Li RY, Ago Y, Liu WJ, Mitani N, Feldmann J, McGrath SP, Ma JF, Zhao FJ (2009) The rice aquaporin Lsi1 mediates uptake of methylated arsenic species. Plant Physiol 150:2071–2080
Li G, Santoni V, Maurel C (2014) Plant aquaporins: roles in plant physiology. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840:1574–1582
Liu WX, Shen LF, Liu JW, Wang YW, Li SR (2007) Uptake of toxic heavy metals by rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivated in the agricultural soil near Zhengzhou City, People’s Republic of China. Bull Environ Contam Toxico 79:209–213
Lokhande VH, Suprasanna P (2012) Prospects of halophytes in understanding and managing abiotic stress tolerance. In: Ahmad P, Prasad MNV (eds) Environmental adaptations and stress tolerance of plants in the era of climate change. Springer, New York, NY, pp 29–56
Lokhande VH, Srivastava S, Patade VY, Dwivedi S, Tripathi RD, Nikam TD, Suprasanna P (2011) Investigation of arsenic accumulation and tolerance potential of Sesuvium portulacastrum L. Chemosphere 82:529–534
Lutts S, Lefevre I, Delpérée C, Kivits S, Dechamps C, Robledo A, Correal E (2004) Heavy metal accumulation by the halophyte species Mediterranean saltbush. J Environ Qual 33:1271–1279
Ma LQ, Komar KM, Tu C, Zhang W, Cai Y, Kennelley ED (2001) A fern that hyperaccumulates arsenic. Nature 409:579
Ma JF, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Xu XY, Su YH, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2008) Transporters of arsenite in rice and their role in arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:9931–9935
Manousaki E, Kalogerakis N (2009) Phytoextraction of Pb and Cd by the Mediterranean saltbush (Atriplex halimus L.): metal uptake in relation to salinity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16:844–854
Manousaki E, Kalogerakis N (2011) Halophytes—an emerging trend in phytoremediation. Int J Phytoremediation 13(10):959–969
Marques IA, Anderson LE (1986) Effects of arsenite, sulfite, and sulfate on photosynthetic carbon metabolism in isolated pea (Pisum sativum L., cv Little Marvel) chloroplasts. Plant Physiol 82:488–493
Mascher R, Lippman B, Holiinger S, Bergmann H (2002) Arsenate toxicity: effects on oxidative stress response molecules and enzymes in red clover plants. Plant Sci 163:961–969
Mateos-Naranjo E, Andrades-Moreno L, Redondo-Gómez S (2012) Tolerance to and accumulation of arsenic in the cordgrass Spartina densiflora Brongn. Bioresour Technol 104:187–194
Meharg AA, Macnair MR (1992) Suppression of the high-affinity phosphate-uptake system-a mechanism of arsenate tolerance in Holcus lanatus L. J Exp Bot 43:519–524
Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD, Trivedi PK (2008) Thiol metabolism and antioxidant systems complement each other during arsenate detoxification in Ceratophyllum demersum L. Aquat Toxicol 86:205–215
Mkandawire M, Dudel EG (2005) Accumulation of arsenic in Lemna gibba L. (duckweed) in tailing waters of two abandoned uranium mining sites in Saxony, Germany. Sci Total Environ 336:81–89
Moreno-Jiménez E, Esteban E, Carpena-Ruiz RO, Peñalosa JM (2009) Arsenic-and mercury-induced phytotoxicity in the Mediterranean shrubs Pistacia lentiscus and Tamarix gallica grown in hydroponic culture. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1781–1789
Mosa KA, Kumar K, Chhikara S, Mcdermott J, Liu Z, Musante C, White JC, Dhankher OP (2012) Members of rice plasma membrane intrinsic proteins subfamily are involved in arsenite permeability and tolerance in plants. Transgenic Res 21:1265–1277
Mukhopadhyay R, Bhattacharjee H, Rosen BP (2014) Aquaglyceroporins: generalized metalloid channels. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840:1583–1591
Muranyi A, Kodobocz L (2008) Heavy metal uptake by plants in different phytoremediation treatments. Cereal Res Commun 36:387–390
Nagarajan VK, Jain A, Poling MD, Lewis AJ, Raghothama KG, Smith AP (2011) Arabidopsis Pht1; 5 mobilizes phosphate between source and sink organs and influences the interaction between phosphate homeostasis and ethylene signaling. Plant Physiol 156:1149–1163
Nearing MM, Koch I, Reimer KJ (2014) Complementary arsenic speciation methods: a review. Spectrochim Acta B At Spectrosc 99:150–162
Niazi NK, Bibi I, Fatimah A, Shahid M, Javed MT, Wang H, Ok YS, Bashir S, Murtaza B, Saqib ZA (2017) Phosphate-assisted phytoremediation of arsenic by Brassica napus and Brassica juncea: morphological and physiological response. Int J Phytoremediation 19:670–678
Norton GJ, Lou-Hing DE, Meharg AA, Price AH (2008) Rice-arsenate interactions in hydroponics: whole genome transcriptional analysis. J Exp Bot 59:2267–2276
Otte ML, Dekkers IMJ, Rozema J, Broekman RA (1991) Uptake of arsenic by Aster tripolium in relation to rhizosphere oxidation. Can J Bot 69:2670–2677
