Abstract
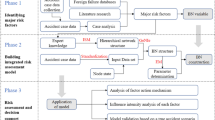
Third-party damage (TPD) is identified as the greatest threat to the safe operation of pipelines in different countries. The traditional TPD risk assessment methods cannot calculate the failure probability quantitatively and ignore the conditional dependence between risk influence factors (RIFs). In view of this, a theoretical system called 3S_BN is proposed based on Statistics, Scenario analysis, Safety barrier, and Bayesian network to realize the quantitative risk analysis of TPD. According to the 3S_BN, RIFs and their causal relationships are analyzed firstly. After that, a BN model including multi-state risk is developed and historical data and experts’ opinions are used for the computation of conditional probability table. Besides, evidence theory is adopted in order to improve experts’ belief. And then, the proposed approach is verified by a fire and explosion accident. Through sensitivity analysis and posterior probability reversal, the key influence factors and possible paths of the incident are confirmed. Finally, as discussed, the model can be applied to the TPD risk management of pipelines to continuously improve the safety level of pipelines.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
EGIG: 10th Report of the European Gas Pipeline Incident Data Group (period 1970–2015), pp. 22–26 (2018)
Lam, C., Zhou, W.X.: Statistical analyses of incidents on onshore gas transmission pipelines based on PHMSA database. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 145, 29–40 (2016)
Peng, X.Y., Yao, D.C., Liang, G.C., et al.: Overall reliability analysis on oil/gas pipeline under typical third-party actions based on fragility theory. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 34, 993–1003 (2016)
Baksh, A., Khan, F., Gadag, V., et al.: Network based approach for predictive accident modeling. Saf. Sci. 80, 274–287 (2015)
Guo, X., Zhang, L., Liang, W., et al.: Risk identification of third-party damage on oil and gas pipelines through the Bayesian network. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 54, 163–178 (2018)
Jiang, H.Y., Yao, A.L., et al.: Sensitivity analysis on risk factors of the third party damage in gas pipeline. Nat. Gas Oil 29(1), 1–4 (2011)
Liang, W., Hu, J., Guo, C., et al.: Assessing and classifying risk of pipeline third-party interference based on fault tree and SOM. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 25(3), 594–608 (2012)
Li, J., Zhang, H., Han, Y., et al.: Study on failure of third-party damage for urban gas pipeline based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. PLoS One 11(11), 112–127 (2016)
Hayhurst, E.R.: Industrial accident prevention, a scientific approach. Ind. Labor Relat. Rev. 4(4), 609 (2011)
Reason, J.: Human Error, pp. 173–216. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1990)
Cai, B., Huang, L., Xie, M.: Bayesian networks in fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 13(5), 2227–2240 (2017)
Lee, E., Park, Y., Shin, J.G.: Large engineering project risk management using a Bayesian belief network. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(3), 5880–5887 (2009)
Jensen, F.V., Nielsen, T.D.: Bayesian Network and Decision Graphs. Springer Science & Business Media (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-68282-2
Bhandari, J., Abbassi, R., Garaniya, V., et al.: Risk analysis of deepwater drilling operations using Bayesian network. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 38, 11–23 (2015)
Wu, S.N., Zhang, L.B., Zheng, W.P., Liu, Y.L., Lundteigen, M.A.: A DBN-based risk assessment model for prediction and diagnosis of offshore drilling incidents. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 34, 139–158 (2016)
Adedigba, S.A., Khan, F., Yang, M.: Process accident model considering dependency among contributory factors. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 102, 633–647 (2016)
Rathnayaka, S., Khan, F., Amyotte, P.: SHIPP methodology: predictive accident modeling approach. Part I: Methodology and model description. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 89(3), 151–164 (2011)
Baksh, A.A., Khan, F., Gadag, V., et al.: Network based approach for predictive accident modeling. Saf. Sci. 80, 274–287 (2015)
Wang, W., Shen, K., Wang, B., et al.: Failure probability analysis of the urban buried gas pipelines using Bayesian networks. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 111, 678–686 (2017)
Yang, Y., Khan, F., Thodi, P., et al.: Corrosion induced failure analysis of subsea pipelines. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 159, 214–222 (2017)
Zhang, C., Wu, J., Hu, X., et al.: A probabilistic analysis model of oil pipeline accidents based on an integrated Event-Evolution-Bayesian (EEB) model. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 117, 694–703 (2018)
Xin, P., Khan, F., Ahmed, S.: Dynamic hazard identification and scenario mapping using Bayesian network. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 105, 143–155 (2017)
Sklet, S.: Safety barriers: definition, classification, and performance. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 19, 494–506 (2006)
Khan, F.I.: Use maximum-credible accident scenarios for realistic and reliable risk assessment. Chem. Eng. Prog. 97(11), 56–64 (2001)
Li, X., Chen, G., Zhu, H.: Quantitative risk analysis on leakage failure of submarine oil and gas pipelines using Bayesian network. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 103, 163–173 (2016)
Cowell, R.G., Dawid, A.P., Lauritzen, S.L., et al.: Probabilistic Networks and Expert Systems, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 289–320. Springer, Berlin (1999)
Ramoni, M., Sebastiani, P.: Parameter estimation in bayesian networks from incomplete databases. Intell. Data Anal. 2(1–4), 139–160 (1998)
Wu, J., Zhou, R., Xu, S., et al.: Probabilistic analysis of natural gas pipeline network accident based on Bayesian network. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 46, 126–136 (2017)
Hua, Z., Gong, B., Xu, X.: A DS–AHP approach for multi-attribute decision making problem with incomplete information. Expert Syst. Appl. 34(3), 2221–2227 (2008)
Khan, F., Hashemi, S.J., Paltrinieri, N., et al.: Dynamic risk management: a contemporary approach to process safety management. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 14, 9–17 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No.2018YFC0809300) and the Major scientific and technological innovation projects of Shandong (Grant No. 2018YFJH0802). The authors are grateful for the valuable suggestions of reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Guo, X., Zhang, G., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Liang, W. (2020). A 3S_BN Based Approach for the Quantitative Risk Assessment of Third-Party Damage on Pipelines. In: Wahab, M. (eds) Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Damage Assessment of Structures. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8331-1_54
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8331-1_54
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-8330-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-8331-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)