Padmavathiamma PK, Li LY (2007) Phytoremediation technology: hyper-accumulation metals in plants. Water Air Soil Pollut 184:105–126
Päivöke AE, Simola LK (2001) Arsenate toxicity to Pisum sativum: mineral nutrients, chlorophyll content, and phytase activity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 49:111–121
Pajuelo E, Rodríguez-Llorente ID, Dary M, Palomares AJ (2008) Toxic effects of arsenic on Sinorhizobium-Medicago sativa symbiotic interaction. Environ Pollut 154:203–211
Pan W, Wu C, Xue S, Hartley W (2014) Arsenic dynamics in the rhizosphere and its sequestration on rice roots as affected by root oxidation. J Environ Sci 26:892–899
Panda A, Rangani J, Kumari A, Parida AK (2017) Efficient regulation of arsenic translocation to shoot tissue and modulation of phytochelatin levels and antioxidative defense system confers salinity and arsenic tolerance in the halophyte Suaeda maritima. Environ Exp Bot 143:149–171
Pavlík M, Pavlíková D, Staszková L, Neuberg M, Kaliszová R, Száková J, Tlustos P (2010) The effect of arsenic contamination on amino acids metabolism in Spinacia oleracea L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1309–1313
Perdiguero E, Muñoz-Cánoves P (2007) Transcriptional regulation by the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in mammalian cells. In: Posas F, Nebreda AR (eds) Stress-activated protein kinases. Topics in current genetics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 51–79
Raab A, Williams PN, Meharg A, Feldmann J (2007) Uptake and translocation of inorganic and methylated arsenic species by plants. Environ Chem 4:197–203
Rabier J, Laffont-Schwob I, Pricop A, Ellili A, D’Enjoy-Weinkammerer G, Salducci MD, Prudent P, Lotmani B, Tonetto A, Masotti V (2014) Heavy metal and arsenic resistance of the halophyte Atriplex halimus L. along a gradient of contamination in a French Mediterranean spray zone. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1993–2103
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Rahman MM, Islam MN, Miah MM, Tasmen A (2007) Effect of arsenic on photosynthesis, growth and yield of five widely cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 67:1072–1079
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Ueda K, Maki T, Rahman MM (2008) Arsenic uptake by aquatic macrophyte Spirodela polyrhiza L.: interactions with phosphate and iron. J Hazard Mater 160:356–361
Rahman MA, Kadohashi K, Maki T, Hasegawa H (2011) Transport of DMAA and MMAA into rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots. Environ Exp Bot 72:41–46
Requejo R, Tena M (2005) Proteome analysis of maize roots reveals that oxidative stress is a main contributing factor to plant arsenic toxicity. Phytochemistry 66:1519–1528
Sakakibara M, Ohmori Y, Ha NTH, Sano S, Sera K (2011) Phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated water and sediment by Eleocharis acicularis. Clean Soil Air Water 39:735–741
Sakurai J, Ishikawa F, Yamaguchi T, Uemura M, Maeshima M (2005) Identification of 33 rice aquaporin genes and analysis of their expression and function. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1568–1577
Santos D, Duarte B, Caçador I (2014) Unveiling Zn hyperaccumulation in Juncus acutus: implications on the electronic energy fluxes and on oxidative stress with emphasis on non-functional Zn-chlorophylls. J Photochem Photobiol B 140:228–239
Sarma H (2011) Metal hyperaccumulation in plants: a review focusing on phytoremediation technology. J Environ Sci Technol 4:118–138
Sghaier DB, Duarte B, Bankaji I, Caçador I, Sleimi N (2015) Growth, chlorophyll fluorescence and mineral nutrition in the halophyte Tamarix gallica cultivated in combined stress conditions: arsenic and NaCl. J Photochem Photobiol B 149:204–214
Sharma I (2012) Arsenic induced oxidative stress in plants. Biologia 67:447–453
Sharma A, Gontia I, Agarwal PK, Jha B (2010) Accumulation of heavy metals and its biochemical responses in Salicornia brachiata, an extreme halophyte. Marine Biol Res 6:511–518
Sheoran V, Sheoran AS, Poonia P (2011) Role of hyperaccumulators in phytoextraction of metals from contaminated mining sites: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 41:168–214
Shevyakova NI, Netronina IA, Aronova EE (2003) Compartmentation of cadmium and iron in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum plants during the adaptation to cadmium stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 50:678–685
Shin H, Shin HS, Dewbre GR (2004) Phosphate transport in Arabidopsis: Pht1; 1 and Pht1; 4 play a major role in phosphate acquisition from both low-and high-phosphate environments. Plant J 39:629–642
Shri M, Kumar S, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Malick S, Mishra P, Shukla D, Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD, Tuli R (2009) Effect of arsenic on growth, oxidative stress, and antioxidant system in rice seedling. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 72:1102–1110
Singh N, Ma LQ, Srivastava M, Rathinasabapathi B (2006) Metabolic adaptations to arsenic induced oxidative stress in Pteris vittata L. and Pteris ensiformis L. Plant Sci 170:274–28210
Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohali RK Arora K (2007) Arsenic induced root growth inhibition in mung bean (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.) is due to oxidative stress resulting from enhanced lipid peroxidation. Plant Growth Regul 53:65–73
Song WY, Park J, Mendoza-Cózatl DG (2010) Arsenic tolerance in Arabidopsis is mediated by two ABCC-type phytochelatin transporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:21187–21192
Srivastava M, Ma LQ, Santos JAG (2006) Three new arsenic hyperaccumulating ferns. Sci Total Environ 364:24–31
Tripathi RD, Tripathi P, Dwivedi S, Dubey S, Chakrabarty D (2012) Arsenomics: omics of arsenic metabolism in plants. Front Physiol 3:275
Tu C, Ma LQ (2002) Effects of arsenic concentrations and forms on arsenic uptake by the hyperaccumulator ladder brake. J Environ Qual 31:641–647
Vamerali T, Bandiera M, Coletto L, Zanetti F, Dickinson NM, Mosca G (2009) Phytoremediation trials on metal- and arsenic-contaminated pyrite wastes (Torviscosa, Italy). Environ Pollut 157:887–894
Vezza ME, Llanes A, Travaglia C, Agostini E, Talano MA (2018) Arsenic stress effects on root water absorption in soybean plants: physiological and morphological aspects. Plant Physiol Biochem 123:8–17
Vromman D, Flores-Bavestrello A, Šlejkovec Z, Lapaille S, Teixeira-Cardoso C, Briceño M, Kumar M, Martínez JP, Lutts S (2011) Arsenic accumulation and distribution in relation to young seedling growth in Atriplex atacamensis Phil. Sci Total Environ 412:286–295
Vromman D, Lefèvre I, Šlejkovec Z, Martínez JP, Vanhecke N, Briceño M, Kumar M, Lutts S (2016) Salinity influences arsenic resistance in the xerohalophyte Atriplex atacamensis Phil. Environ Exp Bot 126:32–43
Wang HL, Tian CY, Jiang L (2014a) Remediation of heavy metals contaminated saline soils: a halophyte choice? Environ Sci Technol 48:21–22
Wang H, Xu Q, Kong YH, Chen Y, Duan JY, Wu WH, Chen YF (2014b) Arabidopsis WRKY45 transcription factor activates phosphate Transporter1;1 expression in response to phosphate starvation. Plant Physiol 164:2020–2029
Williams PN, Islam S, Islam R, Jahiruddin M, Adomako E, Soliaman ARM, Rahman GKMM, Lu Y, Deacon C, Zhu Y-G, Meharg AA (2009) Arsenic limits trace mineral nutrition (selenium, zinc and nickel) in Bangladesh rice grain. Environ Sci Technol 43:8430–8436
Wu Z, Ren H, McGrath SP (2011) Investigating the contribution of the phosphate transport pathway to arsenic accumulation in rice. Plant Physiol 157:498–508
Xu W, Dai W, Yan H, Li S, Shen H, Chen Y, Xu H, Sun Y, He Z, Ma M (2015) Arabidopsis NIP3; 1 plays an important role in arsenic uptake and root-to-shoot translocation under arsenite stress conditions. Mol Plant 8:722–733
Zhang X, Lin AJ, Zhao FJ, Xu GZ, Duan GL, Zhu YG (2008) Arsenic accumulation by the aquatic fern Azolla: comparison of arsenate uptake, speciation and efflux by A. caroliniana and A. filiculoides. Environ Pollut 156:1149–1155
Zhao FJ, Wang JR, Barker JHA, Schat H, Bleeker PM, McGrath SP (2003) The role of phytochelatins in arsenic tolerance in the hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata. New Phytol 159:403–410
Zhao FJ, Ma JF, Meharg AA (2009) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in plants. New Phytol 181:777–794
Zhao FJ, McGrath SP, Meharg AA (2010) Arsenic as a food chain contaminant: mechanisms of plant uptake and metabolism and mitigation strategies. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:535–559
Acknowledgments
MP and AK are thankful to the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, for providing financial support in the form of INSPIRE Fellowship. Financial support of DST (Grant No. SERB/SB/SO/PS-14/2014), Government of India, New Delhi, to AKP is duly acknowledged. This manuscript was assigned CSIR-CSMCRI Communication No. 068/ 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Patel, M., Kumari, A., Parida, A.K. (2020). Arsenic Tolerance Mechanisms in Plants and Potential Role of Arsenic Hyperaccumulating Plants for Phytoremediation of Arsenic-Contaminated Soil. In: Hasanuzzaman, M. (eds) Plant Ecophysiology and Adaptation under Climate Change: Mechanisms and Perspectives II. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-2172-0_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-2172-0_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-2171-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-2172-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)